Chapter: Engineering Mechanics : Dynamics of Particles
Important Questions and Answers: Dynamics of Particles
1.State D’Alembert’s principle
The force
system consisting of external forces and inertia force can be considered to
keep the particle in equilibrium.since the resultant force externally acting on
the particle is not zero ,the particle is said to be in dynamic equilibriums.the
principle is known as D’Alembert’s principle.
2.what is general plane motion.
Any plane
motion which is neither a rotation nor a translation but considered as the sum
of translation and rotation.
3.Define the term co-efficient of restitution.
The
co-efficient of restitution between two bodies in a collision is defined as the
ratio of the relative velocity of their separation after collision to the
relative of their approach before collision.
4.Define angle friction.
Angle of
friction is the angle between resultant reaction of one body on another and
normal to the common tangent between two bodies when the motion is impending.
5.what are motion curves.
The path
described by a particle or a rigid body with respect to time is called motion
curve.
6.what do you understand by kinematics
Kinematics
refers to the study of bodies in motion without considering the force that
causes motion.
7.Define Dynamics.
Dynamics
is the branch of mechanics.which deals with the analysis of particles bodies in
motion.
1. Define
D’Alembert’s principle
2.Write
down the equations of motion of a particle under gravitation
3.A car
accelerates uniformly from a sped of 30 Km/Hr to a speed of 75 Km/Hr in 5 secs.
Determine the acceleration of the car and the distance traveled by the car
during 5 secs. 4.Explain dynamic equilibrium
5.State
the law of conservation of momentum
6.A car
starts from rest with a constant acceleration of 4m/sec2. Determine the distance
traveled in the 7th second.
7.A point
P moves along a straight line according to the equation x= 4t3+2t+5, where x is
in meters and t is in secs. Determine the velocity and acceleration at t=3
secs.
8.A stone
is projected in space at an angle of 45° to horizontal at an initial velocity
of 10 m/sec. Find the range of the projectile.
9.What is
work energy principle
10.Write
the impulse momentum equation.
1. A train is traveling from A to D along the track shown in fig. Its initial velocity at A is zero. The train takes 5 min to cover the distance AB, 2250 m length and 2.5 minutes to cover, the distance BC, 3000 m in length, on reaching the station C, the brakes are applied and the train stops 2250 m beyond, at D (i) Find the retardation on CD, (ii) the time it takes the train to get from A to D, and (iii) its average speed for the whole distance.
2. The
position of the particle is given by the relation S=1.5t3-9t2-22.5t+60, where S
is expressed in meters and t in seconds. Determine (i) the time at which the
velocity will be zero (ii) the position and distance traveled by the particle
at that time (iii) the acceleration of the particle at that time and (iv) the
distance traveled by the particle from t = 5s to t = 7s.
3. A
particle is projected with a initial velocity of 12m/s at an angle M with the
horizontal. After sometime, the position of the particle is observed by its x
and y distances of 6m and 4m respectively from the point of projection. Find
the angle of projection.
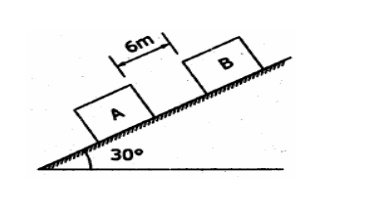
Two
Blocks A and B of weight 100 N and 200 N respectively are initially at rest on
a 30° inclined plane as shown in figure. The distance between the blocks is 6
m. The co efficient of friction between the block A and the plane is 0.25 and
that between the block B and the plane is 0.15. If they are released at the
same time, in what time the upper block (B) reaches the Block (A).
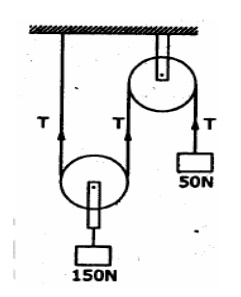
5. Two
blocks of weight 150 N and 50 N are connected by a string and passing over a
frictionless pulley as shown in figure. Determine the acceleration of blocks A
and B and the tension in the string.
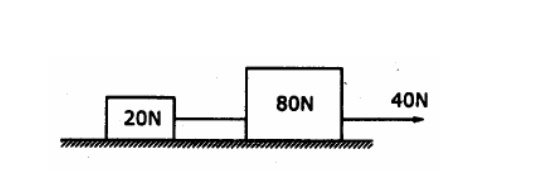
6. Two
weights 80 N and 20 N are connected by a thread and move along a rought
horizontal plane under the action of a force 40 N, applied to the first weight
of 80 N as shown in figure. The coefficient of friction between the sliding
surfaces of the wrights and the plane is 0.3.
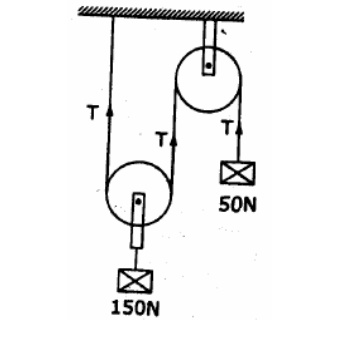
7. Two
blocks of weight 150N and 50N are connected by a string, passing over a
frictionless pulley as shown in fig. Determine the velocity of 150N block after
4 seconds. Also calculate the tension in the string.
8. Two
bodies, one of mass 30kg, moves with a velocity of 9m/s centrally. Find the
velocity of each body after impact, if the coefficient of restitution is 0.8.

Related Topics