Chapter: Clinical Cases in Anesthesia : NonDepolarizing NeuroMuscular Blockade
Differentiate between the commonly employed non-depolarizing muscle relaxants
Differentiate
between the commonly employed non-depolarizing muscle relaxants.
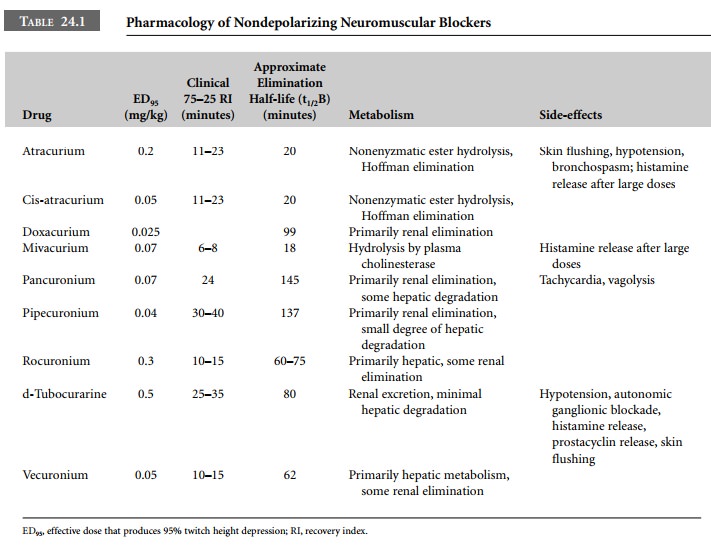
All nondepolarizing muscle relaxants decrease
striated muscle strength by competitive inhibition of postsynaptic
acetylcholine receptors at the neuromuscular junction. Some muscle relaxants
affect prejunctional acetylcholine receptors as well. Clinically important
parameters that distinguish nondepolarizing muscle relaxants from one another
include onset times, elimination times, routes of elimination, and potency
(Table 24.1). Rocuronium is
Intubating doses of 2–3 times the
effective dose that produces 95% twitch height depression (ED95) may
provide intubating conditions in 60–90 seconds, which approaches but does not
equal the onset time for succinylcholine.
Related Topics