Geriatric Care in Nursing - Common Disorder | 12th Nursing : Chapter 7 : Geriatric Care
Chapter: 12th Nursing : Chapter 7 : Geriatric Care
Common Disorder
COMMON DISORDER
·
Immobility and rehabilitation
·
Frequent falls
·
Urinary incontinence
·
Stroke rehabilitation
·
Pressure / bed sores
·
Laterogenic drug reactions
·
Hypertension in the elderly
·
Diabetes in older adults
·
Arthritis and osteoporosis
·
Prostate enlargement
·
Eye diseases
·
Cancer
1. Immobility and Rehabilitation
·
Age changes in neurological and musculoskeletal system lead to
high prevalence of disorders such as stroke, Parkinson disease, osteoarthritis
and osteoporosis interact to make poor mobility.
·
The goal of rehabilitation to reduce limitations of movement and
to improve mobility.
Management
Therapies to reduce pain
and to increase in range of motion.
Heat, cold, massage, electro therapy, hydrotherapy and ultraviolet
radiation.
Occupational therapy and
braces, splints and prostheses, crutch may be used to enhance function.

2. Frequent Falls
Causes
·
Several factors such as neurological, cardiovascular,
musculoskeletal, otological and drugs (hypertension, bradycardia of sick sinus
syndrome) causes falls.
·
Poor vision
·
Muscle weakness
·
Insufficient lighting
·
Uneven carpet or slippery floor
Management
·
Careful history and physical examination.
·
Assessment of standing balance and gait.
·
CT of the brain, blood pressure monitoring.
3. Urinary Incontinence
Definition
The involuntary leakage
of urine it means a person urinates when they do not want to
Causes
·
Involuntary passage of urine due to loss of bladder control.
·
Drugs, abdominal surgery, neurological diseases and physical
disability either lead to percipitate inconvenience.
·
Obesity
·
Smoking
·
Stress
Management
·
Toilet training to anticipate and overcome episodes of
incontinence
·
Bladder relaxant
·
Treatment of the cause
·
Therapeutic devices( catheters)
4. Stroke
Definition: The sudden death of
brain cells
due to lack of oxygen
caused by blockage of blood flow or rupture of an artery to the brain.
Causes
·
Hypertension
·
Smoking
·
Alcohol
·
Diabetes
·
Cardiac diseases

Management
·
Prevention and treatment of acute complications.
·
Rehabilitation to minimise disability.
·
Medical intervention to minimise impairment.
·
Nursing Intervention (nutrition, skin care, positioning, bladder
and bowel care)
·
Drug therapy with anti platelet agents and hunting co-coagulants.
5. Arthritis and Osteoporosis

Definition of
Arthritis
It is a painful
inflammation and stiffness of the joints. Arthritis simply means inflammation
of the joints. The symptoms include pain, swelling and stiffness with
limitation of joint movements.
Causes
·
Abnormal metabolism
·
Genetic inheritance
·
Infection
·
Systemic lupus erythematosus
Definition of
Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis means
“porous bones” causing bones to become weak and brittle.
Causes
·
Low bone mass
·
Calcium and vitamin D deficiency
·
Sedentary life style
·
Thyroid problems
·
Smoking
Management
Taking diet rich in
calcium and Vitamin D
·
Avoiding tobacco, alcohol and excess of tea and coffee
·
Brisk physical exercise
·
Be active which really helps bone and prevents osteopenia.
·
Reduce your chance of falling by making your bones safer.
6. Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy
Definition
Enlargement of the periurethral
position of the prostate lead to theobstruction of urinary outflow which begin
with the fracture of prostatic hyperplasia and ends with urinary obstruction.
Causes
·
Ageing
·
High level of Dihydro testosterone
·
Genetic
Management
·
Transurethral resection of prostate was the mode of surgical
treatment.
·
Medical management with specific long activity adrenergic
antagonists and a reductase inhibitors have been and with excellent results.
7. Diabetes in Older Adults
Definition: Diabets mellitus is a
chronic
multisystem disease
characterized by hyperglycemia related to abnormal insulin production and
impaired insulin utilization.
Causes
·
Auto immune
·
Environmental factors
Management
·
The lifestyle modifications, diet and nutrition, physical
exercise.
·
Overweight elderly should be advised to loss weight and abstain
from alcohol and smoking.
·
Oral hypoglycaemic drugs in NIDDM and insulin in IDDM.
·
Insulin is indicated in NIDDM for proper control despite oral
hypoglycaemic drugs in the presence of infections, ketosis, hyperosmolar state,
surgery and diabetic heuropathy.
8. Hypertension in the Elder
Definition
Hypertension is defined
as a persistent Systolic BP of 140mm Hg or more, Diastolic BP 90mm Hg or more.
Causes
·
Over production of sodium retaining hormones.
·
Increased sodium intake
·
Diabetes
·
Tobacco use
·
Excessive alcohol intake
Management
·
Weight and salt reduction and change in Lifestyle.
·
Initially low dose diuretics of beta blockers are recommended.
9. Pressure Ulcer/Bed Sores
Definition: Pressure ulcer is localized
injury
to the skin and
underlying tissue as a result of pressure or pressure in combination with
shear.
Causes
·
Excessive moisture
·
Obesity
·
Diabetes mellitus
·
Occur due to ischemia, necrosis and ultimate ulceration of the tissue due to
constant pressure at sites with are pressure prove.
·
Immobile following surgery or a spinal cord injury can lead to bed
sore
Management
·
Optimal nutrition can aid in the healing process –food rich in
zinc and vitamin c (green, red and orange vegetables)
·
keeping the wounds clean to prevent infection
·
speed the healing process by keeping the wound moist and the
surrounding skin dry
·
pain management with more serious ulcer
10. Eye Diseases
Definition
A cataract is an opacity
within the lens. Cataract is the commonest cause of Visual impairment in old
age. Cataract is characterized by painless burning gradual loss of vision
increased sensitivity to glare under general darkening of vision.
Cataract
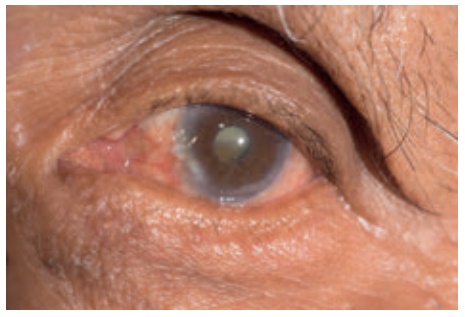
Causes
·
Maternal rubella
·
Radiation or ultraviolet exposure Long term topical corticosteroids Diabetes mellitus
Management
Surgery after the
removal of the lens, which has now been replaced by the implantation of an
inter ocular lens which restore hear normal focusing ability.
11. Glaucoma
Definition
Glaucoma is a group of
disorders characterized by increased IOP and the consequences of elevated
pressure, optic nerve atrophy, and peripheral visual field loss.
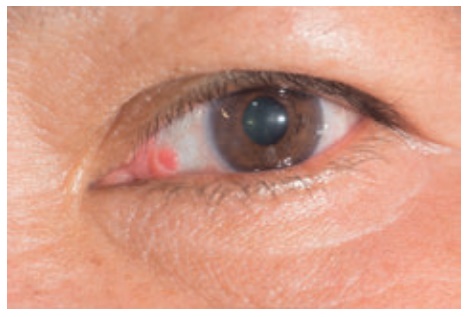
Causes
·
Lens bulging due to aging
·
Damage to the optic nerve.
·
Reduction in the outflow of aqueous humor
12. Cancer
Definition
Cancer is a group of
diseases characterized by uncontrolled and unregulated growth of cells. Among
elderly men concern of the prostrate and colon are the most common while for
women it is a breast cancer. Other concern found in geriatric patients are
skin, lung and pancreas, bladder, rectum and stomach.
Causes
·
Smoking and tobacco
·
Diet and physical activity
·
Sun and other type of radiation
·
Viruses and other infection
Management
·
Quit smoking
·
Moderate your diet, diets high in fruits and vegetables may have a
protective effect against many cancers.
·
Avoid excessive exposure to ionizing radiations.![]()
·
Regular physical activity and maintain a healthy body weight.
13. Drug Reactions
·
Older patients are two of three times more vulnerable to drug
reaction.
·
Drug clearance is markedly reduced due to reaction in Renal blood
flow and glomerular filtration rate.
·
Distribution of the drug is also affected in old age due to
reduction in total body weight content and their relative increases in body
fat.
·
Protein binding of the drug is decreased due to fall in serum albumin
in old age.
Related Topics