Chapter: Mechanical : Maintenance Engineering : Repair Methods For Basic Machine Elements
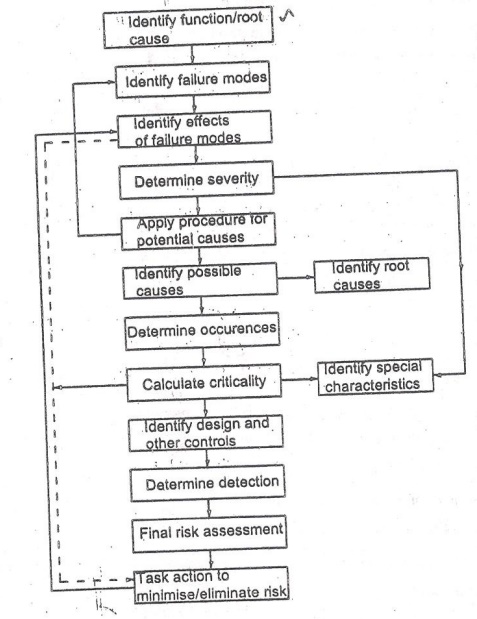
Flow chart for FMEA
Flow chart for FMEA
FMEA is
methodology for analyzing potential reliability problems early in the
development cycle where it is easier to take actions to overcome the issues,
thereby enhancing reliability through design .
FMEA is a
procedure in operations management for analysis of potential failure modes
within a system for classification by severity or determination of the effect
of failures on the system. It is widely used in manufacturing industries in
various phases of the product life cycle and is now increasingly finding use in
the service industry. Failure modes are any errors or defects in a
process, design, or item, especially those that affect the customer, and
can be potential or actual. Effects analysis refers to studying the
consequences of those failures.
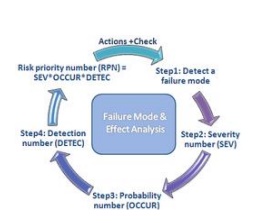
FMEA cycle.
Failure mode:
"The manner by which a failure is observed; it generally describes the way
the failure occurs."
Failure effect:
Immediate consequences of a failure on operation, function or functionality,
or status of some item
Indenture levels: An
identifier for item complexity. Complexity increases as levels are closer
to one.
Local effect: The Failure effect as it
applies to the item under analysis.
Next higher level effect: The
Failure effect as it applies at the next higher indenture level. End effect:
The failure effect at the highest indenture level or total system.
Failure cause: Defects
in design, process, quality, or part application, which are the underlying
cause of the failure or which initiate a process which leads to failure. Severity:
"The consequences of a failure mode. Severity considers the worst
potential consequence of a failure, determined by the degree of injury,
property damage, or system damage that could ultimately
Advantages
•
Improve the quality, reliability and safety of a
product/process
•
Improve company image and competitiveness
•
Increase user satisfaction
•
Reduce system development timing and cost
•
Collect information to reduce future failures,
capture engineering knowledge
•
Reduce the potential for warranty concerns
•
Early identification and elimination of potential
failure modes
•
Emphasize problem prevention
•
Minimize late changes and associated cost
•
Catalyst for teamwork and idea exchange between
functions
•
Reduce the possibility of same kind of failure in
future
Limitations
FMEA is effectively dependent on the members of the committee which examines product failures, it is limited by their experience of previous failures. If a failure mode cannot be identified, then external help is needed from consultants who are aware of the many different types of product failure. FMEA is thus part of a larger system of quality control, where documentation is vital to implementation. General texts and detailed publications are available in forensic engineering and failure analysis. It is a general requirement of many specific national and international standards that FMEA is used in evaluating product integrity. If used as a top-down tool, FMEA may only identify major failure modes in a system. Fault tree analysis (FTA) is better suited for "top-down" analysis. When used as a "bottom-up" tool FMEA can augment or complement FTA and identify many more causes and failure modes resulting in top-level symptoms. It is not able to discover complex failure modes involving multiple failures within a subsystem, or to FaultTree+ is a fully interactive graphics and analysis program for performing probabilistic risk assessment using integrated fault tree, event tree and Markov analyses..
Related Topics