Chapter: Obstetrics and Gynecology: Amenorrhea and Abnormal Uterine Bleeding
Diagnosis of Abnormal Uterine Bleeding
Diagnosis of Abnormal Uterine
Bleeding
Diagnosis of abnormal uterine
bleeding should be sus-pected when vaginal bleeding is not regular, not
pre-dictable, and not associated with premenstrual signs and symptoms that
usually accompany ovulatory cycles. These signs and symptoms include breast
fullness, abdominal bloating, mood changes, edema, weight gain, and uterine
cramps.
Before
anovulatory uterine bleeding can be diagnosed, anatomic causes including
neoplasia should be excluded.
In a reproductive-aged woman,
complications of pregnancy as a cause of irregular vaginal bleeding should be
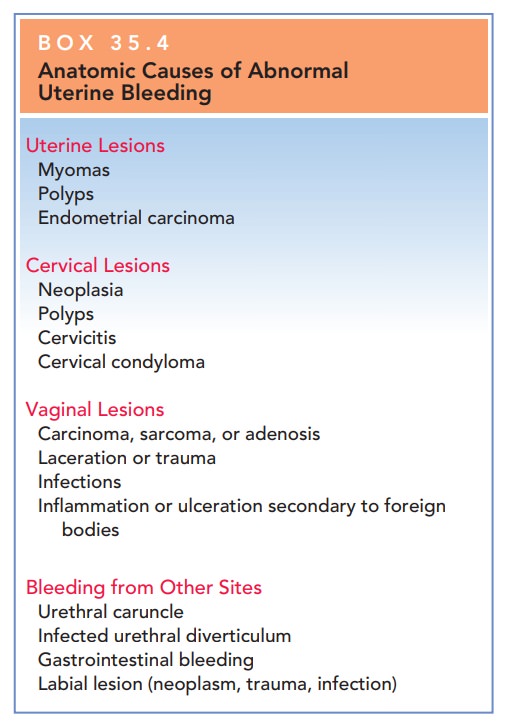
excluded. Other anatomic causes of irregular vaginal bleeding include uterine
leiomyomata, inflammation or infection of the gen-ital tract, hyperplasia or
carcinoma of the cervix or endo-metrium, cervical and endometrial polyps, and
lesions of the vagina (Box 35.4). Pelvic ultrasonography or sonohysterog-raphy
may assist in diagnosing these lesions. Women with organic causes for bleeding
may have regular ovulatory cycles with superimposed irregular bleeding.
If the diagnosis is uncertain
based on history and phys-ical examination alone, a woman may keep a basal body
temperature chart for 6 to 8 weeks to look for the shift in the basal
temperature that occurs with ovulation. An ovu-lation predictor kit may also be
used. Luteal phase pro-gestin may also be measured. In cases of anovulation and
abnormal bleeding, an endometrial biopsy may reveal endometrial hyperplasia.
Because abnormal uterine bleed-ing results from chronic, unopposed estrogenic
stimulation of the endometrium, the endometrium appears prolifera-tive or, with
prolonged estrogenic stimulation, hyperplas-tic. Without treatment, these women
are at increased risk for endometrial cancer.
Related Topics