Light | Science - Curved Mirrors | 9th Science : Light
Chapter: 9th Science : Light
Curved Mirrors
Curved Mirrors
We studied about laws of reflection. These laws are
applicable to all types of reflecting surfaces including curved surfaces. Let
us learn about image formation in curved surfaces in this part.
In your earlier classes, you have studied that
there are many types of curved mirrors, such as spherical and parabolic
mirrors. The most commonly used type of curved mirror is spherical mirror. The
curved surfaces of a shining spoon could also be considered as a curved mirror.
Take a hemispherical spoon. It has an inner and
outer surface like the inside and outside of the ball. See your face on these
surfaces? How do they look?

Move the spoon slowly away from your face.
Observe the image. How does it change?
Reverse the spoon and repeat the activity.
How does the image look like now?
1. Spherical mirrors
In curved mirrors, the reflecting surface can be
considered to form a part of the surface of a sphere. Such mirrors whose
reflecting surfaces are spherical are called spherical mirrors.
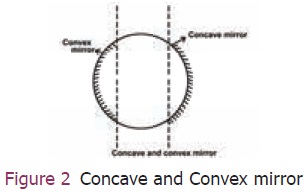
In some spherical mirrors the reflecting surface is
curved inwards, that is, it faces towards the centre of the sphere. It is
called concave mirror. In some other mirrors, the reflecting surface is curved
outward. It is called convex mirror and are shown in Figure 2.
In order to understand reflection of light at
curved surfaces, we need to know the following.
Centre of curvature (C): The centre of the hollow
sphere of which the spherical mirror forms a part.
Pole (P): The geometrical centre of the spherical
mirror.
Principal axis (PC): The perpendicular line joining the pole and the centre of
curvature of the mirror.
Radius of curvature(R): The distance between the
pole and the centre of curvature of the spherical mirror.
Principal focus (F): The point on the principal
axis of the spherical mirror where the rays of light parallel to the principal
axis meet or appear to meet after reflection from the spherical mirror.
Focal length(f): The distance between the pole and
the principal focus.
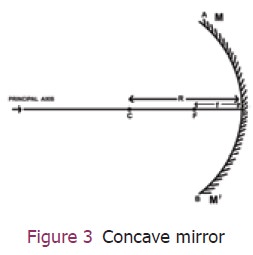
Radius of curvature and focal length are related to
each other by the formula: R=2f. All these are depicted in Figure 3.
Check yourself:
·
Focal length of a concave mirror is 5 cm. Find its
radius of curvature.
·
For a concave mirror the distance between P and C
is 10 cm. Calculate it’s the focal length.
·
A concave mirror has radius of curvature 20 cm.
Find the focal length of the mirror.
Related Topics