Questions with Answers, Solution | Geometry | Term 2 Chapter 4 | 6th Maths - Exercise 4.3 | 6th Maths : Term 2 Unit 4 : Geometry
Chapter: 6th Maths : Term 2 Unit 4 : Geometry
Exercise 4.3
Exercise
4.3
Miscellaneous
Practice Problems
1. What are the angles of an isosceles
right angled triangle?
45°, 45°, 90°
2. Which of the following correctly describes
the given triangle?
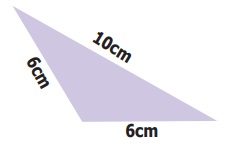
(a) It is a right isosceles triangle.
(b) It is an acute isosceles triangle.
(c) It is an obtuse isosceles triangle.
(d) It is an obtuse scalene triangle.
Answer: ✓(c) It is an obtuse
isosceles triangle.
3. Which of the following is not possible
?
(a) An obtuse isosceles triangle
(b) An acute isosceles triangle
(c) An obtuse equilateral triangle
(d) An acute equilateral triangle
Answer: ✓(c) An obtuse
equilateral triangle
4. If one angle of an isosceles triangle
is 124° , then find the other angles.
One angle of an isosceles triangle = 124°
The sum of three angles of a triangle = 180°
The other two isosceles angles = 180° − 124° = 56°
One angle = 56 / 2 = 28°
The other two angles are 28°, 28°.
5. The diagram shows a square ABCD. If
the line segment joins A and C, then mention the type of triangles so formed.
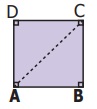
Both triangles are Isoceles
Right angled triangle.
6. Draw a line segment AB of length 6 cm. At each end of this line segment AB, draw a line perpendicular to the line AB. Are these lines parallel?
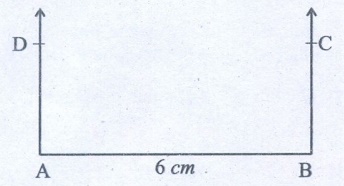
Yes. These two
perpendicular lines are parallel.
Challenge
Problems
7.
Is a triangle possible with the angles 90° , 90° and 0° Why?
90°, 90°, 0°
A triangle can not be formed with the given angles. Because,
Atriangle can not have more than one right angle.
8.
Which of the following statements is true? Why?
(a)
Every equilateral triangle is an isosceles triangle.
(b)
Every isosceles triangle is an equilateral triangle.
'a' is true. Because an
isosceles triangle need not have three equal sides.
9.
If one angle of an isosceles triangle is 70°, then find the possibilities for the
other two angles.
One angle of an isosceles triangle = 70°
If the other angle also = 70°
The third angle = 180° − (70° + 70°)
= 180° − 140° = 40°
The other two angles are 70° and 40° (or)
One angle = 70°
The other two isosceles angles = (180° − 70°) = 110°
Two isosceles angles = 110°
So, one angle = 110 / 2 = 55°
The other two isosceles angles are 55° and 55°
So, the two angles 70°, 40° (or) may be, 55°, 55°..
10.
Which of the following can be the sides of an isosceles triangle?
a) 6cm,
3cm, 3cm
b) 5cm,
2cm, 2cm
c) 6cm,
6cm, 7cm
d) 4cm,
4cm, 8cm
a) 6 cm, 3 cm, 3 cm
The sum of two smaller sides = 3+3 = 6cm=6cm, the third side
The sum of two smaller sides is not greater than the third side.
So, a triangle can not be formed with the given sides.
b) 5 cm, 2 cm, 2 cm
The sum of two smaller sides=2 + 2 = 4 cm < 5 cm the third
side.
The sum of two smaller sides is lesser than the third side.
So, a triangle can not be formed with the given sides.
c) 6 cm, 6 cm, 7 cm
The sum of two smaller sides = 6 + 6 = 12 cm > 7 cm the third
side.
The sum of two smaller sides is greater than the third side.
So, a triangle can be formed with the given sides.
d) 4 cm, 4 cm, 8 cm
The sum of two smaller sides = 4 + 4 = 8 cm = 8 cm the third
side.
The sum of two smaller sides is not greater than the third side.
So, a triangle can not be formed with the given sides.
11.
Study the given figure and identify the following triangles.
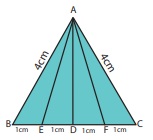
(a) equilateral triangle
(b) isosceles triangles
(c) scalene triangles
(d) acute triangles
(e) obtuse triangles
(f) right triangles
(a) Equilateral triangle
Equilateral triangle ΔABC
(b) Isosceles triangles
Isosceles triangle Δ ABC, Δ AEF
(c) Scalene triangles
Scalene triangle Δ AEB, Δ AED, Δ ADF, Δ AFC, Δ ABD, Δ ADC, Δ ABF,
Δ AEC
(d) Acute triangles
Acute triangles Δ ABC, Δ AEF, Δ ABF, Δ AEC
(e) Obtuse triangles
Obtuse triangles Δ AEB, Δ AFC
(f) Right triangles
Right triangles Δ ADB, Δ ADC, Δ ADE, Δ ADF
12.
Two sides of the triangle are given in the table. Find the third side of the triangle.

i) 7cm, 4 cm
The sum of two smaller sides = 4 + 4 = 8 cm > 7 cm, the third
side
= 4 + 5 = 9 cm > 7 cm, the third side
= 4 + 6 = 10 cm > 7 cm, the third side
The third side is, 4 cm or 5 cm or 6 cm.
ii) 8 cm, 8 cm
The sum of two smaller sides = 5 + 8 = 13 cm >8 cm, the third
side
= 6 + 8 = 14 cm > 8 cm, the third side
= 7 + 8 = 15 cm > 8 cm, the third side
The third side is, 5 cm or 6 cm or 7 cm.
iii) 7.5 cm, 3.5 cm
The sum of two smaller sides = 3.5 + 4.5 = 8cm > 7.5 cm, the
third side
= 3.5 + 5 = 8.5 cm > 7.5 cm, the third side
= 3.5 + 6 = 9.5 cm > 7.5 cm, the third side
The third side is 4.5 cm or 5 cm or 6 cm
iv. 10 cm, 14 cm
The sum of two smaller sides = 10 + 5= 15 cm> 14 cm, the
third side
= 10 + 7 = 17cm > 14 cm, the third side
= 10 + 8 = 18 cm > 14 cm, the third side
The third side is 5 cm or 7 cm or 8 cm
13.
Complete the following table :
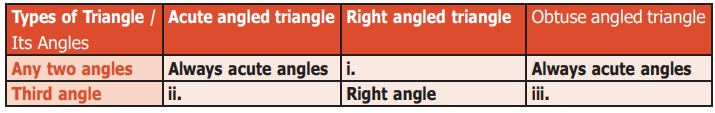
ANSWERS:
Exercise 4.3
1. 90°, 45° , 45°
2. c
3. c
4. 28°, 28°
5. Both are
Isosceles Right angled triangles
6. Yes
7. No, A triangle
cannot have more than one right angle
8. “a” is true,
because an isosceles triangle need not have three equal sides
9. 70°,40° or
55°,55°
10. c
11. a) ∆ABC
b) ∆ABC , ∆AEF
c) ∆AEB, ∆AED,
∆ADF, ∆AFC, ∆ABD, ∆ADC, ∆ABF, ∆AEC
d) ∆ABC, ∆AEF,
∆ABF, ∆AEC
e) ∆AEB, ∆AFC
f) ∆ADB, ∆ADC,
∆ADE, ∆ADF
12. (i) between 3
and 11 (ii) between 0 and 16 (iii) between 4 and 11 (iv) between 4 and 24
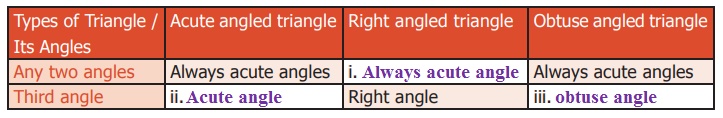
13. i .Always acute
angles
ii. Acute angle
iii. Obtuse angle
Related Topics