Nutritional significance, Role of fats in cooking - Fats and oils | 11th Nutrition and Dietetics : Chapter 5 : Nuts Oil Seeds and Sugar
Chapter: 11th Nutrition and Dietetics : Chapter 5 : Nuts Oil Seeds and Sugar
Fats and oils
Fats
and oils
Fat is an important
component of our diet and serves a number of functions in the body. Fat provides
our body with energy. Although we can get energy from other nutrients in our
diet, we need some fat as it provides essential fatty acids that our body
cannot make. It is also a carrier of the fat- soluble vitamins and is necessary
for their absorption. In general, no more than about one third of our energy
intake should come from fat as too much fat can be associated with high energy
intakes that can lead to weight gain.
Nutritional significance
·
A small amount of fat is an essential part of a healthy,
balanced diet.
·
Fat helps the body to absorb vitamins A, D and E. These vitamins
are fat-soluble, meaning they can only be absorbed with the help of fats.
·
Any fat not used by body's cells or to create energy is
converted into body fat. Likewise, unused carbohydrate and protein are also
converted into body fat.
·
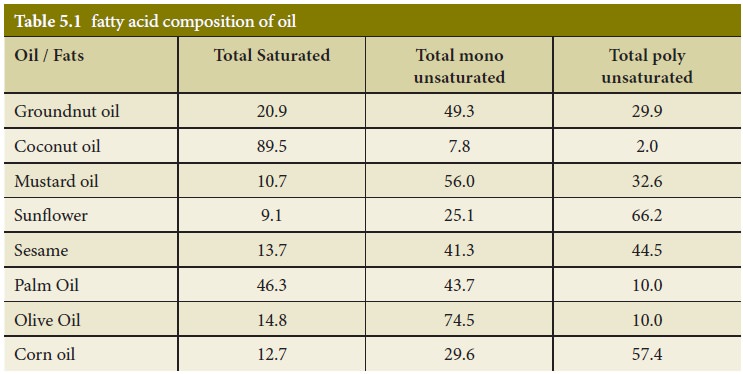
All types of fat are high in energy. A gram of fat, whether
saturated or unsaturated, provides 9kcal (37kJ) of energy compared with 4kcal
(17kJ) for carbohydrate and protein. The fatty acid composition of oil is given
in table 5.1.
Role of fats in cooking
They have
high energy value.
Impart
palatability to diet.
Add
flavour and texture to the food.
Improve
taste and blends well with the food.
Makes the
food crispy.
In common usage,
it is classified as fats and oils. Fats are solid at room temperature where as
oils are liquid at room temperature.
Refined oils
Vegetable oils are
produced from oil- containing seed, fruits or nuts by various pressing
processes, by solvent extraction and also by combination of these. A seed cake
that is relatively high in protein remains, after fat extraction is often used
for animal feed.
Hydrogenation - vanaspathi and margarine
Hydrogenation
Plant oils contain a
large percent of unsaturated fatty acids and hence have a tendency to become
rancid. These unsaturated glycerides in oil can be converted to saturated
glycerides by the addition of hydrogen. This process is known as hydrogenation.
Hydrogenated fat is
manufactured from vegetable oils by the addition of molecular hydrogen to the
double bonds in the unsaturated fatty acids in the presence of nickel.
Unsaturated Fatty
Acids are of two types. There are
·
MUFA – Mono Unsaturated Fatty Acids
·
PUFA – Poly Unsaturated Fatty Acids
Vanaspathi
Hydrogenated oil in
India is known as Vanaspathi. It is manufactured by hydrogenating refined
groundnut oil or a mixture of groundnut oil with other edible vegetable oils.
Good and Bad Fatty Acids are found in Vanaspathi.
Margarine
·
Margarine is made from vegetable oils like cotton seed oil, soya
bean oil, corn oil, groundnut oil, coconut oil and also meat fat.
·
Margarine is made from one or more optional fat ingredients
churned with cultured pasteurized skimmed milk or whey.
·
Margarine is often used as a substitute for butter.

Related Topics