Chapter: Obstetrics and Gynecology: Human Sexuality
Factors Affecting Sexuality
FACTORS AFFECTING SEXUALITY
The relationship between an
overall sense of personal well-being and sexual function is complex.
Approximately one-third of women presenting with sexual dysfunction are
clinically depressed. Among individuals in whom depression has already been
diagnosed, the type and progress of ongo-ing therapy and prescribed medication
should be noted.
The commonly prescribed selective
serotonin-reuptake inhibitors, such as fluoxetine, paroxetine, sertra-line, and
escitalopram, can be associated with decreased sexual desire. The clinical
observation that is helpful when evaluating the contribution of medications to
female sexual dysfunction is that antidepressants that activate dopaminer-gic,
(central) noradrenergic, and 5-hydroxytriptamine (5-HT) 1A and 5-HT2C receptors
may augment sexual response, whereas those that activate other 5-HT receptors,
prolactin, and gamma-amino-butyric acid reduce sexual response. The medications
least likely to interfere with sexual response are nefazodone, mirtazapine,
bupropion, venlafaxine, and buspirone.
Further complicating this picture
is that depression itself causes a decrease in sexual desire. Other medications
that can be associated with female sexual dysfunction are included in Box 47.2.

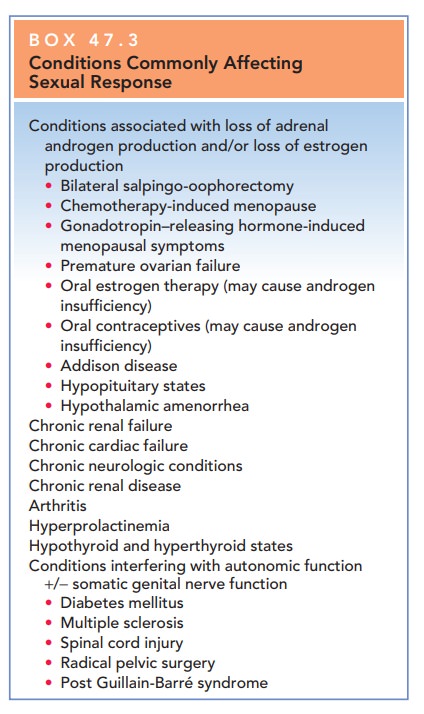
Medical conditions that affect energy and well-being may indirectly affect sexual desire and response, particularly those that are associated with the loss of estrogen and/or androgen production (Box 47.3). Estrogen is thought to have both a direct effect (by producing vulval and vaginal congestion) and an indirect effect (by influencing mood) on female sexual response. There is likewise a strong consensus that androgens are needed for sexual response in women, though the limitations of widely available laboratory assays have made it difficult to establish a direct correlation between specific androgen levels and women’s sexual desire.
Psychologic factors commonly
affect sexual response in women as well (Box 47.4). These factors continuously
modulate any arousal experienced from sexual stimuli and influence the woman’s
motivation to seek or respond to those sexual stimuli—compounding any negative
effects from biologic factors.

Related Topics