Chapter: Mechanical and Electrical : Power Plant Engineering : Power From Renewable Energy
Different tidal power plants
Different
tidal power plants
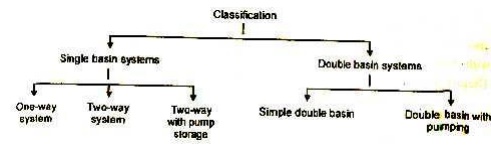
The tidal power plants are generally classified on the
basis of the number of basins used for the power generation. They are further
subdivided as one-way or two-way system as per the cycle of operation for power
generation.
The classification is represented with the help of a line
diagram as given below.
Working
of different tidal power plants
1.
Single basin-one-way cycle
This is the simplest form of tidal power plant. In this
system a basin is allowed to get filled during flood tide and during the ebb
tide, the water flows from the basin to the sea passing through the turbine and
generates power. The power is available for a short duration ebb tide.
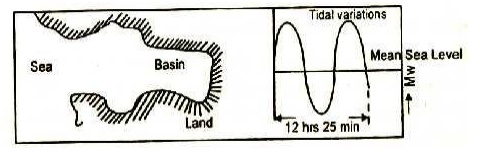
Figure: (a) Tidal region before construction of the power
plant and tidal variation
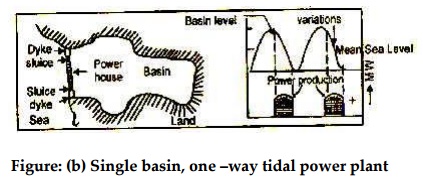
Figure: (b) Single basin, one –way
tidal power plant
Figure
(a) shows a single tide basin before the construction, of dam and figure (b)
shows the diagrammatic representation of a dam at the mouth of the basin and
power generating during the falling tide.
2.
Single-basin two-way cycle
In this arrangement, power is generated both during flood
tide as well as ebb tide also. The power generation is also intermittent but
generation period is increased compared with one-way cycle. However, the peak
obtained is less than the one-way cycle. The arrangement of the basin and the
power cycle is shown in figure.
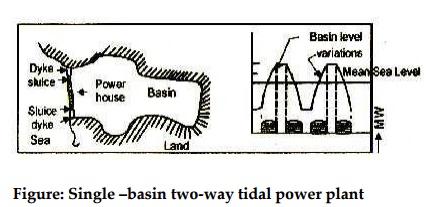
Figure: Single –basin two-way tidal
power plant
The main difficulty with this arrangement, the same
turbine must be used as prime mover as ebb and tide flows pass through the
turbine in opposite directions. Variable pitch turbine and dual rotation
generator are used of such scheme.
3. Single –basin two-way cycle with pump storage
In
this system, power is generated both during flood and ebb tides. Complex
machines capable of generating power and pumping the water in either directions
are used. A part of the energy produced is used for introducing the difference
in the water levels between the basin and sea at any time of the tide and this
is done by pumping water into the basin up or down. The period of power
production with this system is much longer than the other two described
earlier. The cycle of operation is shown in figure.
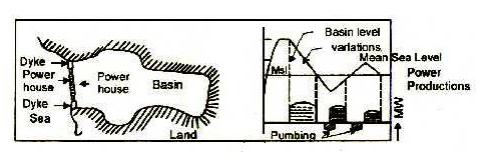
Figure: Single-basin, two-way tidal
plant coupled with pump storage system.
4.
Double basin type
In this arrangement, the turbine is set up between the
basins as shown in figure. One basin is intermittently filled tide and other is
intermittently drained by the ebb tide. Therefore, a small capacity but
continuous power is made available with this system as shown in figure. The
main disadvantages of this system are that 50% of the potential energy is
sacrificed in introducing the variation in the water levels of the two basins.
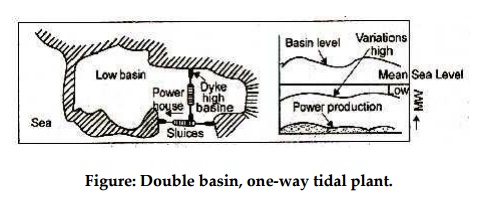
5.
Double basin with pumping
In this case, off peak power from the base load plant in a
interconnected transmission system is used either to pump the water up the high
basin. Net energy gain is possible with such a system if the pumping head is
lower than the basin-to-basin turbine generating head.
Related Topics