Chapter: Web Technology : Web Essentials
HTML
HTML
History:
· The first
version of HTML was created using the Standard
Generalized Mark up Language (SGML).
· In the
early years of HTML, Web developers were free to define and modify HTML in
whatever ways they thought best.
· Competing
browsers introduced some differences in the language. The changes were called extensions.
· A group
of Web developers, programmers, and authors called the World Wide Web Consortium,
or the WC3, created a set of
standards or specifications that all browser manufacturers were to follow.
· The WC3has no enforcement power.
· The
recommendations of the WC3are
usually followed since a uniform approach to Web page creation is beneficial to
everyone.
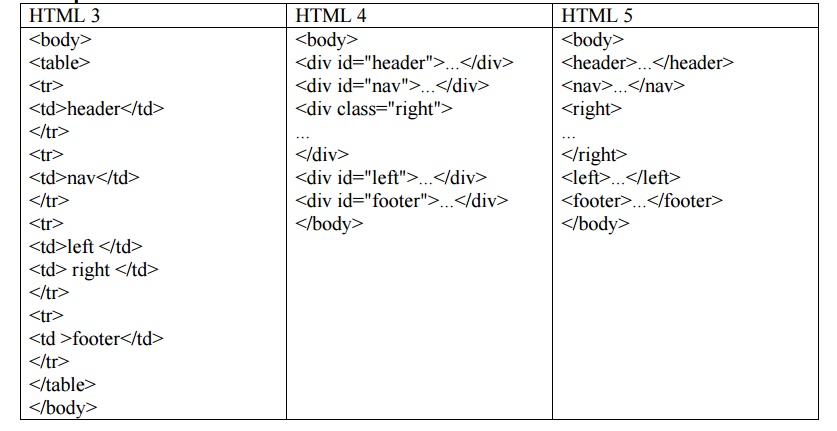
Comparison
of HTML versions:
HTML Basics:
HTML is
primarily composed of two types of markup:
•
Elements or tags
o <html></html>
• Attributes
that modify an element
HTML Elements
• Elements
are the fundamental building blocks of HTML.
• They are
the tags that tell the browser what the enclosed text is.
HTML
Tags:
•
Container Tags
o <Begin formatting>some text</End
formatting> o For example: <B>some bold text</B>
<H1>some
heading </H1>
• Empty
Element Tags
o For
example <HR> <BR>
• Comment
Tag
o <!--
Hi, I'm a comment. -->
o Use
them document complicated layouts!
• Case
insensitive
• Unrecognised
tags are simply ignored by browser!!
• Container
tags must be nested!!
• As a text
document, your HTML in Notepad will contain elements,
such as headers, titles, paragraphs, etc.
• These
elements must be denoted in your script, which is done using tags
• HTML tags
consist of a left angle bracket (<), a name, and a right angle bracket(>)
• For
example: <title>
• Tags must
also close. To do so, you incorporate a slash (/). A starting and ending tag
would be: <title> </title>.
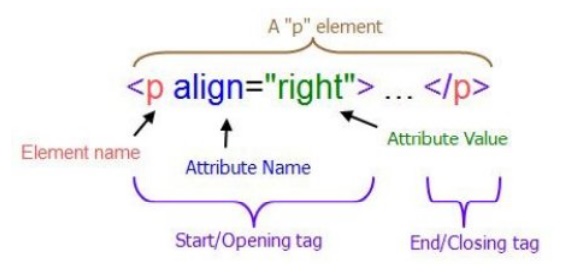
Attributes:
• You can
add attributes to tags to enhance your page.
• Added
attributes go inside the brackets of the opening tag(example: <p
align=center> would center the paragraph)
About HTML file Structure:
· HTML
files .htm or .html extensions
· Name your
files to describe their functionality file name of your home page should be index.html
Common Tags (Elements):
· Always
include the <HTML>…</HTML> tags
· Comments
placed inside <!--…--> tags
· HTML
documents
o HEAD section.
o Info about the document.
o Info in
header not generally rendered in display window. o TITLE element names your Web page.
o BODY section
Page
content
Includes
text, images, links, forms, etc.
Elements
include backgrounds, link colors and font faces P element forms a paragraph, blank line before and after
Structure
of HTML Tag (Element) Alignment

Text Styling
• Underline
style<U>…</U>
• Align
elements with ALIGN attributeright, left or center
• Close
nested tags in the reverse order from which they were opened
• Emphasis
(italics) style<EM>…</EM>
• Strong
(bold) style<STRONG>…</STRONG>
• <B>
and <I> tags deprecated Overstep boundary between content and
presentation
• Logical
Styles:
o
<EM>, <STRONG> a add emphasis to text
o
<BIG>, <SMALL> a increase or decrease text size o <SUB>,
<SUP> a subscript or superscript
•
Physical styles:
o
<B>, <I>, <U> a Bold, Italics, and Underline text
o
<FONT SIZE=# FACE= “name” COLOR=“colorName or #rgb” > o E.g., <FONT
SIZE=+2 FACE = “arial” COLOR = “darkblue”>
eXtensible Mark up Language (XHTML) :
• To
describe the general form and layout of documents
• An XHTML
document is a mix of content and controls
• In XHTML tag names, attributes, and values
are case sensitive and values must be enclosed by double quotes.
• In XHTML all elements must have both
beginning and ending tags.
• Controls
are tags and their attributes
o Tags
often delimit content and specify something about how the content o should be
arranged in the document.
o
Attributes provide additional information about the content of a tag.
• Tools for creating XHTML documents
o XHTML
editors - make document creation easier o Shortcuts to typing tag names,
spell-checker,
o WYSIWYG
XHTML editors
• Plug ins
o
Integrated into tools like word processors,
o
effectively converting them to WYSIWYG o XHTML editors
• Filters
o Convert
documents in other formats to XHTML
Advantages of both filters and plug-ins:
• Existing
documents produced with other tools
• can be
converted to XHTML documents
• Use a
tool you already know to produce XHTML
Disadvantages of both filters and plug-ins:
• XHTML
output of both is not perfect - must be fine tuned
• XHTML may
be non-standard
• You have
two versions of the document, which are difficult to synchronize
Relative URL
HTML Link:
To create a link to a resource identifiable by a
URL o href: specify a URL of the target resource
o target:
specify where to display the target document
e.g.: <a href="index.htm"
target="_blank">Home</a> Open the document
"index.htm" in a new browser window
Can also be used to create an anchor within a
document o name: specify the anchor name
e.g.: <a name="chap1"></a><h2>Chapter
1</h2> The above anchor can be referred to in a URL as
<a
href="http://host/file.html#chap1">Chapter 1</a>
URL (Uniform Resource Locator) in HTML:
URL is
used to create a link in a web document.
Two Types of URL:
1. Absolute URL
•
Absolute URL contains all the information necessary to identify files on the
internet (Example: in postal service, for sending letter to the destination it
necessary to have full information like, name, address, city etc.,)
• Likewise,
an absolute URL contains the protocol, hostname, filename, which are all
essential to link the web document.
Example:
i. http://google.com/index.html
Related Topics