Chapter: Civil : Railway Airport Harbour Engineering : Railway Engineering : Ballast
Design of Ballast Section
Design of Ballast Section
The design of the ballast section
includes the determination of the depth of the ballast cushion below the
sleeper and its profile. These aspects are discussed below.
1 Minimum Depth of Ballast Cushion
The load on the sleeper is
transferred through the medium of the ballast to the formation. The pressure
distribution in the ballast section depends upon the size and shape of the
ballast and the degree of consolidation. Though the lines of equal pressure are
in the shape of a bulb, yet for simplicity, the dispersion of load can be
assumed to be roughly 45 o to the vertical. In order to ensure that the load is
transferred evenly on the formation, the depth of the ballast should be such
that the dispersion lines do not overlap each other.
For the even distribution of load on the formation, the depth
of the ballast is determined by the following formula (refer to Fig. 8.1):
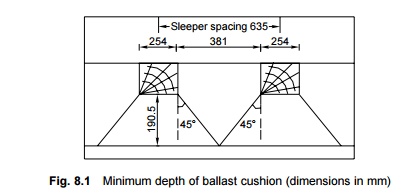
Fig. 8.1 Minimum depth
of ballast cushion (dimensions in mm)
Sleeper spacing = width of the sleeper + 2 × depth of ballast (8.1) If a BG track is laid with wooden
sleepers with a sleeper density of N + 6, then the sleeper spacing would
be 68.4 cm. If the width of the sleeper is 25.4 cm, then the depth of the
ballast cushion would be
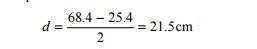
A minimum cushion of 15-20 cm of ballast below the
sleeper bed is normally prescribed on Indian Railways.
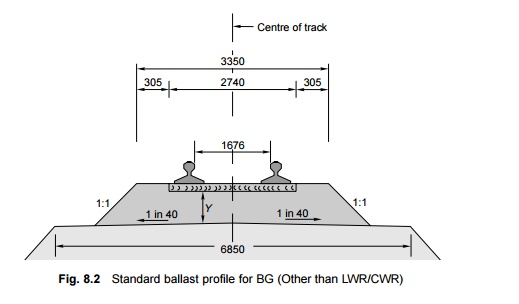
2 Ballast Profile for Fish-plated Track
The ballast profile for a fish-plated track is shown in Fig.
8.2. The requirements of ballast for different groups of railway lines as
adopted by Indian Railways are given in Table 8.2.
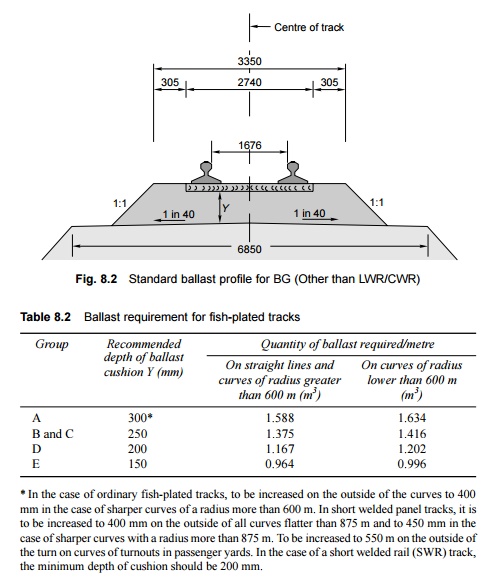
* In the case of ordinary
fish-plated tracks, to be increased on the outside of the curves to 400 mm in
the case of sharper curves of a radius more than 600 m. In short welded panel
tracks, it is to be increased to 400 mm on the outside of all curves flatter
than 875 m and to 450 mm in the case of sharper curves with a radius more than
875 m. To be increased to 550 m on the outside of the turn on curves of turnouts
in passenger yards. In the case of a short welded rail (SWR) track, the minimum
depth of cushion should be 200 mm.
3 Ballast
Profile for Long Welded Rail Tracks
The ballast profile for a long
welded rail (LWR) track is shown in Fig. 8.3. The requirements of ballast for
different types of sleepers on a BG railway line are given in Table 8.3.
The minimum clean stone ballast cushion below the bottom of
sleeper (A) is 250 mm. For routes where speeds are to be more than 130
kmph, A is 300 mm- 200 mm along with 150 mm of sub-ballast. Suitable
dwarf walls should be provided in the case of cuttings, if necessary, for
retaining the ballast.
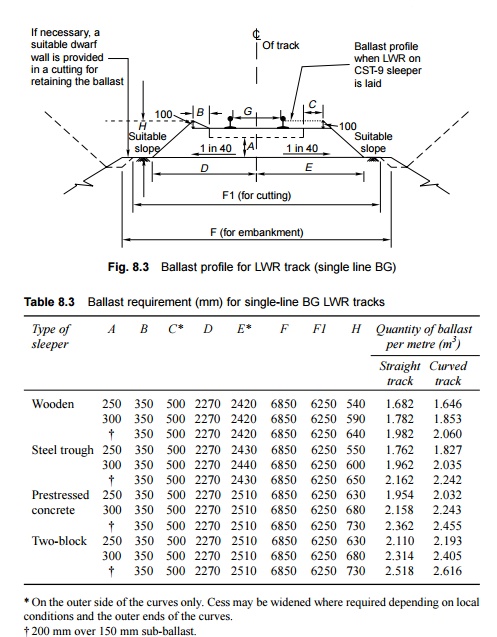
* On the outer side of the curves
only. Cess may be widened where required depending on local conditions and the
outer ends of the curves.
† 200 mm over 150 mm sub-ballast.
Related Topics