The Mughal Empire | Term 2 Unit 2 | History | 7th Social Science - Exercises Questions with Answers | 7th Social Science : History : Term 2 Unit 2 : The Mughal Empire
Chapter: 7th Social Science : History : Term 2 Unit 2 : The Mughal Empire
Exercises Questions with Answers
Evaluation
I. Choose the correct answer
1. Who introduced the Persian style
of architecture in India?
a)
Humayun
b)
Babur
c)
Jahangir
d)
Akbar
Answer: b) Babur
2. In which battle did Akbar defeat
Rana Pratap?
a)
Panipat
b)
Chausa
c)
Haldighati
d)
Kanauj
Answer: c)
Haldighati
3. Whose palace in Delhi was destroyed
by Sher Shah?
a)
Babur
b)
Humayun
c)
Ibrahim Lodi
d)
Alam Khan
Answer: b) Humayun
4. Who introduced Mansabdari system?
a)
Sher Sha
b)
Akbar
c)
Jahangir
d)
Shah Jahan
Answer: b) Akbar
5. Who was the revenue minister of
Akbar?
a)
Birbal
b)
Raja Bhagwan Das
c)
Raja Todarmal
d)
Raja Man Singh
Answer: c) Raja
Todarmal
II. Fill in the Blanks
1.
Chetak
was the name of the horse of Rana Pratap.
2.
Ibadat
Khana was a hall at FatehpurSikri where scholars of all religions
met for a discourse.
3.
The Sufi saint who received Akbar’s utmost respect was Salim Chishti.
4.
During the reign of Shah Jahan the Zabti system was extended to
the Deccan provinces.
5.
Suyurghal
were tax-free lands given to scholars and religious institutions.
III. Match the following
1.
Babur - Ahmednagar
2.
Durgavati - Jaipur
3. Rani Chand Bibi - Akbar
4.
Din IIahi - Chanderi
5. Raja Man Singh - Central Province
Answer:
1. Babur - Chanderi
2. Durgavati - Central Province
3. Rani Chand Bibi - Ahmednagar
4. Din IIahi - Akbar
5. Raja Man Singh - Jaipur
IV. True or False
1.
Babur inherited Farghana, a small kingdom in Central Asia. [True]
2.
Humayun succeeded in recapturing Delhi in 1565. [False]
3.
Aurangzeb married a girl of a notable Rajput family. [False]
4.
Jahangir ordered execution of Sikh leader Guru Arjun for helping his son Khusrau. [True]
5.
During Aurangzeb’s reign, architecture received much patronage. [False]
V. Consider the following
statements. Tick (âś“) the appropriate answer.
1.
Assertion (A): The British established
their first factory at Surat.
Reason (R): Jahangir
granted trading rights to the English.
a)
R is the correct explanation of A.
b)
R is not the correct explanation of A.
c)
A is wrong and R is correct.
d)
(A) and (R) are wrong.
Answer: a) R is the
correct explanation of A.
2.
Assertion (A): Aurangzeb’s intolerance
towards other religions made him unpopular among people.
Reason (R): Aurangzeb
re-imposed the jizya and pilgrim tax on the Hindus.
a)
R is the correct explanation of A.
b)
R is not the correct explanation of A.
c)
A is wrong and R is correct.
d)
(A) and (R) are wrong.
Answer: a) R is the correct explanation of A.
3. Find out the correct statements
(I) Kamran was the son of Afghan noble, Hasan Suri,
ruler of Sasaram in Bihar.
(II)
Akbar abolished the jizya poll tax on non-Muslims and the tax on Hindu pilgrims.
(III)
Aurangzeb acceded the throne after killing his three brothers.
(IV)
Prince Akbar entered into a pact with Shivaji’s son Shambuji in the Deccan.
(i),
(ii) and (iii) are correct
(ii),
iii) and (iv) are correct
(i),
(iii) and (iv) are correct
(ii),
(iii), (iv) and (i) are correct
Answer: (ii), iii)
and (iv) are correct
4. Arrange the battles
in chronological order
i.
Battle of Khanwa
ii.
Battle of Chausa
iii.
Battle of Kanauj
iv.
Battle of Chanderi
Answer:
i. Battle of Khanwa - 1527
ii. Battle of Chanderi – 1528
iii. Battle of Chausa - 1539
iv. Battle of Kanauj - 1540
5. Arrange the following administrative divisions in descending order
i.
Sarkars
ii.
Parganas
iii.
Subhas
Answer: (I) Subhas (II)
Sarkars (III) Parganas
Match the father and son
Father - Son
1.
Akbar Dilawar - Khan
2.
Daulat Khan Lodi - Rana Pratap
3.
Hasan Suri - Humayun
4.
Babur - Sher Shah
5.
Uday Singh – Jahangir
Answer:
Father Son
1. Akbar : Jahangir
2. Daulat Khan Lodi
: Dilawar Khan
3. Hasan Suri :
Sher Shah
4. Babur : Humayun
5. Uday Singh :
Rana Pradap
VI.Give short answer
1. Write the circumstance that led
to the Battle of Panipat in 1526.
Dilawar Khan, who was Daulat Khan Lodi’s son, and Alam Khan, who
was the uncle of Sultan of Delhi, arrived in Kabul to seek Babur’s help in
removing Ibrahim Lodi from power. Babur defeated Ibrahim Lodi in the famous
Battle of Panipat in 1526 and occupied Delhi and Agra. The Mughal dynasty came
to be established in India with Agra as its capital.
2. Mention the Humayun recapture the
Delhi throne in 1555?
Sher Shah defeated Humayun at Chausa (1539) and again at Kanauj
(1540). Humayun, defeated and overthrown, had to flee to Iran. With the help of
the Persian ruler Shah Tahmasp of the Safavid dynasty, Humayun succeeded in
recapturing Delhi in 1555.
3. Write a note on Mansabdari system.
Akbar introduced the Mansabdari system. Mansabdar rank was
dependent on Zat and Sawar. The former indicated ones’s status. Sawar was the
number of horses and horsemen he had to maintain. His salary was fixed on the
basis of the number soldiers each Mansabdar received ranging from 10 to 10,000.
Their horses were branded to prevent theft. The Emperor could use the troops
maintained by a Mansabdar whenever he wished.
VII.Answer the following
1. Describe the land revenue administration
of the Mughals.
Land revenue administration was toned up during the reign of
Akbar. Raja Todar Mal, Revenue Minister of Akbar, adopted and refined the
system introduced by Sher Shah. Todar Mal’s zabt system was put in place in the
north and north-western provinces. According to this system, after a survey,
lands were classified according to the nature and fertility of the soil. The
share of the state was fixed at one-third of the average produce for 10 years.
During the reign of Shah Jahan, the zabt or zabti system was extended to the
Deccan provinces.
The Mughal emperors enforced the old iqta system, renaming it
jagir. It is a land tenure system developed during the period of Delhi
Sultanate. Under the system, the collection of the revenue of an area and the
power of governing it were bestowed upon a military or civil official now named
Jagirdar. Every Mansabdar was a Jagirdar if he was not paid in cash. The
Jagirdar collected the revenue through his own officials. The Amal Guzar or the
revenue collector of the district was assisted by subordinate officers like the
Potdar, the Qanungo, the Patwari and the Muqaddams.
Those appointed to collect the revenue from the landholders were
called zamindars. Zamindars collected taxes and maintained law and order with
the help of Mughal officials and soldiers. The local chieftains and little
kings were also called zamindars. But at the end of the sixteenth century, the
zamindars were conferred hereditary rights over their zamin. The zamindar was
empowered to maintain troops for the purpose of collecting revenue. The emperor
granted lands to scholars, holy men and religious institutions. These lands
called suyurghal were tax-free.
2. Estimate Akbar as a patron of learning.
Akbar was a great patron of learning. His personal library had
more than four thousand manuscripts. He patronised Abul Fazl, Abul Faizi and
Abdur Raahim Khan-i-Khanan, the great storyteller Birbal, competent officials
like Raja Todar Mai, Raja Bhagwan Das and Raja Man Singh. The great composer
and musician Tansen and artist Daswant adorned Akbar’s court as well.
VIII.HOTs
1. Shah Jahan’s time witnessed the
climax of Mughal splendour. Support this statement in comparison with the times
of other Mughal rulers.
Shah Jahan’s time witnessed the climax of Mughal splendour. The
famous peacock throne, covered with expensive jewels, was made for the Emperor
to sit on. Then rose the world famous Taj Mahal, by the side of the Jumna river
at Agra. Besides Taj, he built the Moti Masjid, the pearl mosque at Agra, the
great Jama Masjid of Delhi and the Diwan-i-Khas and Diwan-i-am in his palace in
Delhi. Red Fort, also called Lal Qila, in Delhi was the residence of the Mughal
emperors. It was constructed in 1639 by Emperor Shah Jahan as the palace of his
fortified capital Shajahanabad. The Red Fort is named for its massive enclosing
walls of red sandstone.
Babur introduced the Persian style of architecture to India by
building many structures at Agra, Biana, Dholpur, Gwalior and Kiul (Aligarh),
but only a few of them exist today.
During Akbar's time the Diwan-i-Khas, Diwan-i-Am, Panch Mahal
(pyramidal structure in five stories), Rang Mahal, Salim Chishti’s Tomb and
Buland Darwaza were built. Jahangir completed Akbar’s tomb at Sikandara and the
beautiful building containing the tomb of Itmad-ud- daula, father of Nur Jahan,
at Agra.
During Aurangzeb’s reign, architecture did not receive much
patronage. The Bibi Ka Maqbara in Aurangabad, a mausoleum built by his son
Prince Azam Shah as a loving tribute to his mother in the late seventeenth
century, is, however, worth mentioning.
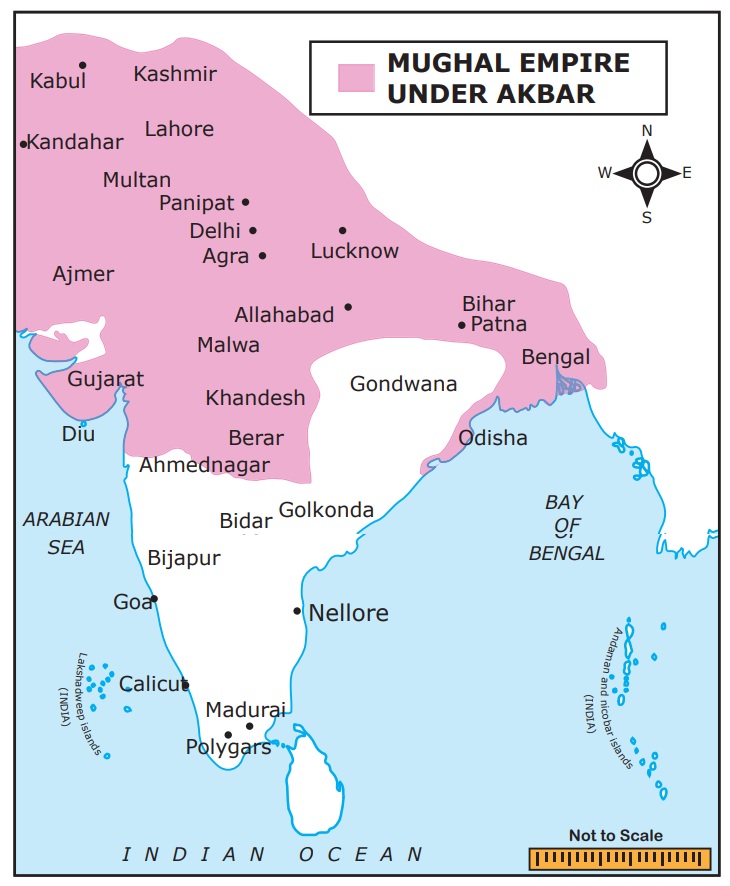
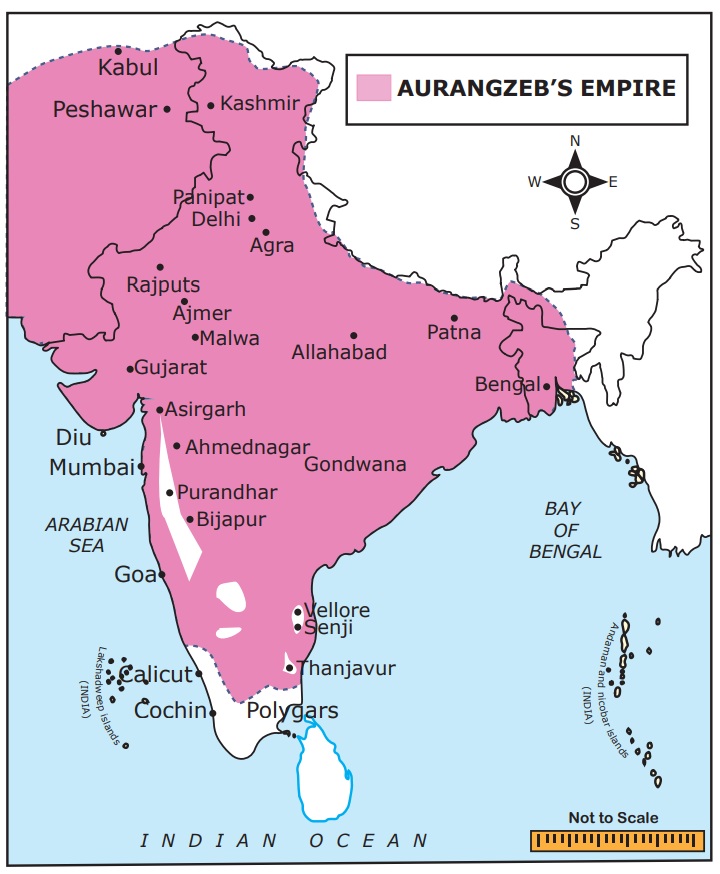
IX. Map
Mark the extent of Mughal Empire during
the reign of Akbar and Aurangzeb with special focus on important battle fields.
IX.Activity
Collect information about the scholars
in Akbar’s court and conduct a mock Ibadat khana in the class.
Related Topics