Chapter: Medical Microbiology: An Introduction to Infectious Diseases: Antibacterial and Antiviral Agents
Clindamycin, Oxazolidinones, Streptogramins - Antimicrobics That Act on Cell Wall Synthesis
Clindamycin
Clindamycin is chemically unrelated to the macrolides but has a similar mode of action and spectrum. It has greater activity than the macrolides against Gram-negative anaerobes, including the important Bacteroides fragilis group. Although clindamycin is a perfectly adequate substitute for a macrolide in many situations, its primary use is in instances where anaerobes are or may be involved.
Oxazolidinones
Linezolid is the most widely used of a new class of antibiotics that act by binding to thebacterial 50S ribosome. The exact mechanism is not known, but it does not involve pep-tide elongation or termination of translation. Oxazolidinones are clinically useful in pneu-monia and other soft tissue infections, particularly those caused by resistant strains of staphylococci, pneumococci, and enterococci.
Streptogramins
Quinupristin and dalfopristin are used in a fixed combination known as quinupristin-dalfopristin in a synergistic ratio. They inhibit protein synthesis by binding to differentsites on the 50S bacterial ribosome; quinupristin inhibits peptide chain elongation, and dalfopristin interferes with peptidyl transferase. Their clinical use thus far has been lim-ited to treatment of vancomycin-resistant enterococci.
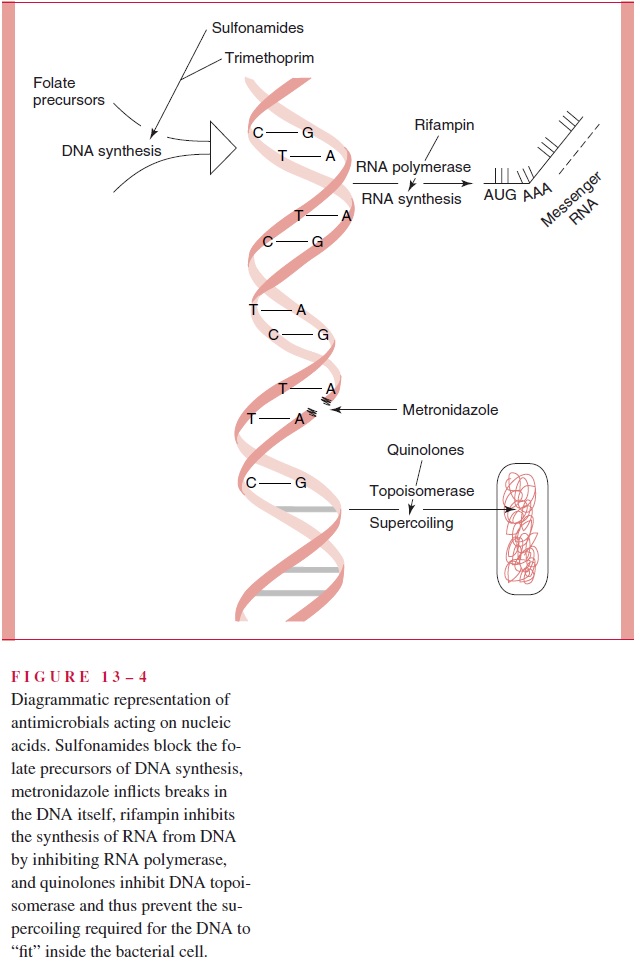
Inhibitors of Nucleic Acid Synthesis (Fig 13 – 4)
Related Topics