Chapter: Java The Complete Reference : The Java Library : Event Handling
Event Listener Interfaces - Java
Event Listener Interfaces
As explained, the delegation event model has two parts: sources and
listeners. As it relates to this chapter, listeners are created by implementing
one or more of the interfaces defined by the java.awt.event package. When an event occurs, the event source
invokes the appropriate method defined by the listener and provides an event
object as its argument. Table 24-3 lists several commonly used listener interfaces
and provides a brief description of the methods that they define. The following
sections examine the specific methods that are contained in each interface.
Interface : Description
ActionListener : Defines one method to receive action events.
AdjustmentListener : Defines one method to receive adjustment
events.
ComponentListener : Defines four methods to recognize when a
component is hidden, moved, resized, or shown.
ContainerListener : Defines two methods to recognize when a
component is added to or removed from a container.
FocusListener : Defines two methods to recognize when a component
gains or loses keyboard focus.
ItemListener : Defines one method to recognize when the state of an
item changes.
KeyListener : Defines three methods to recognize when a key is
pressed, released, or typed.
MouseListener : Defines five methods to recognize when the mouse is
clicked, enters a component, exits a component, is pressed, or is released.
MouseMotionListener : Defines two methods to recognize when the
mouse is dragged or moved.
MouseWheelListener : Defines one method to recognize when the mouse
wheel is moved.
TextListener : Defines one method to recognize when a text value
changes.
WindowFocusListener : Defines two methods to recognize when a
window gains or loses input focus.
WindowListener : Defines seven methods to recognize when a window
is activated, closed, deactivated, deiconified, iconified, opened, or quit.
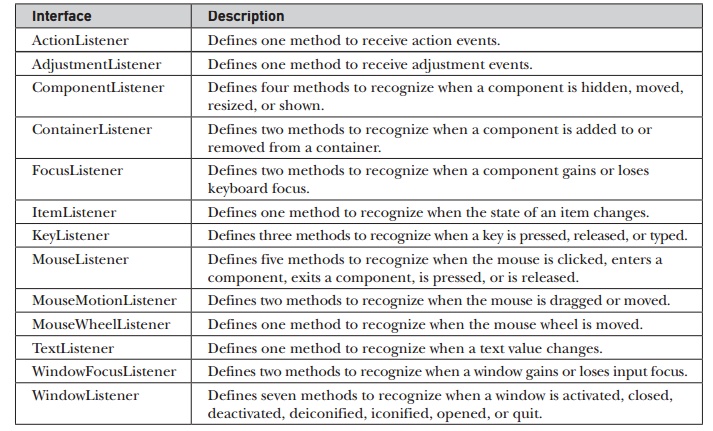
Table 24-3 Commonly Used Event Listener Interfaces
The ActionListener Interface
This interface defines the actionPerformed(
) method that is invoked when an action event occurs. Its general form is
shown here:
void actionPerformed(ActionEvent ae)
The AdjustmentListener Interface
This interface defines the adjustmentValueChanged(
) method that is invoked when an adjustment event occurs. Its general form
is shown here:
void adjustmentValueChanged(AdjustmentEvent ae)
The ComponentListener Interface
This interface defines four methods that are invoked when a
component is resized, moved, shown, or hidden. Their general forms are shown
here:
void componentResized(ComponentEvent ce)
void componentMoved(ComponentEvent ce)
void componentShown(ComponentEvent ce)
void componentHidden(ComponentEvent ce)
The ContainerListener Interface
This interface contains two methods. When a component is added to a
container, componentAdded( ) is
invoked. When a component is removed from a container, componentRemoved( ) is invoked. Their general forms are shown
here:
void componentAdded(ContainerEvent ce)
void componentRemoved(ContainerEvent ce)
The FocusListener Interface
This interface defines two methods. When a component obtains
keyboard focus, focusGained( ) is
invoked. When a component loses keyboard focus, focusLost( ) is called. Their general forms are shown here:
void focusGained(FocusEvent fe)
void focusLost(FocusEvent fe)
The ItemListener Interface
This interface defines the itemStateChanged(
) method that is invoked when the state of an item changes. Its general
form is shown here:
void itemStateChanged(ItemEvent ie)
The KeyListener Interface
This interface defines three methods. The keyPressed( ) and keyReleased(
) methods are invoked when a key is pressed and released, respectively. The
keyTyped( ) method is invoked when a
character has been entered.
For example, if a user presses and releases the a key, three events
are generated in sequence: key pressed, typed, and released. If a user presses
and releases the home key, two key events are generated in sequence: key
pressed and released.
The general forms of these methods are shown here:
void keyPressed(KeyEvent ke)
void keyReleased(KeyEvent ke)
void
keyTyped(KeyEvent ke)
The MouseListener Interface
This interface defines five methods. If the mouse is pressed and
released at the same point, mouseClicked(
) is invoked. When the mouse enters a component, the mouseEntered( ) method is called. When it leaves, mouseExited( ) is called. The mousePressed( ) and mouseReleased( ) methods are invoked
when the mouse is pressed and released, respectively.
The general forms of these methods are shown here:
void mouseClicked(MouseEvent me)
void mouseEntered(MouseEvent me)
void mouseExited(MouseEvent me)
void mousePressed(MouseEvent me)
void
mouseReleased(MouseEvent me)
The MouseMotionListener Interface
This interface defines two methods. The mouseDragged( ) method is called multiple times as the mouse is
dragged. The mouseMoved( ) method is
called multiple times as the mouse is moved. Their general forms are shown
here:
void mouseDragged(MouseEvent me)
void mouseMoved(MouseEvent me)
The MouseWheelListener Interface
This interface defines the mouseWheelMoved(
) method that is invoked when the mouse wheel is moved. Its general form is
shown here:
void mouseWheelMoved(MouseWheelEvent mwe)
The TextListener Interface
This interface defines the textValueChanged(
) method that is invoked when a change occurs in a text area or text field.
Its general form is shown here:
void textValueChanged(TextEvent te)
The WindowFocusListener Interface
This interface defines two methods: windowGainedFocus( ) and windowLostFocus(
). These are called when a window gains or loses input focus. Their general
forms are shown here:
void windowGainedFocus(WindowEvent we)
void windowLostFocus(WindowEvent we)
The WindowListener Interface
This interface defines seven methods. The windowActivated( ) and windowDeactivated(
) methods are invoked when a window is activated or deactivated,
respectively. If a window is iconified, the windowIconified( ) method is called. When a window is deiconified,
the windowDeiconified( )
method is called. When a window is opened or closed, the windowOpened( ) or
windowClosed( ) methods are called, respectively. The windowClosing( ) method is called when a window is being closed.
The general forms of these methods are
void windowActivated(WindowEvent we)
void windowClosed(WindowEvent we)
void windowClosing(WindowEvent we)
void windowDeactivated(WindowEvent we)
void windowDeiconified(WindowEvent we)
void windowIconified(WindowEvent we)
void windowOpened(WindowEvent we)
Related Topics