Functions, Structure - Human System Reproductive | 9th Science : Organ Systems in Animals
Chapter: 9th Science : Organ Systems in Animals
Human System Reproductive
Human System Reproductive
All living organisms
develop from pre-existing organisms. The capacity to reproduce is one of the
most important characteristics of living beings. is process is aimed to
preserve individual species and is called ‘self perpetuation’.
There is a distinct
sexual dimorphism in human beings i.e., males are visibly different from
females in physical build up, external genital organs and secondary sexual
characters. Thus, the structures associated with reproduction are different in
males and females. The reproductive systems of male and female consist of many
organs which are distinguished as primary and secondary sex organs. The primary
sex organs are gonads, which produce gametes (sex cells) and secrete sex
hormones. The secondary sex organs include the genital ducts and glands which
help in the transportation of gametes and enable the reproductive process. They
do not produce gametes or sex hormones.
The reproductive organs
become functional a er attaining sexual maturity. In males, sexual maturity is
attained at the age of 13-14 years. In females, it is attained at the age of
11-13 years. is age is known as the age of puberty. During sexual maturity,
hormonal changes takes place in males and females and secondary sexual
characters are developed under the in uence of these hormones.
1. Male reproductive system
Human male reproductive
system consists of testes (primary sex organs), scrotum, vas deferens, urethra,
penis and accessory glands.
Testes: A pair of testes or
testicles lies outside the abdominal cavity of the male. ese testes are
the male gonads, which produces male gametes (sperms) and male sex
hormone (Testosterone). Along the inner side of each testis lies
a mass of coiled tubules called epididymis. The Sertoli cells of
the testes provide nourishment to the developing sperms.
Scrotum: The scrotum is a loose
pouch-like sac of skin which is divided internally into right and left scrotal
sacs by muscular partition. The two testes lie in the respective scrotal
sacs. It also contains many nerves and blood vessels. The scrotum acts
as a thermoregulator organ and provides an optimum temperature
for the formation of sperms. The sperms develop at a temperature of 1-3˚C lower
than the normal body temperature.
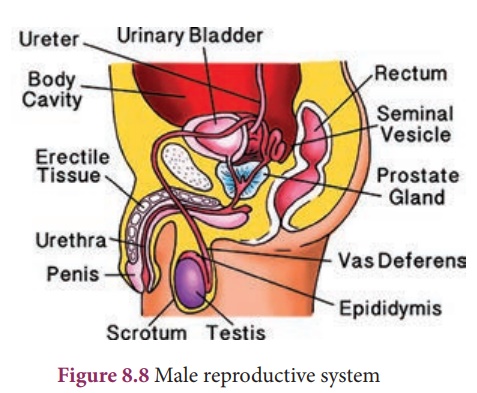
Vas Deferens: It is a straight tube
which carries the sperms to the seminal vesicles. The sperms are
stored in the seminal plasma of seminal vesicle, which is rich in fructose,
calcium and enzymes. Fructose is a source of energy for the sperm. The vas
deferens along with seminal vesicles opens into ejaculatory duct. The
ejaculatory duct expels the sperm and secretions from seminal vesicles into the
urethra.
Urethra: It is contained inside
the penis and conveys the sperms from the vas deferens which pass
through the urethral opening.
The accessory glands
associated with the male reproductive system consist of seminal vesicles,
prostate gland and Cowper’s glands. The secretions of these glands form seminal
fluid and mixes with the sperm to form semen. This fluid provides nutrition and
helps in the transport of sperms.
The Leydig cells of the testes secrete the male sex hormone testosterone which controls spermatogenesis and plays a role in the development of male secondary sexual characters like growth of beard, moustache, body hair and hoarse voice.
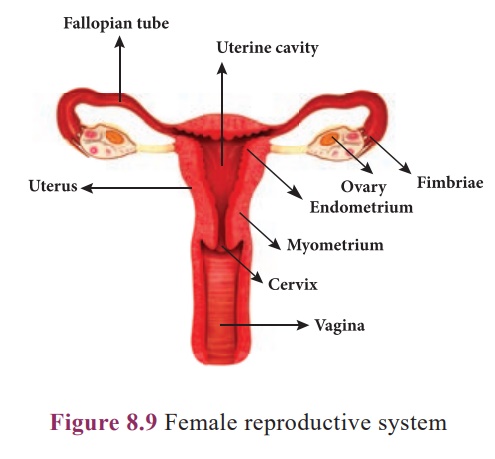
2. Female reproductive system
The female reproductive
system consists of ovaries primary sex organs , oviducts, uterus and vagina.
Ovaries: A pair of almond-shaped
ovaries is located in the lower part of abdominal cavity near the kidneys
in female. he ovaries are the female gonads, which produce female gametes (
eggs or ova)and
secrete female sex hormones (Oestrogen and Progesterone).
A mature ovary contains a large number of ova in different stages of
development. nly one ovum usually ripens every month. ne mature ovum is
released from either side of the ovary at an interval of every days menstrual cycle . The process of
release of ovum from the ovary is known as ovulation.
Fallopian tubes
(Oviducts): These are paired tubes originating from uterus, one on
either side. The terminal part of fallopian tube is funnel-shaped with
finger-like projections called fimbriae lying near the ovary. The
fimbriae pick up the ovum released from ovary and push it into the fallopian
tube.
Uterus: Uterus is a pear-shaped
muscular, hollow structure present in the pelvic cavity. It lies between
urinary bladder and rectum. Development of foetus occurs inside the uterus. The
narrower lower part of uterus is called cervix, which leads into vagina.
Vagina: The uterus narrows down
into a hollow muscular tube called vagina. It connects cervix and the
external genitalia. It receives the sperms, acts as birth canal during child
birth (parturition) and also serves as passage for menstrual flow.
The female sex hormone oestrogen
is secreted by the graafian follicle of the ovum. It controls the
development of accessory sex organs and secondary sexual characters. It
regulates menstrual cycle and fertility. Progesterone is secreted by the
corpus luteum. It prepares the uterus for implantation of
fertilized ovum, formation of placenta and for maintaining pregnancy.
Related Topics