Chapter: Medical Electronics : Recent Trends in Medical Insrumentation
Diathermy Units
DIATHERMY UNITS
Definition: Diathermy is the treatment
process by which cutting, coagulation of tissues are obtained.
· Application of high-frequency electromagnetic energy
·
Used to generate heat in body tissues
·
Heat produced by resistance of tissues
·
Also used for non-thermal effects
Advantages:
·
Treatment can be controlled easily.
·
Use of appropriate electrodes permit the heat to be
localized only in the region to be treated.
·
Amount of heat that is to be delivered can be
adjusted accurately.
·
Inter lying tissues, muscles, bones, internal
organs, etc, can be provided with heat by using high frequency
Physiologic Responses To Diathermy
·
Not capable of producing depolarization and
contraction of muscles
·
Wavelengths too short
Physiologic
Effects Are Those of Heat In General
·
Tissue temperature increase
·
Increased blood flow (vasodilation)
·
Increased venous and lymphatic flow
·
Increased metabolism
·
Changes in physical properties of tissues
·
Muscle relaxation
·
Analgesia
Diathermy Heating
Doses are
not precisely controlled thus the amount of heating cannot be accurately
measured
Heating=
Current2 X Resistance
Types of diathermy
·
Shortwave diathermy
·
Ultrasonic diathermy
·
Microwave diathermy
·
Surgical diathermy
1. SHORTWAVE DIATHERMY
·
Power supply powers radio frequency oscillator
(RFO)
·
RFO provides stable drift-free oscillations at
given frequency
·
Power amplifier generate power to drive electrodes
·
Output resonant tank tunes in the patient for
maximum power transfer
•
Power output should provide energy to raise tissue
temp to therapeutic range (40-45 deg c) (80-120 watts)
•
Should exceed sar-specific absorption rate (rate of
energy absorbed /unit area of tissue mass)
•
Generates both an electrical and a magnetic field
SWD Electrodes
•
Capacitor electrodes
•
Inductor electrodes
•
Selection of appropriate electrodes can influence
the treatment
1.1 Capacitor Electrodes
·
Create stronger electrical field than magnetic
field
·
Ions will be attracted or repelled depending on the
charge of the pole
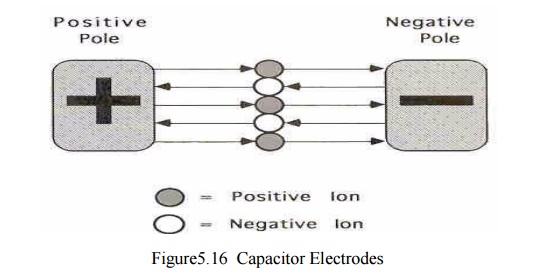
•
Electrical field is the lines of force exerted on
charged ions that cause movement from one pole to another
•
Center has higher current density than periphery
•
Patient is between elec trodes and becomes part of
circuit
•
Tissue is between electrodes in a series circuit
arrangement
• The tissue
that offers the greatest resistance to current flow develop s the most heat
•
Fat tissue resists curre nt flow
•
Thus fat is heated in a n electrical field
•
Typical with capacitor electrodes
Air Space Plates
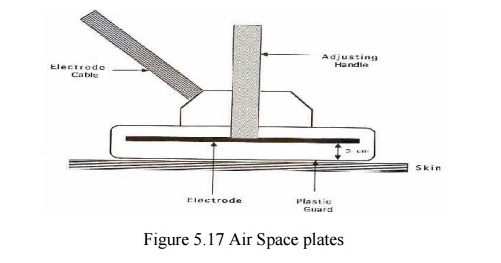
•
Two metal plates surroounded by plastic guard
•
Can be moved 3cm within guard
•
Produce high-frequency oscillating current
•
When overheated discharges to plate of lower
potential
•
Area to be treated is pllaced between electrodes
becoming part of circuit
•
Sensation of heat in direct proportion to distance
of electrode from skin
•
Closer plate generates more surface heat
•
Parts of body low in subcutaneous fat best treated
Pad Electrodes
•
Greater electrical field
•
Patient part of circuit
•
Must have uniform contact (toweling)
•
Spacing equal to cross-sectional diameter of pads
•
Part to be treated should be centered
•
Increasing the spacing will increase the depth of
penetration but will decrease the current density
1.2 Induction Electrodes
Creates a
stronger magnetic field than electrical field. A cable or coil is wrapped
circumferentially around an extremity or coiled within an electrode
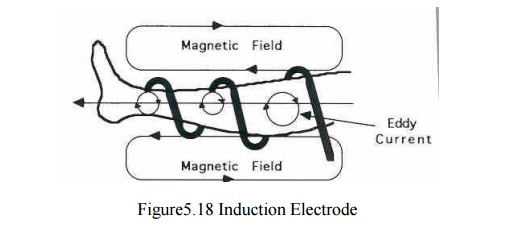
·
Passing current through a coiled cable creates a
magnetic field by inducing eddy currents (small circular electrical fields)
that generate heat
·
Patient in a magnetic field not part of a circuit
·
Tissues in a parallel arrangement
·
Greatest current flow through tissue with least
resistance
·
Tissue high in electrolytic content respond best to
a magnetic field
Cable Electrode
Two
arrangements:
Pancake
coils
Wraparound
coils
Toweling
is essential
Pancake
coil must have 6” in center then 5-10cm spacing between turns
Drum Electrode
One or more
monopolar coils rigidly fixed in a housing unit
May use
more than one drum depending on area treated.
Toweling
important.
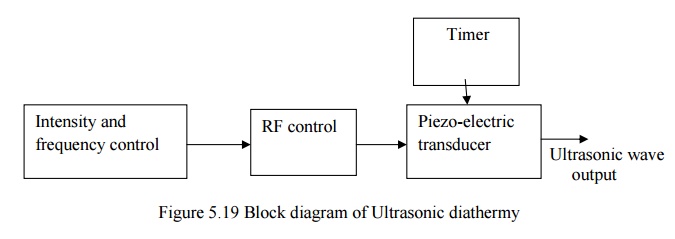
2. ULTRASONIC DIATHERMY
·
It is used for curing the diseases of peripheral
nervous system, skeletal muscle system and skin ulcers.
·
It is adopted when the short wave treatment has
failed and it helps to achieve the localization of heart to the affected part.
·
The heating effect is produced in the tissues by
the absorption of ultrasonic energy. The absorption effect is similar to that
of a micro massage.
·
It is better than the manual massage because the
micro massage provides a greater depth of massage without causing any pain to
the patient.
·
Piezo-electric transducer is excited by the high
frequency alternating current produced by the Rf oscillator.
·
Ultrasonic wave from the piezo electric transducer
is used for the purpose of treatment.
·
It can be applied in continuous mode or pulse mode.
·
Frequency range of 800 KHz to 1MHz is suitable for
the ultrasonic method of treatment
3. MICROWAVE DIATHERMY
·
In this method the tissues are heated by the
absorption of microwave energy. The frequency used is about 2450 MHz.
·
Better results are obtained by the microwave method
and it is more advantageous than the short wave method.
·
There is no pad electrodes and flexible cable.
·
Microwave is transmitted into body and treat
directly from the direction of unit.
·
Microwaves are produced with the help of magnetron
·
Proper cooling arrangements are made for the
purpose of cooling the magnetron
Precautions
·
Necessary precautions should be taken during this
method of treatment
·
Excessive dosage causes skin burns and the skin
should be dry as the waves are rapidly absorbed by water.
Disadvantages
·
Patients with implanted pacemaker should not
undergo this treatment
·
There are possibilities of over heating
·
Care should be taken while the treatment is made
near the eyes.
4. SURGICAL DIATHERMY
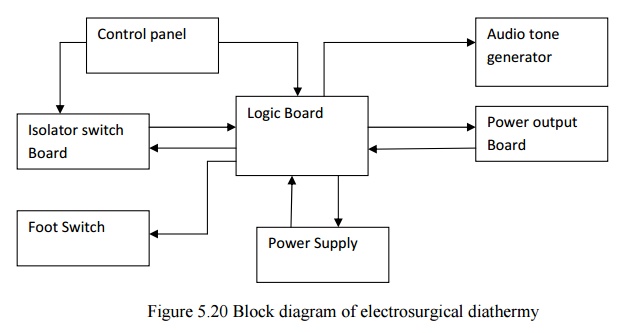
·
Logic board is the main part of the unit which
produces the necessary waveforms for cutting, coagulation and hemostasis modes
of operation.
·
An astable multivibrator generates 500 kHz square
pulses. The output from this oscillator is divided into a number of frequencies
using binary counters.
·
These frequencies are used as system timing
signals, A frequency of 250 KHz provides a split phase signal to drive output
stages on the power output board.
·
Frequency of 250 Hz is used for cutting , after the
high power amplification by push pull amplifier.
·
The output of the push pull amplifier is given to a
transformer so that the voltage is stepped up and the output signal from the
unit is well isolated.
·
The isolator switch provides an isolated switching
control between the active hand switch and the rest of the unit.
Related Topics