Chapter: 12th Commerce : Chapter 23 : Entrepreneurship Development : Elements of Entrepreneurship
Entrepreneurial Functions
Entrepreneurial Functions
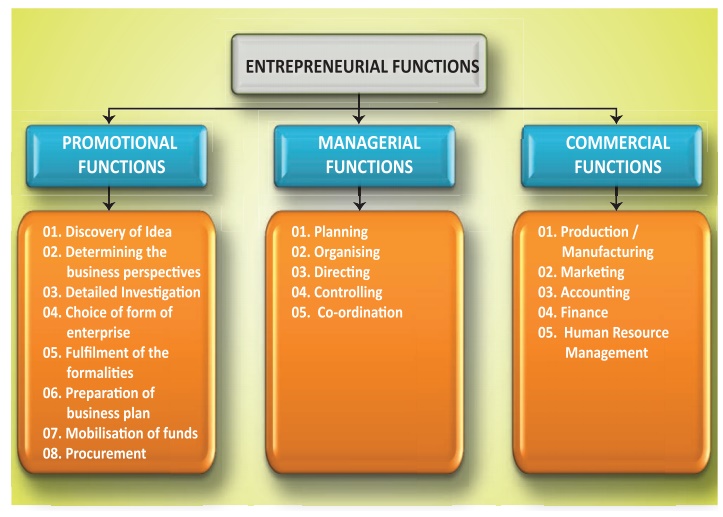
I. Promotional Functions
(1) Discovery of Idea
The first and foremost function of entrepreneur is
idea generation. A person may conceive his own ideas or develop the ideas
contributed by others. Ideas can be generated through several ways like own
experience and exposure of entrepreneur, keen observation of environment,
education, training, market survey, environmental scanning and so on. After the
ideas were collected, entrepreneur has to weigh objectively each and every idea
and finally select an idea which is worth pursuing commercially.
(2) Determining the business objectives
Entrepreneur has to develop business objectives in
the backdrop of nature of business and type of business activity i.e. nature of
business, manufacturing or trading, type of business organisation chosen so
that he/she can organise the venture in accordance with the objectives
determined by him/her.
(3) Detailed Investigation
Entrepreneur has to analyse in detail the product
proposes to produce. In other words, Entrepreneur should investigate commercial
feasibility of the product proposed to be produced and conduct market study to
ascertain the potential demand for the product. Besides, Entrepreneur has to
probe the sources of supply of various inputs required for manufacturing the
proposed product, their respective prices and other terms and conditions
(4) Choice of form of enterprise
Entrepreneur has to choose the appropriate form of
organisation suited to implement the venture. There are various forms of
organisation namely sole proprietor, partnership, company and co-operatives
etc. which are in existence. The selection of appropriate form of organisation
is made after considering the factors like nature of product to be produced,
size of investment, nature of activities, size of organisation, nature of
liability of owners, retention of control, degree of risk involved, scale of
operations, stability and so on.
(5) Fulfilment of the formalities
Having chosen the appropriate type of organisation,
entrepreneur has to take necessary steps to establish the form of organisation
chosen. As regards sole trader, the formalities are barest minimum. In the case
of partnership firm, entrepreneur has to arrange for partnership deed and he
has to get the deed registered. There are lot of formalities to be fulfilled in
the case of registration of company and co-operative form of organisation.
Promoter has to take all necessary steps for establishing the form of
organisation.
(6) Preparation of Business Plan
Entrepreneur has to prepare a business plan or
project report of the venture that he is proposing to take up. This plan helps
entrepreneur to achieve various objectives formulated within a specified period
of time.
(7) Mobilisation of funds
Entrepreneur has to take steps to mobilise capital
needed to implement the venture. Entrepreneur has to estimate the fixed capital
and working capital required for running the project. Then the entrepreneur has
to initiate steps to build funds from various channels like own funds,
borrowing from close circles, banks, financial institutions, venture
capitalists, issue of shares and debentures, term loans and so on to finance
his fixed capital requirement.
(8) Procurement of Machines and Materials
Entrepreneur has to locate the various sources of
supply of machineries and equipments and materials. Entrepreneur has to collect
details from the various sources of supply and screen them for selecting the
best source of supply.
II. Managerial Functions
(i) Planning
Under planning, entrepreneur has to lay down the
objectives, goals, vision, mission, policies, procedures, programmes, budget,
schedules etc., for enabling the venture to proceed towards established
destinations.
(ii) Organising
Entrepreneur puts in place suitable organisational
structure to perform various managerial functions namely choosing the type of
organisation, creating department, fitting the human resources to appropriate
organisation slots, defining and delegating authority, distributing
responsibility and creating accountability for efficient performance of
activities.
(iii) Directing
In the realm of directing, entrepreneur has to
motivate, lead, guide and communicate with subordinates on an ongoing basis in
order to accomplish pre-set goals. The process of directing involves issuing
orders and instructions, guiding, counselling and mentoring of employees,
supervising employees, maintaining discipline, motivating employees and
providing leadership.
(iv) Controlling
Entrepreneur has to put in mechanism to evaluate
the performance of employees across the organisation. The various steps
involved in control function includes fixing performance standards, measuring
the actual performance, comparing actual performance with standards, finding
out causes for deviation if any, undertaking corrective measures to bring
actual performance to standards set. He/she may use various control techniques
like account, auditing, management information system, network analysis, cost
control, financial tools etc.,
(v) Coordination
Entrepreneur has to evolve mechanism to pull
together the diverse functions performed by various departments or teams and
direct them towards the established goals of the organisation for
accomplishment.
III. Commercial Functions
(i) Production or Manufacturing
Under production function, entrepreneur has to take
decision relating to selection of factory site, design and layout, type of
products to be manufactured, research and development, product design etc., The
efficient and effective performance of production function depends on the
proper production planning and control to a major extent.
(ii) Marketing
Entrepreneur has to carry out following functions
pertaining to marketing aspect namely consumer research, product planning and
development, standardisation, packaging, pricing, warehousing, distribution,
promotion etc., The very success of marketing function is very much linked with
selection of appropriate marketing mix. The term marketing mix denotes the
combination of four components namely product, price, promotion and physical
distribution in the case of physical products and three more components are
included in the case of service products namely people, process and physical
evidence.
(iii) Accounting
Entrepreneur has to arrange to prepare trading and
profit and loss account in order to know the profit or loss incurred out of operation
of the business and prepare balance sheet to know the financial status of
business at a particular day. Besides, cash flow and fund flow statements are
prepared to ensure the adequacy of funds and cash for meeting various working
capital needs of the business.
(iv) Finance
In the sphere of financial function, an
entrepreneur has to take decisions like choosing the right type of financing,
framing the best dividend policy, acquiring of funds, efficiently managing
fixed and current assets, maximising shareholders wealth and investing of funds
efficiently and effectively.
(v) Human Resource Management
Entrepreneur has to estimate the manpower needs of
the enterprise and accordingly decide the size of manpower required for various
slots of organisational structure. After determining the required man power the
entrepreneur has to organise the performance of following functions pertaining
to human resources namely arranging for recruitment, selecting manpower,
induction and training, determining compensation structure and incentives,
designing motivation programmes, structuring well being measures for employees,
putting in place safety mechanism at work place, performance evaluation and
career advancement and structuring social security programmes.
For Own Thinking
After the completion of the academic
career, which engagement would you like to opt for after considering the
following factors:
Case Study 1
GoliVadaPav 1 (Indian Street-food Vendor
Challenge: Handmade patties are not uniform inquality and have a short span of shell life. Decreasein the profit margin due to acute increase in theprice of ingredients. Bankwhich rendered loans to Mr. Venkatesh insisted tothe losses which arose dueto these problems or repay the bank loans
Inception: VenkateshIyer co-founded GoliVAdaPav
with Shiv Menonto 2004 in Kalyan, near Mumbai for selling affordable, clean,ethnic fast good to lower income
customers in India.

Product - Vadapav:
A typical Mumbai street-fooddish of a spicy vegetable patty in a bun. The goal was to sellhygienically prepared food withan authentic touch.
Strategy:
Outsourcing th supply chainand operations
from VistaProcessing foods, a US company to supply frozen vegetables
andpattiesto GoliVAdaPav whichensures consistency in qualityand short shell
life. Installation ofautomated fryer machines in their outlets improved their
business.
Decision to penetrate the second-tier
cities in western and southerncities for their marketing.
Success Story:
i. GoliVadaPav has 300 stores in 100
cities across 20 states of India.
ii. Goli fast food chain products are
prepared in fully automated ‘HACCP’ certified hands free plant frozen at -18
degree Celsius.
iii. GoliVadaPav was set up in over
40 cities with 150 outlets with a success rate of sale of 75,000-100,000
vadapavs per day.
Key words
Entrepreneurship, Investigation,
Innovator, Mobilisation, Leadership, GDP, Intrapreneur, Manager
Related Topics