The Mughal Empire | Term 2 Unit 2 | History | 7th Social Science - Akbar (1556-1605) | 7th Social Science : History : Term 2 Unit 2 : The Mughal Empire
Chapter: 7th Social Science : History : Term 2 Unit 2 : The Mughal Empire
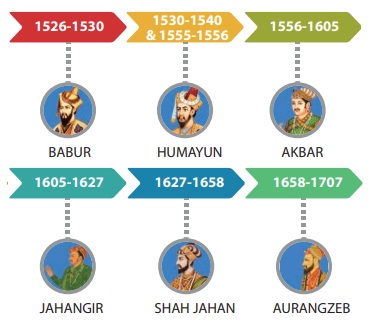
Akbar (1556-1605)
Akbar (1556–1605)
Accession to Throne
After the death of Humayun in 1556, his
14-year-old Son Akbar was crowned the King. Humayun’s trusted general Bairam Khan
became the regent and ruled on behalf of Akbar, as the latter was a minor.

Hemu, a general of Sur dynasty, soon
captured Agra and Delhi I 1556. In the same year, Bairam Khan defeated and killed
Hemu in the battle at Panipat (Second Battle of Panipat, 1556). As Bairam Khan was
murdered in Gujarat, allegedly at the instance of Akbar who could not tolerate his
dominance in day-to-day governance of the kingdom, Akbar assumed full control of
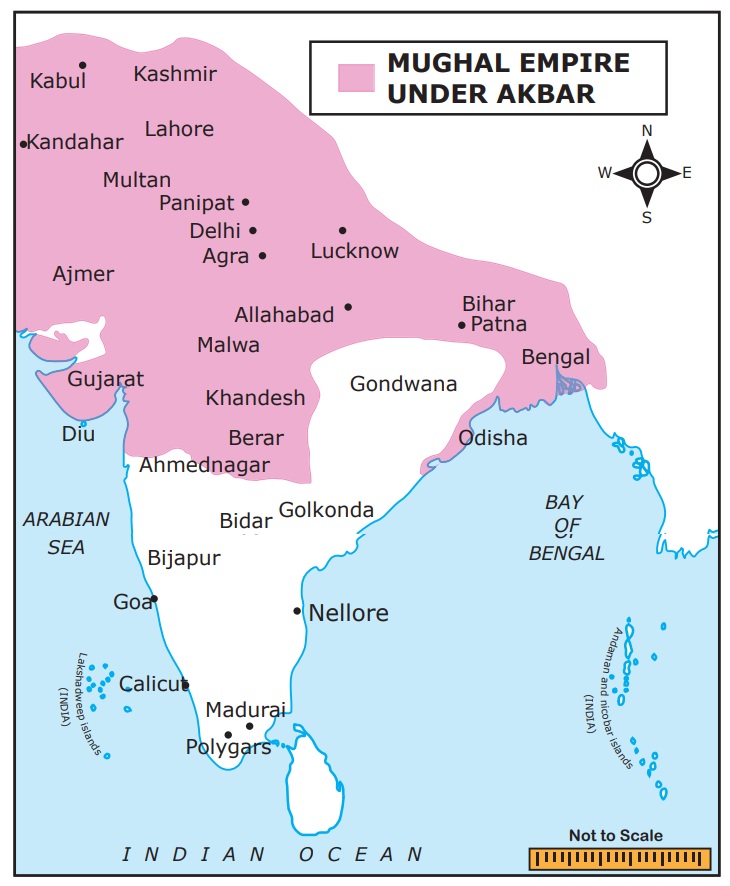
the government. Akbar brought most of India under his control through conquests
and alliances.
Conquests of Women Rulers
Akbar
conquered Malwa and parts of Central India. His defeat of Rani Durgavati, a ruler
in the Central Province, is not appreciated,since the brave Rani did him no harm.
Yet urged by his ambition to build an empire, Akbar hadno consideration for the
good nature of the ruler. Similarly, another woman ruler Akbarhad to confront in
South India was the famous Rani Chand Bibi, regent of Ahmednagar. Thefight this
woman put up impressed the Mughal army so much that they gave her favourable terms
of peace.

Battle of Haldighati
Akbar defeated Rana Uday Singh of Mewar
and captured the fort of Chittoor in 1568 and then Ranthambore in 1569. In 1576,
he won over Uday Singh’s son Rana Pratap at the Battle of Haldighati. Though defeated,
Rana Pratap escaped on his horse, Chetak, and continued his fight, leading a life
in the jungle. The memory of this gallant Rajput is treasured in Rajputana, and
many a legend has grown around him.

Commercial Access to Arabia,
Southeast Asia and China
Akbar’s conquest of Gujarat helped him
to establish control over Gujarat’s overseas trade with the Arabs and the Europeans.
Akbar’s military campaigns in East Bihar and Odisha and victory over Bengal facilitated
access to Southeast Asia and China.
Related Topics