Chapter: Computer Networks : Fundamentals & Link Layer
Framing in Computer Networks
FRAMING
The sream
of bits are not advisible to mqaintain in networks. When an error occurs, then
the entire stream have to retransmitted. To avoid this, the framing concept is
used. In this, the stream of bits are divided into manageable bit units called
frames. To achive, we are using several ways. They are,
1. Byte
Oriented Protocols
2. Bit
Oriented Protocols
3. Clock
Based Protocols
1. BYTE ORIENTED PROTOCOLS:
Each
frame is considered as a collection of bytes rather than a collection of bits.
There are two approaches. They are,
1. Sentinel approach
In this
approach it uses special characters called sentinel characters to indicate
where frames start and end. This approach is called character stuffing because extra
characters are inserted in the data portion of the frame.
Ex: 1. Binary Synchronous
Communication (BISYNC)
2. Point to
Point Protocol
2. Byte Count Approach
In this
approach no of bytes in frame are counted and entered in the header. The COUNT
Field specifies how many bytes are contained in the frame‟s body.
Ex: 1.Digital Data Communication
Message Protocol
2. BIT ORIENTED PROTOCOLS:
It views
the frames as a collection of bits. The Synchronous Data Link Control (SDLC)
protocol developed by IBM is an example of a bit oriented protocol. It was
later standardized by the ISO as the High Lever Data Link Control (HDLC)
HDLC – HIGH LEVEL DATA LINK CONTROL
It is a
bit oriented data link protocol designed to support both half duplex and full
duplex communication over point to point and multi point links.
FRAME FORMAT
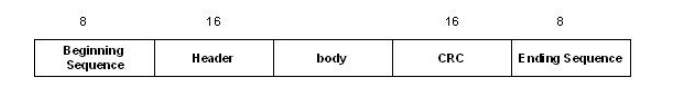
HDLC
denotes both the beginning and the end of a frame with the distinguished bit
sequence 01111110. To guarantee that a special sequence does not appear in
advertently anywhere else in the frame, HDLC uses a process called bit
stuffing.
On the
sending side, any time five consecutive 1s have been transmitted from the body
of the message, the sender inserts a 0 before transmitting the next bit. On the
receiver side, should five consecutive 1s arrive, the receiver makes its
decision based on the next bit it sees. If the next bit is a 1, then one of the
two things is true. Either this is the end of the frame or an error has been
introduced. By looking at the next bit, it can conclude. If it sees a 0, then
it is the end of frame. It else, then there must have an error and the whole
frame has been discarded.
3. CLOCK BASED PROTOCOLS:
The
Synchronous Optical NETwork (SONET) is one of the protocols using the clock
based framing approach.
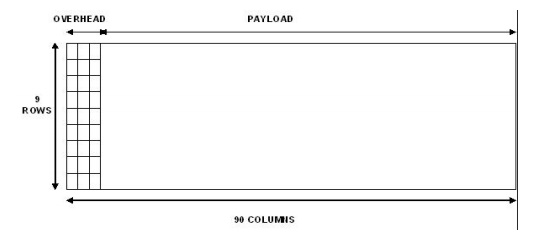
SONET:
It was
developed by the ANSI for digital transmission over optical network. It
addresses both the framing and encoding problems. A SONET frame has some
special information to distinguish where the frame starts and ends.
Related Topics