Chapter: Engineering Mechanics : Equilibrium of Rigid Bodies
Important Questions and Answers: Equilibrium of Rigid Bodies
1.State varignon’s theorem?
The
algebraic sum of moments due to all forces acting on the object about any point
is equal to the moment of their resultant about the same point.
2.Define couple?
Twonon
collinear parallel forces having same magnitude but opposite direction from a
couple.
3.Why the couple moment is said to be a free
vector?
Couple
moment is said to be a free vector as it can be transferred to any point in the
plane without causing any change in its effect on the body.
4.Distinguish between couple and moment?
Moment
represents the turning effect of a force where as couple consists of two equal
and opposite forces separate by some distance.moment of force various from
point to point but moment of a couple is same about any point in the plane.
5.What is meant by force-couple system?
A system
of coplanar non concurrent force system acting in a rigid body can be replaced
by a single resultant force and couple moment at a point known as force couple
system.
6.Can a coplanar non concurrent system with zero
resultant force necessarily be in equilibrium?
A
coplanar non concurrent system with zero resultant force is not necessarily In
equilibrium as it can have a non zero resultant moment.
7.When is moment of force zero about a point?
The
moment of force about a point is zero its line of action passes through that
point.
8.When is moment of force maximum about a point ?
Moment of
force is maximum about a point when,
i)Its
applied at maximum result from the point and,
ii)It is
applied perpendicular to the line joining the point to the point of application
of force.
9.When is moment of force zero about a line?
Moment of
force about a line is zero when, i)Force is parallel to that line or,
ii)Line
of action of force intersects that line.
10.Explain free body diagram with one example?
Free body
diagram is the isolated diagram of an object\system of objects\any point in the
system in which all forces at couple moment acting on it are shown including
support reactions example:consider a ladder of weight W having rollers at it’s
end’s as shown in figure.
11.Statethe necessary and sufficient conditions for
equilibrium of rigid bodies in two dimensions?
The
necessary and sufficient conditions for equilibrium of rigid bodies in two
dimensions are:
1)algebraic
sum of horizontal components of all forces acting on the body is must be zero,
2)Algebraic
sum of vertical components all forces acting on the body is must be zero,
3)Algebraic
sum of moments due to all forces and couple moments acting the body is in must
be zero.
12.Write the equation of equilibrium of a rigid
body?
The three
equations of a rigid body are:
∑Fx=0,;
∑Fy=0,;
∑M=0.
13.Write the conditions equilibrium of a system of
parallel force acting in a plane ?
The two
conditions of equilibrium of a system of parallel forces acting in a plane are
:
1)Algebraic
sum of all forces must be zero,
2)Algebraic
sum of moments due to all forces about any point must be zero.
14.What are the reactions at a fixed support of a
plane beam that are possible?
The
reaction at fixed support of a plane beam consist of ,
1)A
reaction force in the plane which can be represented by it’s two
components(Generally taken to be horizontal and vertical)&,
2)Areaction
moment.
15.How many scalar equations can be obtained for
equilibrium of rigid body in three dimensions?
Six
scalar equations can be obtained for equilibrium of a rigid body in three
dimensions.
1. State
Varignon’s theorem
2. What is a
couple? what is a moment of a couple?
3. A force
vector F has the components Fx = 150N, Fy= -200N and Fx = 300N. Determine the
magnitude F and the angle made by the force with coordinate axes.
4. Sketch
the different types of supports.
5. Write
down the conditions of equilibrium of a particle in space
6. A force
vector of magnitude 100N is represented by a line of coordinates A (1, 2, 3)
and B (5, 8, 12). Determine components of the force along X, Y and Z axes.
7. Explain
will you reduce a force into an equivalent force-couple system with an example.
9. Draw
Compute the moment of the 100 N force about point A and B
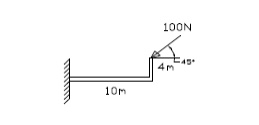
PART-B
1. Four
forces act on a 700mm X 375mm plate as shown in fig. a) Find the resultant of
these forces b) Locate the two points where the line of action of the resultant
intersects the edge of the plate.
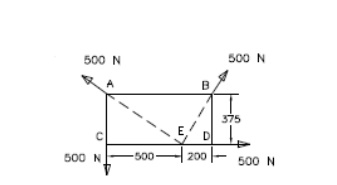
2. Four
coplanar non concurrent non parallel forces act on a square plate of side 2m as
shown in fig. Locate the resultant force.
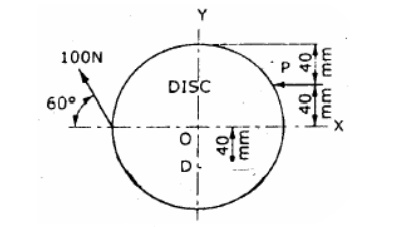
3. In
figure below, two forces act on a circular disc as shown. If the resultant
moment of all these forces about point D on the disc is zero, determine: a)
Magnitude of force P (b) Magnitude of the resultant of two forces (c) The point
on the Y-axis through which the line of action of the resultant passes through.
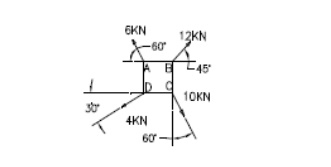
4. Four
forces act on a square of side 1 m as shown in fig. Reduce the force system
into an equivalent force – couple system at A.
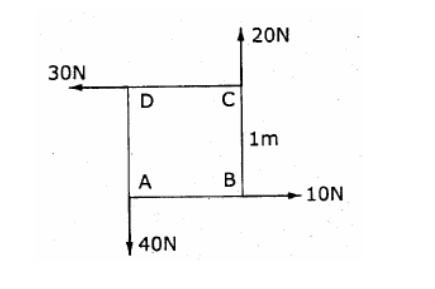
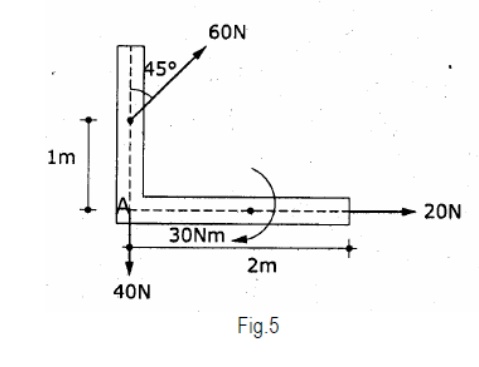
5. Reduce
the system of forces shown in fig.5 to a force – couple system at A.
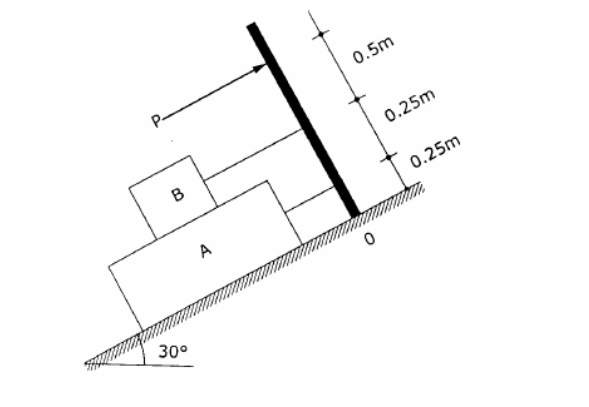
6. Blocks
A and B of weight 200N and 100N respectively, rest on a 30 inclined plane and
are attached to the post which is held perpendicular to the plane by force P,
parallel to the plane, as shown in fig. Assume that all surfaces are smooth and
that the cords are parallel to the plane. Determine the value of P. Also find
the Normal reaction of Blocks A and B.
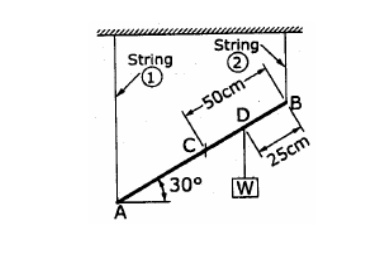
8. A
Uniform meter rod AB, assumed rigid of mass 0.5 kg is suspended from its ends
in an inclined position and a mass of 1 kg is suspended from a point D, as
shown in fig. etermine the tension in each string. Where should the suspended
mass be placed in order to get equal tension in the strings.
9. A rod
AB of weight 200 N is supported by a cable BD and the corner of wall and floor
surface as shown in fig. Find the reaction at A and tension in the cord.
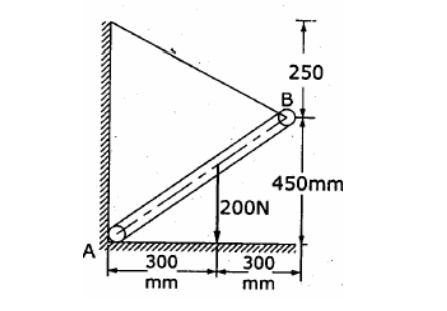
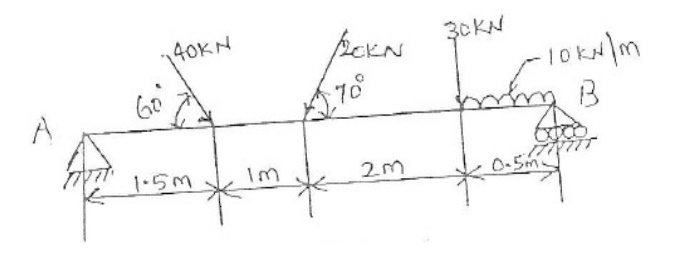
10. Find
reactions at points A & B
Related Topics