Chapter: Engineering Mechanics : Friction and Elements of Rigid Body Dynamics
Important Questions and Answers: Friction and Elements of Rigid Body Dynamics
(FRICTION AND ELEMENTS OF RIGID BODY DYNAMICS)
1.Define instantaneous centre of rotation.
Instantaneous centre of rotation is a point identified with in a body
where the velocity is zero.
2.Define co-efficient of restitution.
It is ratio of magnitudes of impulses corresponding to the period of
restitution and to the period of deformation is called coefficient of
restitution .
3.Define kinetics.
Study of bodies subjected to forces which are unbalanced is called
kinetics.
4. Define kinematics
The study
of geometry and time dependent aspects of motion without considering forces
causing motion.
5.Define Angular momentum.
Momentum
of linear momentum is called angular momentum.
6.what is general plane motion ? give some
examples.
When
motion of particles and rigid bodies
defined in a plane is called
plane
motion.
Example
:All planets revolving around the sun.
7.Define Relative velocity.
Assume particle A moves with a velocity of Va and particle B moves with
a velocity Vb.
8.Define Resultant velocity.
Assume
particle A moves to x direction Vx and in y direction Vy this resultant
velocity.
9.How will you calculate the linear restoring force
of an elastic material.
Linear restoring force of an elastic material. F=kx
Where k
is the stiffness of the material and x is the displacement.
10.state the principle of work and energy.
The
principle of work and energy or work energy equation is written as Work done
=final kinetis energy - initial kinetis energy
11.Define instantaneous centre of rotation.
A rigid
body in plane motion can be considered to rotate about a point that remains at
a particular instant. This point having zero instantaneous velocity is called
the instantaneous centre of rotation.
1.Give
mathematical definitions of velocity and acceleration.
2.A Car
traverses half of a distance with a velocity of 40 Kmph and the remaining half
of distance with a velocity of 60 Kmph. Find the average velocity.
3.Define
friction and classify its types. 4.Classify the types of friction.
5.Define
Limiting friction.
6.Define
coefficient of static friction. 7.Stat coulomb’s laws of dry friction. 8.Define
rolling resistance.
9.What is
coefficient of rolling resistance?
10.Define
coefficient of friction and express its relationship with angle of friction.
11.If
x=3.5t3– 7 t2, determine acceleration, velocity and position of the particle,
when t = 5 sec. 12.Consider a wheel rolling on a straight track. Illustrate the
characteristics of general plane motion.
13.Write
work energy equation of rigid body. Mention the meaning for all parameters used
in the equation.
14.What
us general plane motion? Give some examples. 15.Define Limiting friction.
16.Define
Co-efficient of friction and angle of friction 17.Define coulomb’s laws of dry
friction.
18.Define
impending motion. 19.Define angle of repose 20.Define cone of friction.
21.Define
the following terms i) Ladder friction. ii) Wedge friction iii) Screw friction
iv) Belt friction.
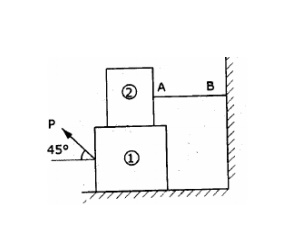
1. Block
(2) rests on block (1) and is attached by a horizontal rope AB to the wall as
shown in fig. What force P is necessary to cause motion of block (1) to impend?
The co-efficient of friction between the blocks is ¼ and between the floor and
block (1) is 1/3. Mass of blocks (1)and(2) are 14kg and 9 kg respectively
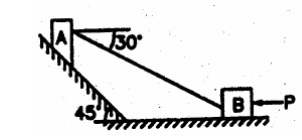
2. Block
A weighing 1000 N rests on a rough inclined plane whose inclination to the
horizontal is 45°. It is connected to another block B, weighing 3000 N rests on
a rough horizontal plane by a weightless rigid bar inclined at an angle of 30°
to the horizontal as shown in fig. Find the horizontal force required to be
applied to the block B just to move the block A in upward direction. Assume
angle of friction as 15° at all surfaces where there is sliding.
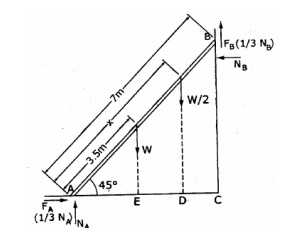
3. A 7m
long ladder rests against a vertical wall, with which it makes an angle of 45°
and on a floor. If a man whose weight is one half that of the ladder climbs it,
at what distance along the ladder will he be, when the ladder is about to slip?
Take coefficient of friction between the ladder and the wall is 1/3 and that
between the ladder and the floor is ½.
4. In a
screw jack, the pitch of the square threaded screw is 5.5 mm and means diameter
is 70 mm. The force exerted in turning the screw is applied at the end of lever
210 mm long measured from the axis of the screw. If the co-efficient of
friction of the screw jack is 0.07. Calculate the force required at the end of
the lever to (i) raise a weight of 30 KN (ii) lower the same weight.
5. An effort
of 200 N is required just to move a certain body up an inclined plane of angle
15°, the force is acting parallel to the plane. If the angle of inclination of
the plane is made 20°,
the
effort required being again parallel to the plane, is found to be 230 N. Find
the weight of the body and coefficient of friction.
Find the
force P inclined at an angle of 32° to the inclined plane making an angle of 25
degree with the horizontal plane to slide a block weighing 125 KN (i) up the
inclined plane (ii) Down the inclined plane, when P = 0.5.
Related Topics