Chapter: Microbiology and Immunology: Bacteriology: Haemophilus, Pasteurella, and Actinobacillus
Clinical Syndromes - Haemophilus influenza
Clinical Syndromes
The clinical syndromes caused by H. influenzae can be classified into two types as follows (Fig. 38-2):
1. Infections caused by encapsulated H. influenzae
2. Infections caused by noncapsulated H. influenza
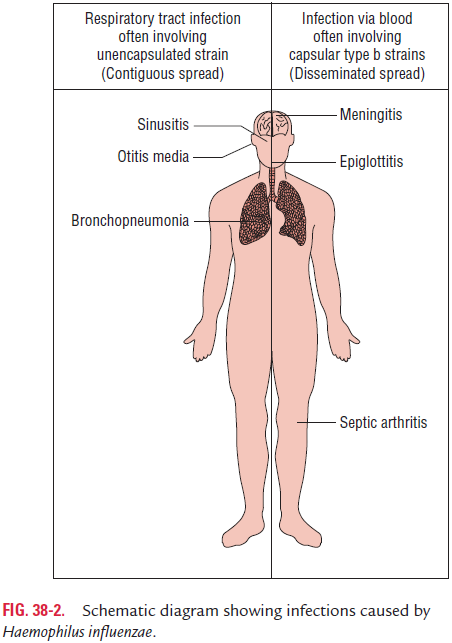
◗ Infections caused by encapsulated H. influenzae
Meningitis: Meningitis is the most serious manifestation ofHib infection. It occurs primarily in children of 2 months to 2 years of age. Altered mental state and fever are most common symptoms. Headache and photophobia are usually present in older children. Mortality rate is above 90% in untreated chil-dren. Hib meningitis is rare in adults.
Epiglottitis: Epiglottitis is the second most common infec-tion of H. influenzae and is a life-threatening emergency. This condition is seen in children of 3–18 months of age after Hib vaccine era. This condition is characterized by cellulites and obstructive laryngeal edema.
Cellulitis: H. influenzaecausing cellulitis is typically seen inchildren. The buccal and periorbital regions are most com-monly involved. Fever, indurations, and tender area in the head and neck particularly in the buccal and preseptal areas charac-terize the condition.
Septic arthritis: Septic arthritis in children is characterizedby involvement of single large joint, such as knee, ankle, hip, or elbow. In adults, joint involvement can be monoarticular or polyarticular.
Pneumonia: Pneumonia typically occurs in infantsand is clinically indistinguishable from other bacterial pneumonias.
Suppurative lesions: Hib can cause suppurative lesions, suchas epiglottitis, pericarditis, and septic arthritis. Endophthalmitis, cervical adenitis, osteomyelitis, and endocarditis are less com-mon invasive infections caused by Hib.
◗ Infections caused by nonencapsulated strains
The nontypable influenzae are the opportunistic bacteria causing infections of the upper and lower respiratory tract. These strains cause otitis media, bronchitis, pneumonia, and conjunctivitis. Nonencapsulated H. influenzae along with Streptococcus pneumoniae is the most common cause of otitismedia. Nontypable H. influenzae is a major causative agent of conjunctivitis in older children, next only to S. pneumoniae. This is the most common cause of community-acquired bacterial pneumonia in adults.
Related Topics