Chapter: Medical Immunology: Diagnosis of Immunodeficiency Diseases
Diagnosis of Immunodeficiency Diseases: Introduction
Diagnosis of Immunodeficiency Diseases
INTRODUCTION
Immunodeficiency diseases and syndromes are the cause of significant mortality and mor-bidity, as well as a source of extremely valuable information about the physiology of the human immune system. Most immunodeficient patients have secondary forms of immun-odeficiency, caused either by pathological conditions that affect the immune system or by the administration of therapeutic compounds with immunosuppressive effects.
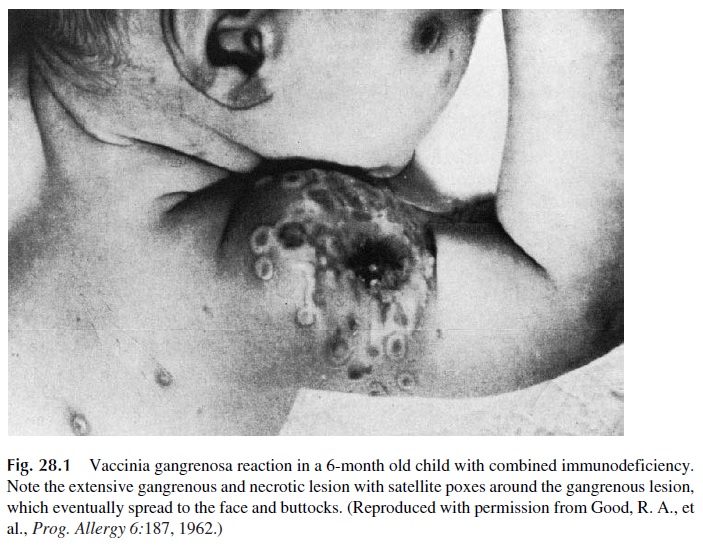
A functional defect of the immune system is suspected when a patient has unusual frequency of infections with common or opportunistic microorganisms, complications after the administration of attenuated vaccines (see Fig. 28.1), unusually severe infec-tions, or failure to eradicate infections with antibiotics to which the microorganisms are sensitive.
A good history, careful work-up of the infectious episodes, and a thorough physical examination are essential for the initial evaluation of a suspected immunodeficiency, pro-viding useful clues about the type of immunodeficiency (Table 28.1). Obtaining family his-tory is equally important. Early death of older siblings suffering from repeated infectious episodes is often the only way to document the hereditary character of a congenital im-munodeficiency.

Once an immunodeficiency is suspected, investigations need to be undertaken with the purpose of documenting the immunodeficiency state. Known causes of secondary immunodeficiency need to be ruled out (Table 28.2) and, if present, therapy will be di-rected at their elimination, whenever possible.

If a diagnosis of primary immunodeficiency is made, it will be important to define the degree of compromise of the different mechanisms of immunological defense-cellular immunity, humoral immunity, phagocy-tosis, and complement in order to select the most effective type of therapy. Finally, the definitive diagnosis needs to be established, and in patients with primary immunode-ficiency, this often involves identification of the genetic abnormality underlying the disease.
Related Topics