Chapter: 10th Science : Chapter 3 : Thermal Physics
Fundamental Laws of Gases
FUNDAMENTAL
LAWS OF GASES
The three fundamental
laws which connect the relation between pressure, volume and temperature are as
follows:
1.
Boyle’s Law
2.
Charles's law
3.
Avogadro's law
1. Boyle’s law:
When the temperature of
a gas is kept constant, the volume of a fixed mass of gas is inversely
proportional to its pressure. This is shown in Figure 3.6.
P α 1/V
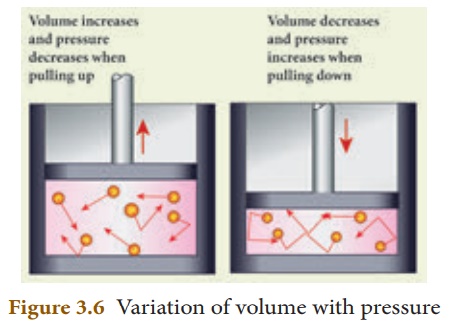
In other words, for an
invariable mass of a perfect gas, at constant temperature, the product of its
pressure and volume is a constant.
(i.e) PV = constant
2. Charles's law (The law of volume)
Charles’s law was
formulated by a French scientist Jacques Charles. According to this law, When
the pressure of gas is kept constant, the volume of a gas is directly
proportional to the temperature of the gas.
V α T
or V/T = constant
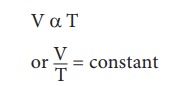
3. Avogadro's law
Avogadro's law states
that at constant pressure and temperature, the volume of a gas is directly
proportional to number of atoms or molecules present in it.
i.e. V α n
(or) V/n = constant

Avogadro’s number (NA)
is the total number of atoms per mole of the substance. It is equal to 6.023 ×
1023 /mol.
Related Topics