Functions, Structure - Human Excretory System | 9th Science : Organ Systems in Animals
Chapter: 9th Science : Organ Systems in Animals
Human Excretory System
Human Excretory System
Metabolic activities
continuously take place in living cells. All metabolic products produced by the
biochemical reactions are not utilized by the body because certain nitrogenous
toxic waste substances are also produced. They are called excretory products. In
human beings urea is the major excretory product. The tissues and organs
associated with the removal of waste products constitute the excretory system.
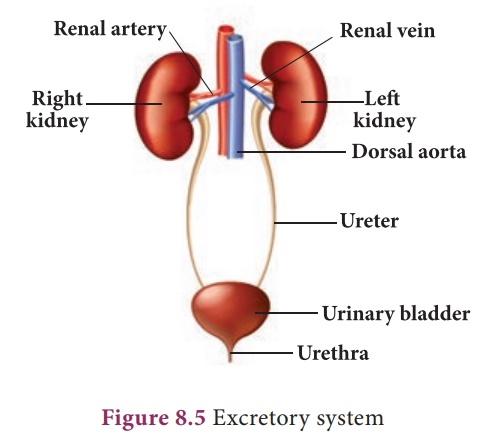
The human excretory
system consists of a pair of kidney, which produce the urine, a pair of ureters
which conduct the urine from kidneys to the urinary bladder, where urine is
stored temporarily and urethra through which the urine is voided by bladder
contractions.
If the waste products
are accumulated and not eliminated, they become harmful and poisonous to the
body. Hence, excretion plays an important role in maintaining the homeostatic
condition of the body.
Some of the excretory
organs other than kidneys are skin (removes small amounts of water, urea
and salts in the form of sweat) and lungs (eliminate carbon-dioxide and
water vapour through exhaling).
1. Skin
Skin is the outer most
covering of the body. It stretches all over the body in the form of a layer. It
accounts for 15% of an adult’s human body weight. ere are many structures and
glands derived from the skin. It eliminates metabolic wastes through
perspiration.
The human body functions
normally at a temperature of about 370C. When it gets hot sweat glands start
secreting sweat, which contains water with small amounts of other chemicals
like ammonia, urea, lactic acid and salts (mainly sodium chloride). The sweat
passes through the pores in the skin and gets evaporated.
2. Kidneys
Kidneys are bean-shaped
organs reddish brown in colour. The kidneys lie on either side of the vertebral
column in the abdominal cavity attached to the dorsal body wall. The right
kidney is placed lower than the le kidney as the liver takes up much space on
the right side. Each kidney is about 11 cm long, 5 cm wide and 3 cm thick. The kidney
is covered by a layer of brous connective tissue, the renal capsules, adipose
capsule and a brous membrane.
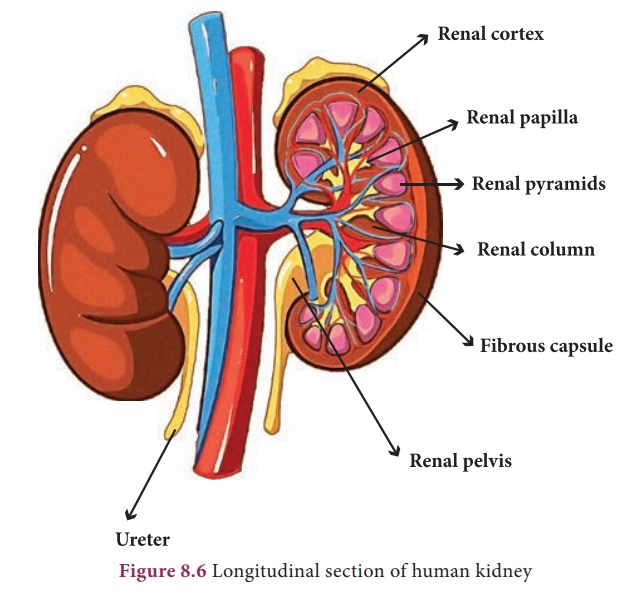
Internally the kidney consists of an outer dark region, the cortex and an inner lighter region, the medulla.
Both of these regions contain uriniferous tubules or nephrons.
The medulla consists of multitubular conical
masses called the medullary pyramids or renal pyramids whose bases are adjacent
to cortex. On the inner concave side of each kidney, a notch called hilum is
present through which blood vessels and nerves enter in and the urine
leaves out.
Ureters: Ureters are thin
muscular tubes emerging out from the hilum. Urine enters the ureter from
the renal pelvis and is conducted along the ureter by peristaltic movements of
its walls. The ureters carry urine from kidney to urinary bladder.
Urinary bladder: Urinary bladder is a
sac-like structure, which lies in the pelvic cavity of the abdomen. It stores
urine temporarily.
Urethra: Urethra is a
membranous tube, which conducts urine to the exterior. The urethral
sphincters keep the urethra closed and opens only at the time of micturition
(urination).
Functions of kidney
·
Maintain the fluid and electrolytes balance in our body.
·
Regulate acid-base balance of blood.
·
Maintain the osmotic pressure in blood and tissues.
·
Help to retain the important plasma constituents like glucose and
amino acids.
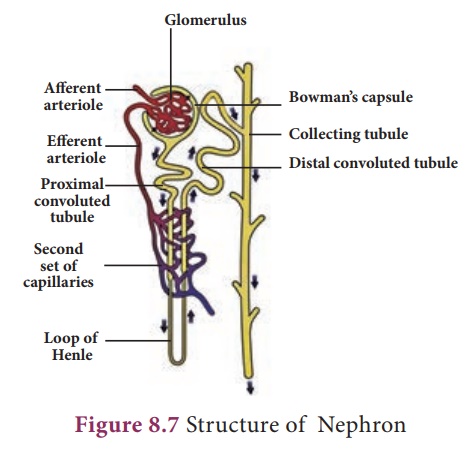
3. Structure of Nephron
Each kidney consists of
more than one million nephrons. Nephrons or uriniferous tubules are
structural and functional units of the kidneys. Each nephron consists of
Renal corpuscle or Malphigian corpuscle and renal
tubule. The renal corpuscle consists of a cup-shaped structure
called Bowman’s capsule containing a bunch of capillaries called
glomerulus. Blood enters the glomerular capillaries through a
erent arterioles and leaves out through e erent arterioles. The Bowman’s
capsule continues as the renal tubule which consists of three regions proximal
convoluted tubule, U-shaped hair pin loop, the loop of Henle and
the distal convoluted tubule. The distal convoluted tubule which opens
into the collecting tubule. The nitrogenous wastes are drained
into renal pelvis which leads to ureters and stored in the urinary bladder.
Urine is expelled out through the urethra.
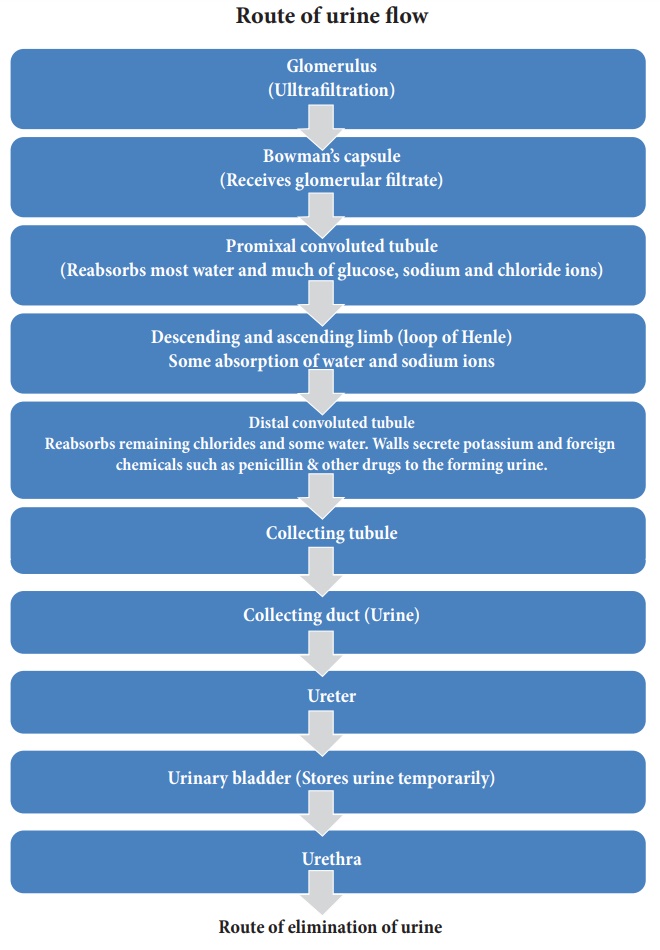
4. Mechanism of Urine Formation
The process of urine
formation includes the following three stages.
·
Glomerular ltration
·
Tubular reabsorption and
·
Tubular secretion
Glomerular ltration: Urine formation begins
with the ltration of blood through epithelial walls of the glomerulus and
Bowman’s capsule. The ltrate is called as the glomerular ltrate. Both essential
and non-essential substances present in the blood are ltered.
Tubular reabsorption: The filtrate in the
proximal tubule consists of essential substances such as glucose, amino acids,
vitamins, sodium, potassium, bicarbonates and water that are reabsorbed into
the blood by a process of selective reabsorption.
Tubular secretion: Substances such as H+
or K+ ions are secreted into the tubule. Certain substances like potassium
and a large number of drugs like penicillin and aspirin are passed into the
ltrate in the distal convoluted tubule. is tubular ltrate is nally known as
urine, which is hypertonic in man. Finally the urine passes into
collecting ducts to the pelvis and through the ureter into the urinary bladder
by urethral peristalsis (waves of constriction in the ureters). The relaxation
of sphincter muscles located at the opening of the urinary bladder into the
urethra. When the urinary bladder is full the urine is expelled out through the
urethra. is process is called micturition. A healthy person excretes one
to two litres of urine per day.
Dialysis or Artificial kidney
When kidneys lose their
filtering efficiency, excessive amount of fluid and toxic waste accumulate in
the body. This condition is known as kidney (renal) failure. For
this, an artificial kidney is used to filter the blood of the patient. The
patient is said to be put on dialysis and the process of purifying blood by an
artificial kidney is called haemodialysis. When renal failure cannot be
treated by drug or dialysis, the patients are advised for kidney
transplantation.
Related Topics