Chapter: Solid State Drives : Drive Characteristics
Dynamics of Motor Load System
Dynamics of Motor Load System
A motor generally drives a load (Machines) through
some transmission system. While motor always rotates, the load may rotate or
undergo a translational motion.
Load speed may be different from that of motor, and
if the load has many parts, their speed may be different and while some parts
rotate others may go through a translational motion.
Equivalent
rotational system of motor and load is shown in the figure.
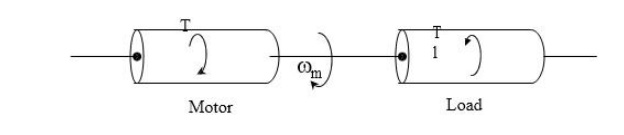
J =
Moment of inertia of motor load system referred to the motor shaft kg / m2
ωm
= Instantaneous angular velocity of motor shaft, rad/sec.
T =
Instantaneous value of developed motor torque, N-m
Tl
= Instantaneous value of load torque, referred to the motor shaft N-m
Load
torque includes friction and wind age torque of motor. Motor-load system shown
in figure can be described by the following fundamental torque equation.
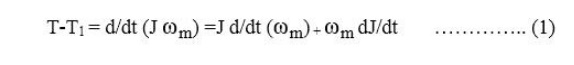
Equation
(1) is applicable to variable inertia drives such as mine winders, reel drives,
Industrial robots.
For
drives with constant inertia
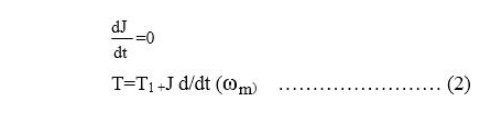
Equation
(2) shows that torque developed by motor
Related Topics