Chapter: Medical Microbiology: An Introduction to Infectious Diseases: Persistent Viral Infections of the Central Nervous System
Diseases Associated With Conventional Agents
DISEASES ASSOCIATED WITH CONVENTIONAL AGENTS
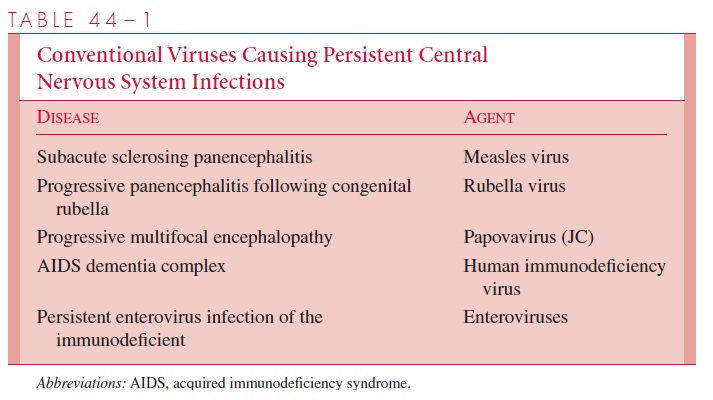
The following conditions are the major persistent infections caused by conventional viral agents. They are summarized in Table 44–1.
Subacute Sclerosing Panencephalitis
Subacute sclerosing panencephalitis, It is a rare chronic measles virus infection of children that produces progressive neurologic disease charac-terized by an insidious onset of personality change, progressive intellectual deterioration, and both motor and autonomic nervous system dysfunctions.
Progressive Postrubella Panencephalitis
Even more rarely, a degenerative neurologic disorder similar to subacute sclerosing pan-encephalitis may be related to persistent rubella virus infection of the central nervous sys-tem (CNS). This condition is seen most often in adolescents who have had the congenital rubella syndrome. Rubella virus has been isolated from brain tissue in these patients us-ing cocultivation techniques.
Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy
Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML) is a subacute, degenerative disease of the brain found primarily in adults with (1) immunosuppressive diseases, especially acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) and reticuloendothelial malignancies; or (2) diseases requiring therapy with immunosuppressive agents. PML is due to a papova-virus.
Persistent Enterovirus Infection
Persons with congenital or severe acquired immunodeficiency, especially those with agammaglobulinemia, may develop a chronic CNS infection due to an echovirus or other enterovirus. Headache, confusion, lethargy, seizures, and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) pleo-cytosis are common manifestations. The virus can be isolated from the CSF. Clinical im-provement may be achieved by the administration of human hyperimmune globulin to the infecting virus type. Relapse, however, occurs if therapy is discontinued, indicating per-sistence of virus despite the therapy.
AIDS Dementia Complex
Human immunodeficiency virus causes a persistent infection of the CNS in many patients with symptomatic AIDS. The clinical course may vary from a mild subacute illness to se-vere progressive dementia .
Related Topics