Chapter: Medical Electronics : Recent Trends in Medical Insrumentation
Electrical Safety of Medical Equipment
ELECTRICAL SAFETY OF MEDICAL
EQUIPMENT
The
patient in hospital is the center of care, but he is also helpless in the
center of potential dangers, which are in the industry, long time ago, as such
identified (i.e. chemicals, electricity, radiation). Safety in hospital means
firstly patient safety, but it means also safety of operators and
others.Electrical safety is a very important element in hospital safety. The
electrical safety of the medical equipment in hospital is the most important of
it.
Medical. Enggineering. & El. Safety
Assurance
the highest possible level of med. Equipment safety in hospital is one of the
most important tasks of the med. / clinical engineer.The med. / clinical
engineer, therefore, must be aware of and very familiar with the issues of the
electrical safety of the medical equipment in hospital. Electrical Safety means
electrical shock protection.
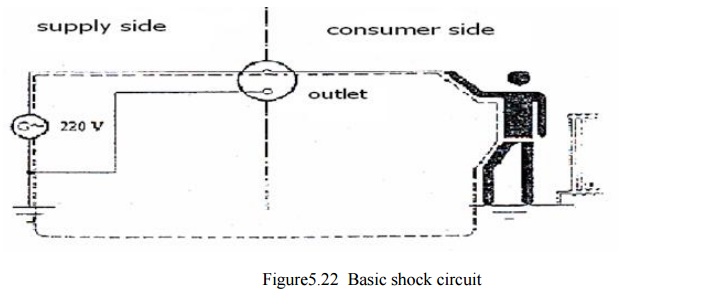
The Mechanism of the El. Shock
El. Shock
occurs when a victim is a part of an electrical circuit (an element closing
it), in which an electrical current can flow and has the ability to harm the
victim or even cause death (electrocution).That means consequently that there
must be a simultaneous two-points contact of the victim with the electrical
shock circuit.
El. Shock
= Closing the El. Shock Circuit
El. Power Distribution System
For technical reasons, neutral point (and consequently the neutral line) is deliberately connected to earth. It is this connection that makes the electrical service a “grounded system”.Understanding this is the key for understanding the mechanism of electric shock and electrocution.The voltage between the two power-carrying wires (Phase (P) & Neutral (N) or “hot & cold”) is also present between Phase and Ground (which is not considered as power carrying wire) and every thing connected to earth.
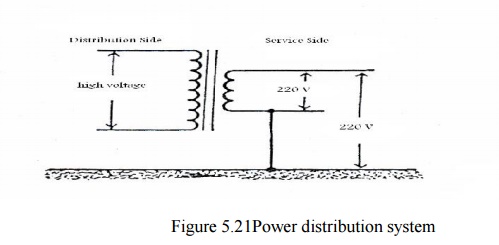
Two Kinds of Grounding / Earthing
Grounding of Electrical Systems:
Connecting
N-line of the service side to earth due to technical reason and for protection
of systems and plants (removing the floating high voltage in the secondary
(service) side of the distribution transformer).
Protective Grounding:
Connecting
conducting parts, which are not intended for carrying current in normal
circumstances (enclosures; switch-, fuse-, outlet- metal boxes; etc.) via 3rd conductor
(which, in normal situations, does not carry current) to earth.
Leakage
Currents: Caused by stray capacitances, which are always present between
conducting surfaces.
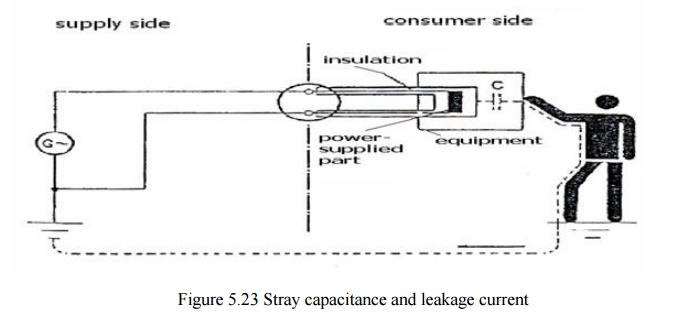
Leakage Current & Fault Current
Due to
the relatively low values of the stray capacitances and frequency, the
resulting el. Pathway is very high resistive , and hence, the resulting leakage
currents are very low.Distinguishing between leakage and fault current depends
on the internal resistance of the source in relation to the load in a given
circuit.
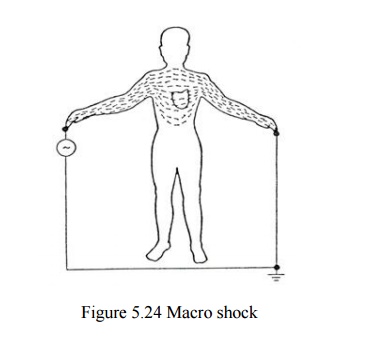
MACRO-SHOCK:
External
or touch - current shock (voltage applied externally, current pass through the
skin in and out
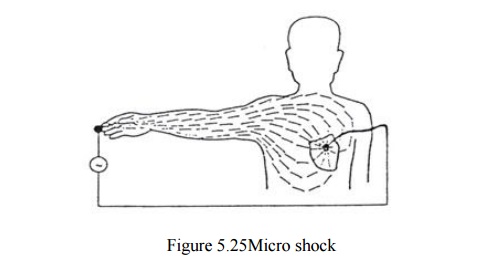
MICRO-SHOCK
Current
affect heart directly (through pacemaker leads or catheter) Currents less than
(100) micro-Ampere have the potential to cause VF (it is possible from (25)
micro-Ampere up).
Methods of Protection Against El. Shock
·
Over-current protection (indirect protection).
·
Protective earthing (grounding).
·
Double insulation.
·
Low voltage power supply.
·
Differential circuit breaker (Ground Fault Circuit
Interrupter GFCI) .
·
Isolated power system (IPS).
Protective Earthing
Simple,
efficient, and inexpensive, but it is not “fail-safe” (i.e. if it fails,
equipment does not go in a safe mode (alarm, power interruption for example)).
Double insulation
All
surfaces which can be contacted are made of non- conductive materials, or all
voltage carrying parts are double insulated. Equipment protected this way are
referred to as class II, and need not to be earthed.
Low Voltage Supply
·
Referred to as class III.
·
Supply voltage less than 50 Volt.
·
Equipment need not to be earthed.
·
For wet areas: voltage less than 25 Volt.
·
If skin immersed in water: voltage less than 12
Volt.
·
If supply is via transformer, then primary and
secondary must be galvanically separated.
Differential Circuit Breaker &GFCI
If
difference between currents in “hot” and neutral wires is more than 6 mA, the
circuit
breaker
is activated within 5 ms.
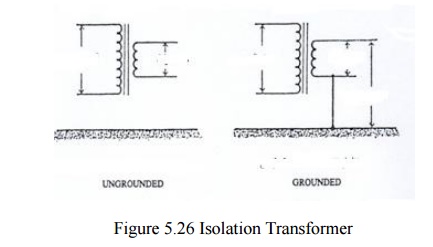
Isolated Power System (IPS) & Isolation
Transformer
Isolation
transformer is used to omit the ground connection so that the el. System on
service side is no more “ground seeking
·
IPS & Line Isolation Monitor (LIM)
·
IPS are not 100% isolated. It has certain
“resistance” to earth (caused by stray capacitances).
·
LIM measure this resistance.The monitored value in
LIM represent a virtual current which would flow if a short-circuit occurred
between a power carrying line and earth (prognostic value, worst case
condition).
·
LIM gives audio-visual alarm if the a.m. prognostic
value exceeds 5 mA (USA standard).
·
The 5 mA could be annoying, but it is normally not
dangerous.
·
Grounding of the equipment is independent of the
power system (isolated or not).
IPS Applications
·
IPS is a protection against macro-shock. It is not
(and has never been) a protection against micro-shock ( even if it makes the
related safety level higher).
·
IPS is necessary for operation theatres (OT), but is
not necessary (and not required) for ICU.
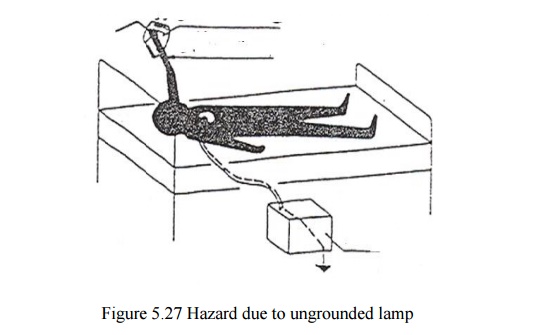
Hazard due to ungrounded lamp
(lamp failure → lamp metal cover carries voltage → patient connected to grounded equipment touches cover → current path through patient to earth)
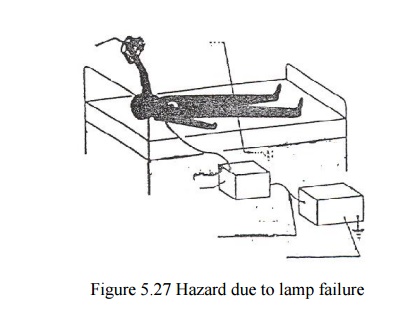
Protection
through non-conductive signal transfer (lamp failure → lamp metal cover carries
voltage → patient connected to grounded equipment (but here via battery
operated amplifier which is connected to equipment via glass fiber ) touches
cover → no current path
through
patient to earth).
Hazards due to using open sockets (extensions)
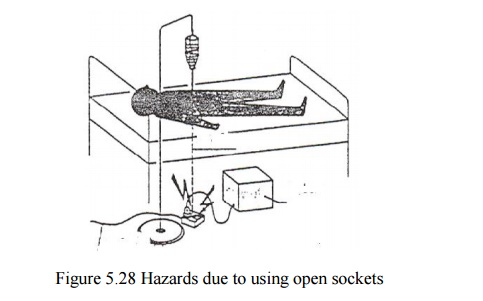
If
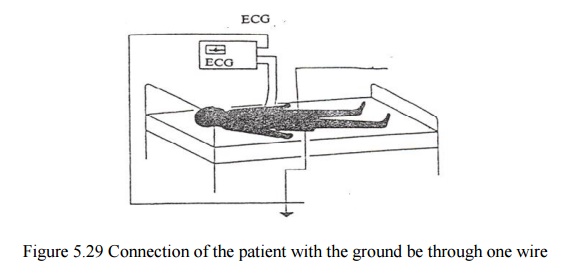
patient connected to more than one equipment , and the equipment are powered
from a socket-block, then the connection of the patient with the ground must be
through one wire only.
Rules for Med. Equipment Electrical Safety
·
Equipment connected to a patient to be powered from
one socket, or a block of sockets having the same protective grounding point.
·
All metal subjects in the vicinity of the patient
to be grounded one at a time with the same protective ground point.
·
Patient to be connected to the common ground
through only one grounding pole.
·
Isolation amplifiers to be used for measurements if
possible.
·
If possible, avoid using material which can be
charged electro-statically .
·
Deal carefully with electric wires and sockets and
let it be checked periodically. Do not use extension cables. Do not use faulty
cables / plugs and ask for replacement.
·
If an equipment has a failure, which can cause
electric shock, it has to be taken out of service immediately. Reversing the
plug (this “advice” is heard often) , which might lead to eliminate the shock,
is a wrong action / behavior.
·
If, by touching the metallic surface of an
equipment, you sensed an electric prickle (even a light one), then plug off the
equipment immediately and ask for check. This equipment is either badly earthed
or not earthed at all.
·
Do not use any medical equipment you do not know
the basics of its operation and did not read its instruction manual carefully.
Related Topics