Chapter 1 | Economics | 8th Social Science - Evolution of Money | 8th Social Science : Economics : Chapter 1 : Money, Savings and Investments
Chapter: 8th Social Science : Economics : Chapter 1 : Money, Savings and Investments
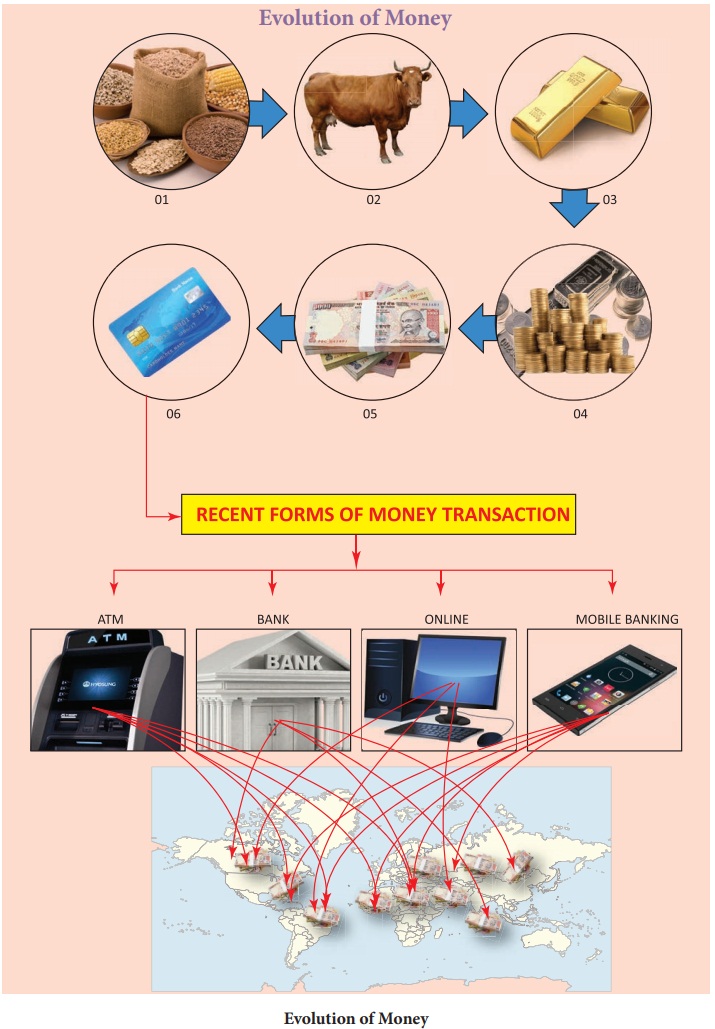
Evolution of Money
Evolution of Money
The word Money is derived from Roman
word “Moneta Juno”. It is the roman goddesses and the republic money of roman
empire. The Indian rupee is derived from Sanskrit word ‘Rupya’ which means
silver coin. Today we use paper notes, coins as money. But the evolution of this
stage has not happened overnight. It took thousands of years to reach such a
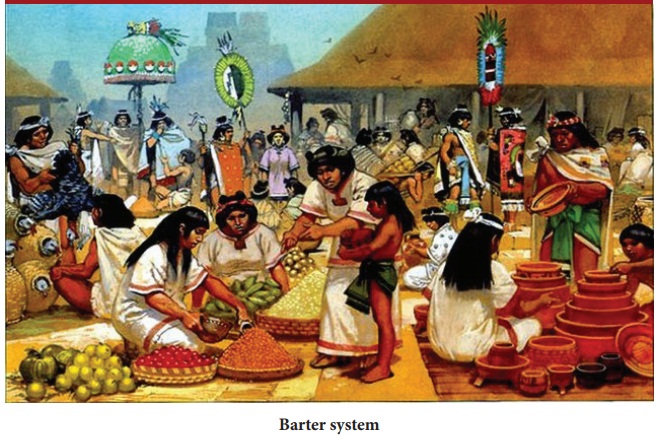
stage. There are many stages of evolution of money. The earliest and primitive
stage is Barter system.
Barter system
Barter system is exchanging goods
for goods without the use of money in the primitive stage. A barter system is
an old method of exchange. This system has been used for centuries and long
before money was invented. People exchanged services and goods for other
services and goods in return. The value of bartering items can be negotiated
with the other party. Bartering doesn’t involve money which is one of the
advantages.
Hence Barter system had many
deficiencies like,
1.
Lack of double coincidence of wants,
2.
Common measure of value
3.
Indivisibility of commodities
4. Difficulties of storing wealth
Major stages of Evolution of Money
Commodity Money, Metallic Money,
Paper Money, Credit Money or Bank Money, Near Money and recent forms of Money.
Money has evolved through different stages according to the time, place and
circumstances.
Commodity Money
In the earliest period of human
civilization, any commodity that was generally demanded and chosen by common
consent was used as money. Goods like furs, skins, salt, rice, wheat, utensils,
weapons etc. were commonly used as money. Such exchange of goods for goods was
known as ‘Barter Exchange’.
Metallic Money
With progress of human civilization,
commodity money changed into metallic money. Metals like gold, silver, copper,
etc. were used as they could be easily handled and their quantity can be easily
ascertained. It was the main form of money throughout the major portion of
recorded history.

History of Metallic Money
The precious metals
especially gold, silver, bronze were used for metallic money. The standard
weight and fineness of metal particularly gold and silver with a seal on it
became medium of exchange. They were of different denomination easily
divisible, portable and were convenient in making payment.
King Midas of Lydia
innovated metal coin in the 8th century BC (BCE) by the ancient historian
Herodotus. But gold coins were in use in india many centuries than in Lydia.
The earliest issuers
of coins in the world are the ancient Indians along with Chinese and lydians
from the middle east. The first time Indian coins were minted in the 6th
century BC (BCE) by the Mahajanpadas known as Puranas, Karshapanas or Panas.
The Mauryas came up
with the Punch Marked Coins minting of silver, gold copper or lead and
Indo-Greek Kushan kings introduced the Greek custom of engraving portraits on
the coins. Turkish sultans of Delhi has replaced the royal designs of Indian
kings with Islamic Calligraphy by the 12th century AD (CE). The currency was
made up of gold, silver and copper known as Tanka and lower valued coin known
as Jittals.
The Mugual Empire from
1526 AD (CE) consolidate the monetary system for the entire empire. In this era
evolution of rupee occurred with Sher Shah Suri defeated Humayun and issued a
silver coin of 178 gms known as rupiya and was divided into 40 copper pieces or
paisa and during the whole Mugual period silver coin remained in use. During
the British East India company i.e. 1600, the mughal currency remained popular
but in 1717 AD (CE), Farrukhsiyar the Mughal Emperor gave permission to the
Britishes to coin Mughal Money at the Bombay mint. The British gold coins were
termed as Carolina, the silver coins as Angelina, the copper coins as cupperoon
and the tin coins as tinny.

Paper Money

It was found inconvenient as well as
dangerous to carry gold and silver coins from place to place. So, invention of
paper money marked a very important stage in the development of money. The
development of paper money started on the basis of storage of gold and the
receipts were issued by the goldsmiths for these storages. This receipts of
goldsmiths were a substitute for money and became paper money. Paper money is
regulated and controlled by Central Bank of the country. In India, printing,
regulating, controlling the paper currencies are done by the Reserve Bank of
India (RBI) which was established in 1935. At present, a very large part of
money consists mainly of currency notes or paper money issued by the Reserve
Bank of India.
ACTIVITY: 1

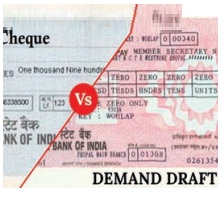
Credit Money or Bank Money
Emergence of credit money took place
almost side by side with that of paper money. People keep a part of their cash
as deposits with banks, which they can withdraw at their convenience through
cheques. The cheque (known as credit money or bank money), itself, is not
money, but it performs the same as functions of money.
Near Money
The final stage in the evolution of
money has been the use of bills of exchange, treasury bills, bonds, debentures,
savings certificate etc.
Recent forms of Money
Plastic Money
The latest type of money is plastic
money in the form of Credit cards and Debit cards. They aim for cashless
transactions.

E-Money
Electronic Money is money which
exists in banking computer systems and is available for transactions through
electronic system.

Online Banking (Net Banking)
Online Banking, also known as
internet banking is an electronic payment system that enables customers of a
bank or other financial institutions to conduct a range of financial
transactions through website.
E-Banking
Electronic banking, also known as
National Electronic Funds Transfer (NEFT), is simply the use of electronic
means to transfer funds directly from one account to another rather than by
cheque or cash.

ACTIVITY: 2
* Prepare the duplicate model of different stages of Money, like
Commodity money, Metal money, Plastic Money, etc.(including Barter System)
* Give the models to the each group students.
* Teacher and students
discuss about the different stages of money
Related Topics