Chapter: Microbiology and Immunology: Virology, Virus: Laboratory Diagnosis of Viral Diseases
Detection of Viral Genome - Methods of Laboratory Diagnosis of Viral Diseases
Methods of Laboratory Diagnosis
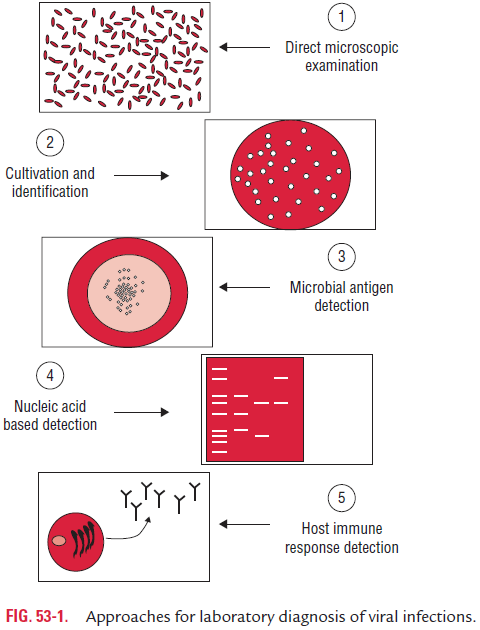
Laboratory diagnosis of viral infections can be carried out by many methods. These methods include
(a) demonstration of virus-induced cytopathic effects (CPEs) in the cells,
(b) direct detection of viruses,
(c) virus isolation and viral assays,
(d) detection of viral proteins and other enzymes,
(e) detection of viral genome, and
(f) viral serology (Fig. 53-1).
Detection of Viral Genome
The unique genomic structure and genetic sequences are the most important characteristics of the type and family of virus. Therefore, recently molecular methods are increasingly used for diagnosis of viral diseases. The restriction endonucle-ase fragment lengths from the genome of DNA viruses, such as HSV-1 and HSV-2 or the electrophoretic pattern of RNA viruses, such as influenza and reo viruses are considered as genetic fingerprints for these viruses.
The methods for detection of viral genome include (a) DNA probes, (b) dot blot or Southern blot analysis, (c) Northern blot or RNA:DNA probe hybridization, (d) polymerase chain reaction (PCR), and (e) reverse transcriptase PCR (RT PCR).
Related Topics