Chapter: Biology laboratory Practicals: Biology Activities
Essential Minerals in Plants
Essential Minerals in Plants
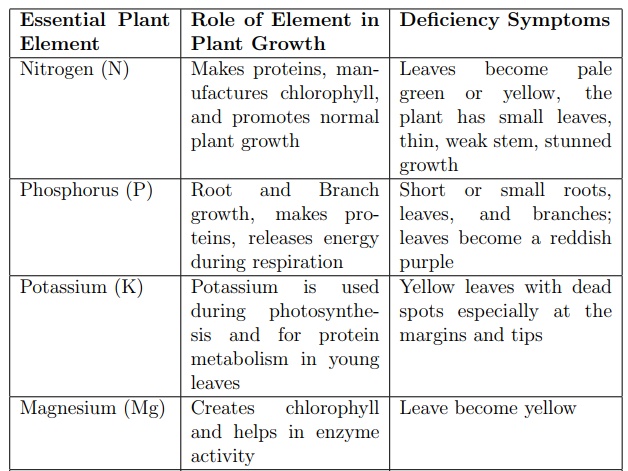
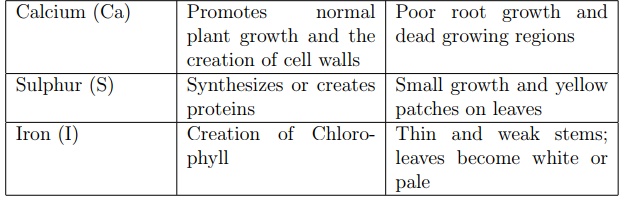
Plants need mineral elements in addition to the food they manufacture. Min-eral elements are found in the soil or dissolved in water and they are absorbed by plants in the form of ions. Mineral elements required for normal healthy plant growth include nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, magnesium, calcium, sulphur and iron. Each mineral element has a specific function in the plant body some are used in the production of building materials while others play an important role in the metabolic activities of the plant.
Learning Objectives
To investigate the roles of essential mineral elements in plant nutrition. To identify different mineral de ciencies in plants.
Materials
Inorganic fertilizers: CAN, DAP, NPK and SA; magnesium sulphate*, iron pills*, sodium chloride*, beakers*, cotton wool*, maize plants, and rain wa-ter.
Preparation Procedure
1. Sow maize seeds and wait for about 5-7 days for the seedling to develop.
2. Label six beakers A, B, C, D, E and F and put a bundle of cotton wool into each beaker.
3. Grind CAN, DAP, NPK, SA, MgSO4, Fe and NaCl so they are in ne powder form.
Activity Procedure
1. Make seven solutions of salts by dissolving the speci ed amounts in approximately 1 L of rainwater
(a) Solution 1: one slightly heaped teaspoon of sodium chloride
(b) Solution 2: one at teaspoon of sodium chloride + a pinch of CAN (a few crystals)
(c) Solution 3: one at teaspoon of sodium chloride + a pinch of DAP (a few crystals)
(d) Solution 4: one at teaspoon of sodium chloride + a pinch of NPK (a few crystals)
(e) Solution 5: one at teaspoon of sodium chloride + a pinch of SA (a few crystals)
(f) Solution 6: one at teaspoon of sodium chloride + a pinch of MgSO4 (a few crystals)
(g) Solution 7: one at teaspoon of sodium chloride + a pinch of iron (a few crystals)
2. Combine these solutions in beakers as follows. Put 2 mL of each men-tioned solution in the beaker:
(a) Beaker A (all nutrient) solutions 2, 4, 6 and 7
(b) Beaker B (calcium de cient) solutions 4, 6 and 7
(c) Beaker C (iron de cient) solutions 2, 4, and 6
(d) Beaker D (magnesium de cient) solutions 2, 4, 5, and 7
(e) Beaker E (potassium de cient) solutions 2, 3, 6, and 7
(f) Beaker E (no nutrients) 6 mL of solution 1
3. Place 3 seedlings in each beaker and place beakers near a window.
4. Measure and record the height of each of each seeding every day
5. Observe and record the colour of the leaves of the seedlings in each bottle every three days.
6. Make sure that plants do not dry out { if the water level gets low, increase by adding 1 mL of each solution added initially.
Results and Conclusions
When plants lack one of the mineral elements, their growth will be disturbed. The plants will have slow growth and leaves may drop or change colour.
Clean Up Procedure
Collect all the used materials, cleaning and storing items that will be used later. No special waste disposal is required.
Notes
Minerals are required by plants in small quantities. Solutions that are too concentrated may kill the plant because of water loss through osmosis. The purpose of the sodium chloride is to set the proper osmotic pressure.
Related Topics