Chapter: 10th Science : Chapter 21 : Health and Diseases
Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetes mellitus is a
chronic metabolic disorder. In Greek (Diabetes – running through; mellitus-
sweet). It is characterised by increased blood glucose level due to insufficient,
deficient or failure of insulin secretion. This is the most common
pancreatic endocrine disorder. The incidence of Type- 1 and Type-2
diabetes is increasing worldwide.
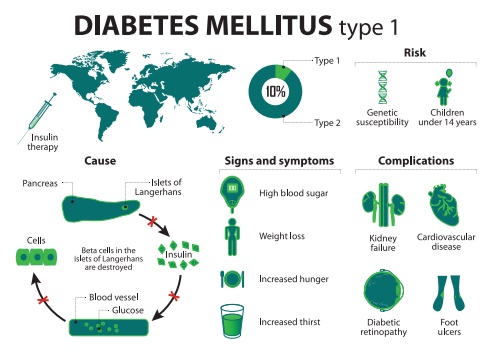
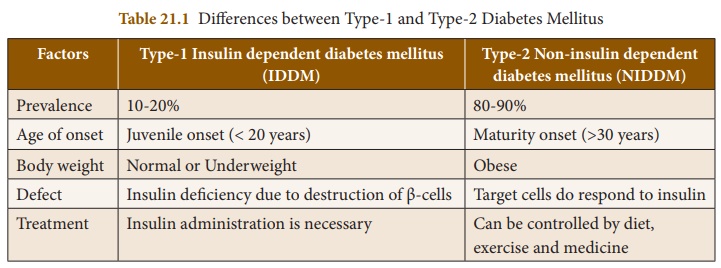
1. Type-1 Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus (IDDM)
IDDM accounts for 10 to
20% of the known diabetics. The condition also occurs in children ( juvenile
onset diabetes) and young adults, the onset is usually sudden and
can be life threatening. This is caused by the destruction of β -cells
of the pancreas. It is characterized by abnormally elevated blood
glucose levels (hyperglycemia ) resulting from inadequate insulin
secretion.
Causes : Genetic inheritance
and environmental factors (infections due to virus, acute stress) are
the cause for this condition.
2. Type-2 Non-Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus (NIDDM)
This is also called as adult
onset diabetes and accounting for 80 to 90% of the diabetic population. It
develops slowly, usually milder and more stable. Insulin production by the
pancreas is normal but its action is impaired. The target
cells do not respond to insulin. It does not allow the movement of glucose into
cells.
Causes: The causes are
multifactorial which include increasing age (affecting middle aged and
older people), obesity, sedentary life style, overeating and physically
inactive.
Symptoms: Diabetes mellitus is
associated with several metabolic alterations.The most important
symptoms are
·
Increased blood glucose level (Hyperglycemia)
·
Increased urine output (Polyuria) leading to dehydration
·
Loss of water leads to thirst (Polydipsia) resulting in
increased fluid intake
·
Excessive glucose excreted in urine (Glycosuria)
·
Excess hunger (Polyphagia) due to loss of glucose in urine.
·
Fatigue and loss of weight
3. Prevention and Control of Diabetes
Diet, hypoglycemic drugs,
insulin injection and exercise are the management options based on the type and
severity of the condition. The overall goal of diabetes management is to
maintain normal blood glucose level.
Dietary management: Low carbohydrate and
fibre rich diets are more appropriate. Carbohydrates should be taken in the
form of starch and complex sugars. Refined sugars (sucrose and glucose) should
be avoided. Diet comprising whole grains, millets (jowar, bajra, ragi), green
leafy vegetables, wheat and unpolished rice should be included in diet
regularly.
Carbohydrates is
maintained to about 50-55% of the total calories. High protein content of
10-15% of the total intake is required to supply essential amino acids. Fat
content in the diet should be 15-25% of the total calories. Saturated fat
intake should be reduced. Polyunsaturated fatty acid content should be higher.
Management with insulin: Commercially available
insulin preparations (short and long acting) are also used to maintain blood
glucose levels.
Physical activity: Exercise plays an
important role in facilitating a good control of diabetes, in addition
to strengthening and toning up the muscles.
Education and Awareness: People with diabetics
should be educated on the nature of disease they have and the possibility of
complications of the disease, if blood sugar is not kept under control.
Instructions regarding diet, exercise and drugs should be explained.
Related Topics