Chapter: Civil : Engineering Geology : Application Of Geological Investigations
Application Of Geological Investigations: Roads And Highways
ROADS AND HIGHWAYS
Their planning, designing, construction and maintenance are
among the major duties of civil engineers the world over.
geological investigations play important role in the design,
stability and economical construction and maintenance of the roads.
Such investigations are aimed at providing full details
regarding topography of the area, lithological characters of the rocks or soil
and the ground water conditions.
Topography
Topography or the landform of a region is single most
important factor that controls the selection of alignment of a road project.
Topographic maps would reveal the existence of various land
features like valleys and the inflowing streams, the hills and their undulations,
the plateaus and the plains with all their varying configuration from place to
place.
Obviously, knowledge of all such features is not only
important but very essential for a right alignment.
Preliminary surveys, including aerial surveys followed by
detailed surveys are often necessary to obtain desired topographical
Lithological
Character
Broadly speaking, ground may be divided into two types:
consolidated, massive hard rock type and soft, unconsolidated type.
The Massive groups of rocks include all varieties of igneous,
sedimentary and metamorphic rocks which can stand even with vertical slopes.
For making roads through them, however, these
rocks require extensive blasting operations.
They cannot be simply cut out or dug out, Once cut, especially
if they are free from joints and fractures and un favorably inclined bedding
planes, these rocks stand erect for year without much maintenance.
The Unconsolidated group presents the engineer many
complicated problems. Thorough soil investigations regarding their mode of
origin, texture, structures, porosity, permeability, degree of compaction,
consolidation characteristics or compressibility, etc all are requited to be
known within broad limits to design safe.
and
stable roads over them.
Residual soils are generally homogeneous and
properties evaluated from selective bore hole samples might prove sufficient.
Geological
Structures
The structural features of rocks, especially in those of
sedimentary and metamorphic origin, have very important bearing upon the design
of cuts as well as on the stability of the road as a whole.
A given rock might be quite hard and otherwise
sound for a cut as road foundation.
But, if in the same rock some planes of weakness
(such as bedding planes, joints, foliation, cleavage) are present in such a way
that these are inclined towards the free side of the valley, the rock could
likely fail along these planes.
Such structural features include dip and strike,
joints, fault planes and shear zones.
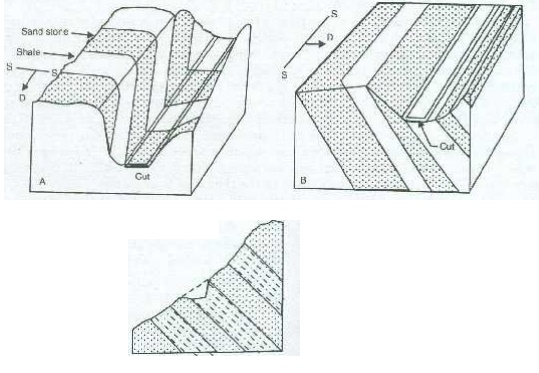
Dip and Strike.
There may be three possibilities for making a cut in the
inclined beds: it can be made parallel, at right angles or inclined to the dip
direction.
The relative merits of the cut vis-a-vis its stability would
be as follows assuming other things are favourable:
Cut is
parallel to the dip direction: In such a case, the layers offer a uniform
behaviour on either side of the cut and as such the risk of failure is minimal
on this account.
Cut is made parallel to the strike, that is, at
right angles to the dip direction. In some cases where the layers dip into the
hill rather than
in the
road, the cut is considered quite stable
Related Topics