Chapter: Measurements and Instrumentation : Transducers and Data Acquisition Systems
Hall-effect transducers
Hall-effect
transducers
Basically,
a Hall-effect sensor is a device that is used to measure the magnitude of a
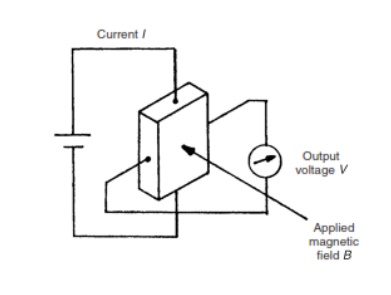
magnetic field. It consists of a conductor carrying a current that is aligned
orthogonally with the magnetic field, as shown in Figure 13.4. This produces a
transverse voltage difference across the device that is directly proportional
to the magnetic field strength. For an excitation current I and magnetic field
strength B, the output voltage is given by V D KIB, where K is known as the
Hall constant
The
conductor in Hall-effect sensors is usually made from a semiconductor material
as opposed to a metal, because a larger voltage output is produced for a
magnetic field of a given size. In one common use of the device as a proximity
sensor, the magnetic field is provided by a permanent magnet that is built into
the device. The magnitude of this field changes when the device becomes close
to any ferrous metal object or boundary. The Hall Effect is also commonly used
in keyboard pushbuttons, in which a magnet is attached underneath the button.
When the button is depressed, the magnet moves past a Hall-effect sensor. The
induced voltage is then converted by a trigger circuit into a digital output. Such
pushbutton switches can operate at high frequencies without contact bounce.
Related Topics