Chapter: Microbiology and Immunology: Virology, Virus: Laboratory Diagnosis of Viral Diseases
Demonstration of Virus-Induced CPEs in the Cells - Methods of Laboratory Diagnosis of Viral Diseases
Methods of Laboratory Diagnosis
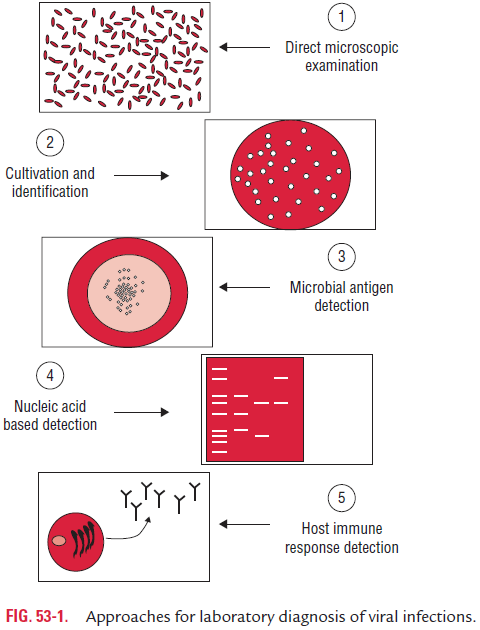
Laboratory diagnosis of viral infections can be carried out by many methods. These methods include
(a) demonstration of virus-induced cytopathic effects (CPEs) in the cells,
(b) direct detection of viruses,
(c) virus isolation and viral assays,
(d) detection of viral proteins and other enzymes,
(e) detection of viral genome, and
(f) viral serology (Fig. 53-1).
Demonstration of Virus-Induced CPEs in the Cells
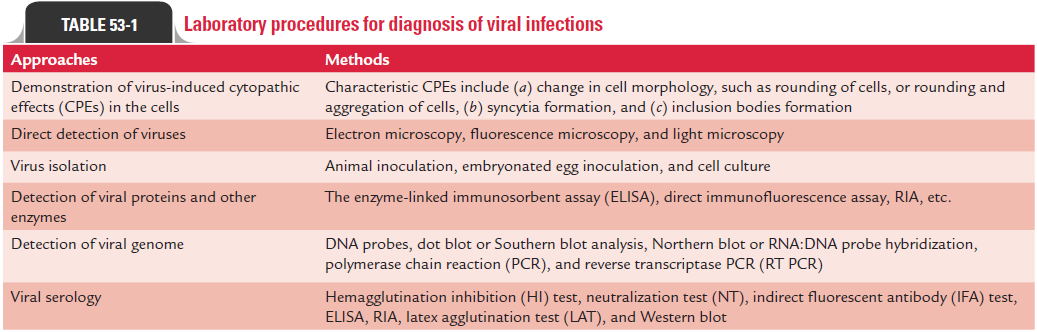
Many viruses produce characteristic morphological changes in the cells they infect. These changes are known as CPEs, and the viruses causing the CPEs are known as cytopathogenic viruses. The characteristic CPEs include (a) change in cell morphology, such as rounding of cells or rounding and aggregation of cells, (b) syncytia formation, and (c) inclusion bodies formation.
· Replication of virus in infected cells may cause rounding, refractility, degeneration, and nuclear pyknosis. This may finally lead to complete or partial cell lysis as well as vacuolation, as seen in picornaviruses. Viruses, such as adenoviruses, may cause rounding of cells and aggregate to form grape-like clusters.
· Viruses, such as paramyxovirus, varicella zoster, respiratory syncytial virus, and herpes simplex virus (HSV), cause for-mation of syncytia containing several (up to 100) nuclei in infected cells. These syncytia are multinucleated giant cells formed by fusion of virus-infected cells with neighboring or uninfected cells.
· Inclusion bodies are intranuclear or cytoplasmic bodies pro-duced by viruses in infected cells. They are produced as a result of histological changes in infected cells caused by viral components. These are also produced as a result of virus-induced changes in cell structures.
These inclusion bodies can be demonstrated on staining by light microscopy. These inclusion bodies may be acidophilic or basophilic, small or large, round or irregular; and single or multiple. These bodies may be present either in nucleus or cytoplasm, or in both. Many viruses produce different types of inclusion bodies. For example, rabies virus produces intracyto-plasmic inclusion bodies called Negri bodies in neural tissue of the brain. Cytomegalovirus (CMV) produces intranuclear owl’s eye inclusion bodies (Color Photo 53) in infected cells or in cell sediments excreted in the urine of the patient infected with CMV. Human herpes viruses produces Cowdry type A inclusion bodies. Measles virus produces inclusion bodies that are seen both in the cytoplasm and nucleus of infected cells (Table 53-1).
Related Topics