Chapter: Civil : Engineering Geology : Application Of Geological Investigations
Geological Characters For Investigation
GEOLOGICAL CHARACTERS FOR
INVESTIGATION
Geology
of the Area
Preliminary geological surveys of the entire catchments area
followed by detailed geological mapping of the reservoir area have to be
conducted. These should reveal
main topographic features, natural drainage patterns,
general characters and structures of rock formations such as
their stratification, folding and faulting and igneous intrusions, and
the trend
and rate of weathering and erosion in the area.
Geology of the site Lithology.
Ø The
single most important feature that must be known thoroughly at the site and all
around and below the valley up to a reasonable depth is the Lithology, i.e.
types of the rocks that make the area.
Ø Surface
and subsurface studies using the conventional and latest techniques of
geological and geophysical investigations are carried out.
Ø Such
studies would reveal the type, the composition and textures of the rocks
exposed along the valley floor, in the walls and up to the required depth at
the base.
Ø Rocks are
inherently anisotropic materials, showing variation in properties in different
directions.
Ø Complex
litho logy definitely poses challenging design problems.
Structures
Ø This involves detailed mapping of planes of
weakness like bedding planes, schistosity, foliation, cleavage, joints, shear
zones, faults and fault zones, folding and the associated features.
Ø While
mapping these features, special attention is given to recording their attitude,
spacing and nature.
Ø Shear
zones have to be searched, mapped and treated with great caution.
Ø In some cases, these may be developed to such an
extent that the rock may necessitate extensive and intensive rock treatment
(e.g. excavation, backfilling and grouting etc.).
Following is a brief account of the influence of
more important structural features of rocks on dam foundations
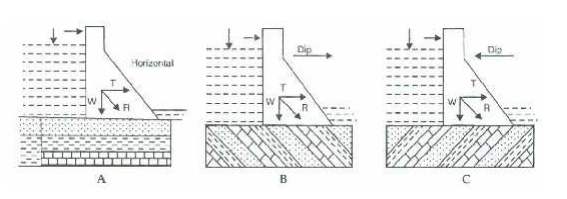
Dip and
Strike
Ø The
strength of sound, un fractured stratified rock is always greater when the
stresses are acting normal to the bedding planes than if applied in other
directions.
Ø This
being so, horizontal beds should offer best support for the weight of the dam.
Ø But as is
shown in a latter section, the resultant force is always inclined downstream.
Ø the most
UNFAVOURABLE strike direction is the one in which the beds strike parallel to
the axis of the dam and the dip is downstream
Ø It must
be avoided as far as possible.
Ø Therefore,
other conditions being same, beds with upstream dips are quite favorable sites
for dam foundations.
Faults
These structures can be source of danger to the dam in a
number of ways. Thus,
v The
faulted rocks are generally shattered along the rupture surfaces;
v Different
types of rocks may be present on either side of a fault plane. Hence, sites
with fault planes require great caution in calculating the design strength in
various sections of the dam.
v Dams
founded on beds traversed by fault zones and on major fault planes are more
liable to shocks during an earthquake compared to dams on non-faulted rocks.
Related Topics