Chapter: Modern Medical Toxicology: Neurotoxic Poisons: Hallucinogens (Psychedelic Drugs)
Hallucinogens (Psychedelic Drugs)
Hallucinogens (Psychedelic Drugs)
Hallucinogens
(also called psychedelics or psychotomimetic agents) are substances that induce
changes in thought, perception, and mood, without causing major disturbances in
the autonomic nervous system. Perceptual alterations can take the form of
illu-sions, synaesthesias, or hallucinations. An illusion is the result of misinterpretation of an actual
experience, while synaesthesias are
sensory misperceptions (e.g. hearing colour or seeing sounds). Both require
external stimuli for their institution. Hallucinations
differ from them in this important respect, since they are percep-tual
alterations without any external stimulation whatsoever.
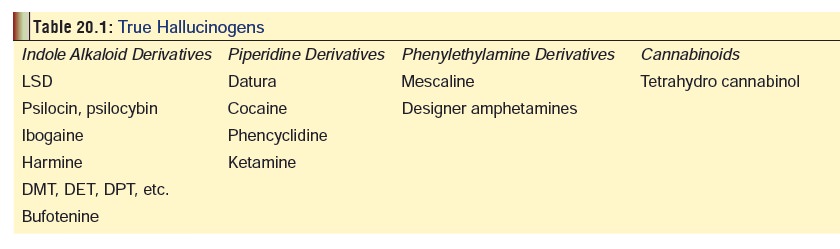
Hallucinations may be visual, auditory, olfactory, gustatory, or tactile in nature. Most hallucinogens induce visual or auditory hallucinations; a few cause tactile or olfactory manifestations. While a number of therapeutic drugs can cause hallucinations in overdose, they are not classified as hallucinogens. A true hallucinogen is a drug that induces hallucinations in small doses (sometimes, as in the case of LSD, in microgram doses). Most genuine hallucinogens cause vivid visual hallucinations, while the other types of hallucinations are relatively uncommon. Table 20.1 lists common hallucinogens, some of which will bediscussed in detail in this section, while the others have been discussed in appropriate sections elsewhere.
Related Topics