Objectives, Principles | Administrative Machinery in India | Political Science - Financial Administration | 12th Political Science : Chapter 6 : Administrative Machinery in India
Chapter: 12th Political Science : Chapter 6 : Administrative Machinery in India
Financial Administration
Financial Administration
Financial Administration : Objectives
Financial administration which is characterised by
deficit budgets, massive public debt and deficit financing.
These are as follows:
1) Management of the finances of public household
2) Implementation of projects and programmes
3) Provision for public goods and social services
4) Growth, Employment and Price Stability
5) Capital formation
6) Productive deployment of national funds
7) Facilitating smooth flow of parliamentary processes
8) Achieving equity and equality.
Principles of Financial Administration
The following may be listed as some of the important principles
of financial administration
1. The principle of primacy of public interest,
public choice and public policy
2. The principle of political direction and control
3. The principle of correspondence
4. The principle of unity of organisation and
management
5. The principle of stability and balance
6. The principle of simplicity and flexibility
7. The principle of conduct, discipline and
regularity
8. The principle of public trust and
accountability.
Four Distinct Phases- Financial Administrative History of India
Period I
(1765-1858) - Creation of
structure and concretisation.
Period II
(1860-1919) - Development of systems and Procedures.
Period
III (1919-1947) - Democratisation and Decentralisation
Period IV
(1950-till date) - Development
orientation.
New Emerging Trends - Financial Administration in India
1) Regulation and control of fiscal deficit
2) Cutback on non-development expenditure
3) Development of zero base perspective
4) De-emphasised public sector
5) Non-bureaucratic delivery of public goods and
services
6) Focus on decentralized responsibility for
financing development plans
7) Towards deregulation and liberalization
1. Enactment and Execution of Budget
Budgetary Cycle
In order to allow time for the executive and
legislative processes to go through, budgeting is geared to a cycle. The
process of approval is very significant in are possible form of government.
The cycle consists of four phases:
Preparation and submission;
Approval;
Execution; and Audit
At any given point of time, several cycles would be
in operation and would be over lapping. Nevertheless, various segments of a
cycle have different operational life.
Budget Preparation
In India, budget preparation formally begins on the
receipt of a circular from the Ministry of Finance sometime during
September/October, that is, about six months before the budget presentation.
The circular prescribes the time-schedule for sending final estimates
separately for plan and non-plan, and the guidelines to be followed in the
examination of budget estimates to be prepared by the department concerned. The
general rule is that the person who spends money should also prepare the budget
estimates. Budget proposals normally contain the following information:
i) Accounts classification
ii) Budget estimates of the current year
iii) Revised estimates of the current year
iv) Actuals for the previous year; and
v) Proposed estimates for the next financial year.
Financial Year
When the first modern budget was presented in 1860,
the financial year adopted by the government was from 1st May to 30th April.
Beginning with the year 1866, however, the financial year was changed to 1st
April to 31stMarch, in conformity with the practice in England.
2. Tax Structure in India
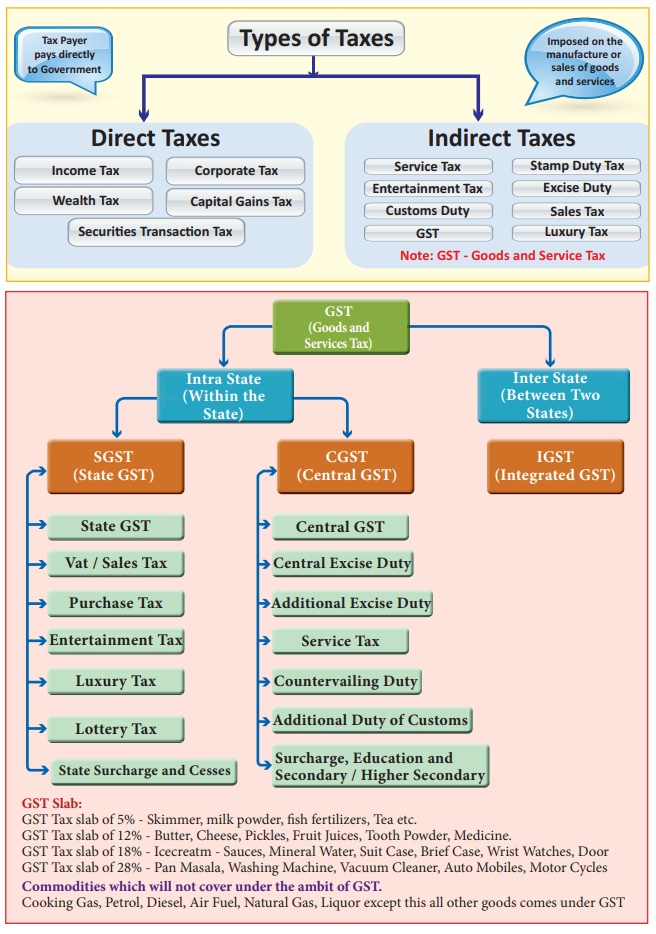
Related Topics