Chapter: Embedded Systems Design : Buffering and other data structures
Double buffering
Double buffering
The problem with single buffering is that there is a tremendous
overhead in managing the buffer in terms of maintaining pointers, checking the
pointers against water marks and so on. It would be a lot easier to separate
the filling from the extraction. It removes many of the contention checks that
are needed and greatly simplifies the design. This is the idea behind double
buffering.
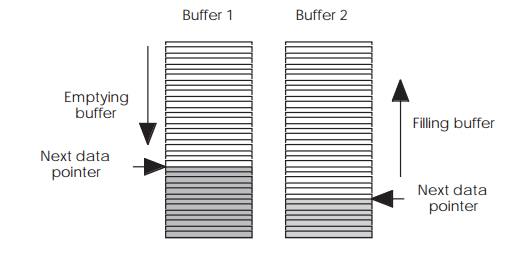
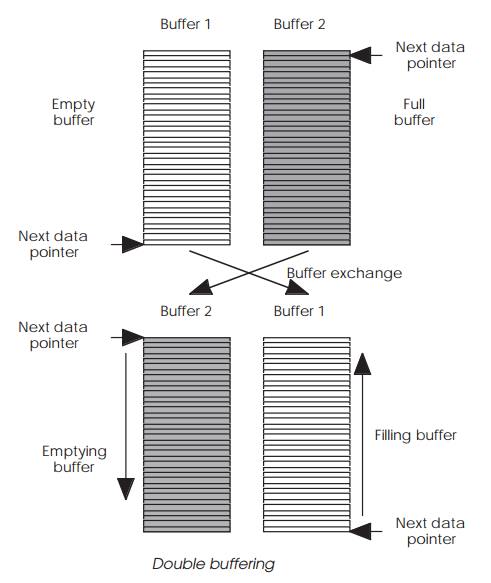
Instead of a single buffer, two buffers are used with one allocated for
filling and the second for extraction. The process works by filling the first
buffer and passing a pointer to it to the extraction task or routine. This
filled buffer is then simply used by the software to extract the data. While
this is going on, the second buffer is filled so that when the first buffer is
emptied, the second buffer will be full with the next set of data. This is then
passed to the extraction software by passing the pointer. Many designs will
recycle the first buffer by filling it while the second buffer is emptied. The
process will add delay into the system which will depend on the time taken to
fill the first buffer.
Care must be taken with the system to ensure that the buffer swap is
performed correctly. In some cases, this can be done by passing the buffer
pointer in the time period between filling the last entry and getting the next
one. In others, water marks can be used to start the process earlier so that
the extraction task may be passed to the second buffer pointer before it is
completely filled. This allows it the option of accessing data in the buffer if
needed instead of having to wait for the buffer to complete filling. This is
useful when the extraction timing is not consistent and/or re-quires different
amounts of data. Instead of making the buffers the size of the largest data
structure, they can be smaller and the double buffering used to ensure that
data can be supplied. In other words, the double buffering is used to give the
appearance of the presence of a far bigger buffer than is really there.
Related Topics