Chapter: Nutrition and Diet Therapy: Diet During Pregnancy and Lactation
Concerns during Pregnancy
CONCERNS DURING PREGNANCY
Nausea
Sometimes nausea (the
feeling of a need to vomit) occurs during the first tri-mester of pregnancy.
This type of nausea is commonly known as morningsickness,
but it can occur at any time. It typically passes as the
pregnancyproceeds to the second trimester. The following suggestions can help
relieve morning sickness:
• Eat dry crackers or dry toast before rising.
• Eat small, frequent meals.
• Avoid foods with offensive odors.
• Avoid liquids at mealtime.
In rare cases, the
nausea persists and becomes so severe that it is life-threatening. This
condition is called hyperemesis
gravidarum. The mother may be hospitalized and given parenteral nutrition. This means the
patient is given nutrients via a vein. Such cases are difficult, and the
patients need emotional support and optimism from those who care for them.
Constipation
Constipation and
hemorrhoids can be relieved by eating high-fiber foods, get-ting daily
exercise, drinking at least 8 glasses of liquid each day, and responding
immediately to the urge to defecate.
Heartburn
Heartburn can result
from relaxation of the cardiac sphincter and smooth muscles related to
progesterone. Heartburn is a common complaint during preg-nancy. As the fetus
grows, it pushes on the mother’s stomach, which may cause stomach acid to move
into the lower esophagus and create a burning sensation there. Heartburn may be
relieved by eating small, frequent meals; avoiding spicy or greasy foods; avoiding
liquids with meals; waiting at least an hour after eating before lying down;
and waiting at least 2 hours before exercising.
Excessive Weight Gain
If weight gain becomes
excessive, the pregnant woman should reevaluate her diet and eliminate foods
(except for the extra pint of milk) that do not fit within MyPyramid. Examples
include candy, cookies, rich desserts, chips, salad dress-ings (other than fat
free), and sweetened beverages. In addition, she might drink fat-free milk, if
not doing so, which would reduce her calories but not her intake of proteins,
vitamins, and minerals. Except in cases in which the woman cannot tolerate
lactose (the sugar in milk), it is not advisable to substitute cal-cium pills
for milk because the substitution reduces the protein, vitamin, and mineral
content of the diet.
A bowl of clean,
crisp, raw vegetables such as broccoli or cauliflower tips, carrots, celery,
cucumber, zucchini sticks, or radishes dipped in a fat-free salad dressing or
salsa can provide interesting snacks that are nutritious, filling, sat-isfying,
and low in calories. Fruits and custards made with fat-free milk make
nutritious, satisfying desserts that are not high in calories. Broiling,
baking, or boiling foods instead of frying can further reduce the caloric
intake.
Pregnancy-Induced Hypertension
Pregnancy-induced hypertension (PIH) was formerly calledtoxemiaorpreeclampsia. It is a condition that sometimes occurs during the
third trimes-ter. It is characterized by high blood pressure, the presence of
albumin inthe urine (proteinuria), and edema. The edema
causes a somewhat sud-den increase in weight. If the condition persists and
reaches the eclamptic (convulsive) stage, convulsions, coma,
and death of mother and child may occur. The cause of this condition is not
known, but it occurs more frequently in first-time pregnancies, in multifetal
pregnancies, in those women with morbid obesity, and among pregnant women on
inadequate diets, especially protein-deficient diets. Pregnant adolescents have
a higher rate of PIH than do pregnant adults.
Pica
Pica is the craving for
nonfood substances such as starch, clay (soil), or ice.The reasons people get
such a craving are not clear. Although both men and women are affected, pica is
most common among pregnant women. Some believe it relieves nausea. Others think
the practice is based on cul-tural heritage. The consumption of soil should be
highly discouraged. Soil contains bacteria that would contaminate both mother
and fetus. Ingest-ing soil can lead to an intestinal blockage, and substances
in the soil would bind with minerals, preventing absorption by the body and
thus leading to nutrient deficiencies. If any of the nonfood substances
replaces nutrient-rich foods in the diet, this will result in multiple nutrient
deficiencies. Eating laundry starch, in addition to a regular diet, will add
unneeded calories and carbohydrates.
Anemia
Anemia is a condition caused
by an insufficiency of red blood cells, hemoglobin,or blood volume. The patient
suffering from it does not receive sufficient oxygen from the blood and
consequently feels weak and tired, has a poor appetite, and appears pale. Iron deficiency is its most common form.
During pregnancy, the increased volume of blood creates the need for additional
iron. When this need is not met by the diet or by the iron stores in the
mother’s body, iron deficiency anemia develops. This may be treated with a
daily iron supplement.
Folate deficiency can result in a form
of megaloblastic anemia that canoccur during pregnancy. It is characterized by
too few red blood cells and by large immature red blood cells. The body’s
requirement for folic acid increases dramatically when new red blood cells are
being formed. Consequently, the obstetrician might prescribe a folate supplement
of 400 to 600μg a day during pregnancy.
Alcohol, Caffeine, Drugs, and Tobacco
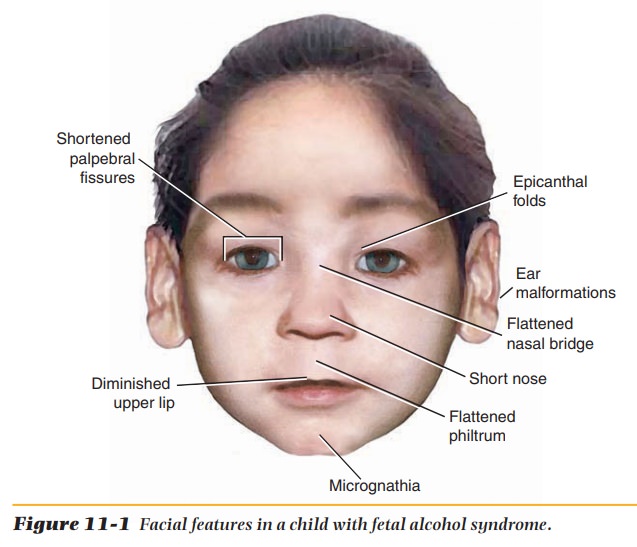
Alcohol consumption is
associated with subnormal physical and mental devel-opment of the fetus. This
is called fetal alcohol syndrome
(FAS). Many infants with FAS are premature and have a low birth
weight. Physical characteristics may include a small head, short eye slits that
make eyes appear to be set far apart, a flat midface, and a thin upper lip.
There is usually a growth deficiency(height, weight), placing the child in the
lowest tenth of age norms. There is also evidence of central nervous system
dysfunction, including hyperactivity, sei-zures, attention deficits, and
microcephaly (small head) (Figure 11-1). Another condition caused by ingesting
alcohol while pregnant is fetal alcohol effect (FAE). Children with FAE are
born with less dramatic or no physical defects but with many of the behavioral
and psychosocial problems associated with FAS. Those with FAE are not able to
lead normal lives due to deficits in intelligence and behavioral and social
abilities. When the mother drinks alcohol, it enters the fetal bloodstream in
the same concentration as it does the mother’s. Unfor-tunately, the fetus does
not have the capacity to metabolize it as quickly as the mother, so it stays
longer in the fetal blood than it does in the maternal blood. Abstinence is
recommended.
Caffeine is known to
cross the placenta, and it enters the fetal blood-stream. Birth defects in
newborn rats whose mothers were fed very high doses of caffeine during
pregnancy have been observed, but there are no data on humans showing that
moderate amounts of caffeine are harmful. As a safety measure, however, it is
suggested that pregnant women limit their caffeine intake to 2 cups of
caffeine-containing beverages each day, or less than 300 mg/day.
Drugs vary in their effects, but self-prescribed drugs, including vitamins and mineral supplements and dangerous illegal drugs, can all damage the fetus. Drugs derived from vitamin A can cause fetal malformations and spontaneous abortion. Illegal drugs can cause the infant to be born addictedto whatever substance the mother used and, possibly, to be born with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). If a pregnant woman is known to be infected with HIV, her physician may prescribe AZT in an attempt to prevent the spread of the disease to the developing fetus.
Tobacco
smoking by pregnant women has for some time been associated with babies of
reduced birth weight. The more the mother smokes, the smaller her baby will be
because smoking reduces the oxygen and nutrients carried by the blood. Other
risks associated with smoking include SIDS (sudden infant death syndrome),
fetal death, spontaneous abortion, and complications at birth. Smoking during pregnancy
may also affect the intellectual and behavioral development of the baby as it
grows up.
Because the substances
discussed in this section may cause fetal prob-lems, it is advisable that
pregnant women avoid them.
Related Topics