Chapter: Forensic Medicine: Head injuries
Classification of head injuries
Classification of head injuries
Although the brain can be injured by hypoxic,
toxic and biochemical conditions, this study unit focuses primarily on injury
to the brain and head due to physical forces.
Head injuries can be classified in two ways.
First, according to type of injury: an injury can be limited to the impact
area, in other words, where the blow landed, and it is then called the focal
area. If it is more widespread and involves the whole brain or large areas, it
is called a diffuse injury.
Head injuries are also classified according to
time of origin and clinical presentation. If the injury occurs at impact (such
as a contusion) it is regarded as an immediate injury. If it occurs later, it
is regarded as a delayed injury - these
are usually the complications of a head injury and include increased
intra-cranial pressure and herniations. Please note that intra-cranial injuries
occur at the moment of impact but only have an effect later as the bleeding
first has to become sufficient to have an effect on the brain volume.
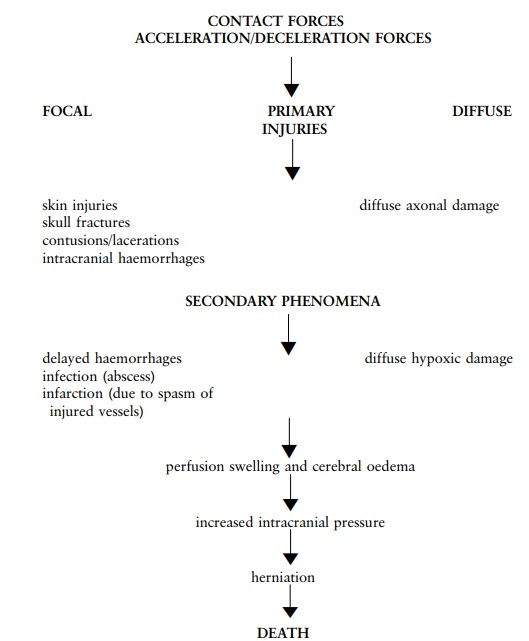
An injury can be either focal or diffuse, as has
been said. Focal injuries can be skin injuries, skull fractures, contusions of
the brain or intracranial haemorrhages.
The most common diffuse injury is diffuse axonal
injury. In severe trauma to the brain, diffuse brain injury with numerous small
haemorrages throughout the brain may occur, and this is incompatable with life.
As these primary injuries are complicated by other events like hypoxia,
infection, delayed haemorrhages, et cetera, the brain may start to enlarge due
to swelling.
As the brain is enclosed in the rigid cranial
cavity, an increase in size will have detrimental effects on the brain tissue.
Brain tissue will be forced from one region to another by the process of
herniation. Ultimately, the increased pressure on the brainstem will impact
negatively on the vital centres controlling respiration, et cetera. This is
usually the final route for any type of intracranial pathology, be it an
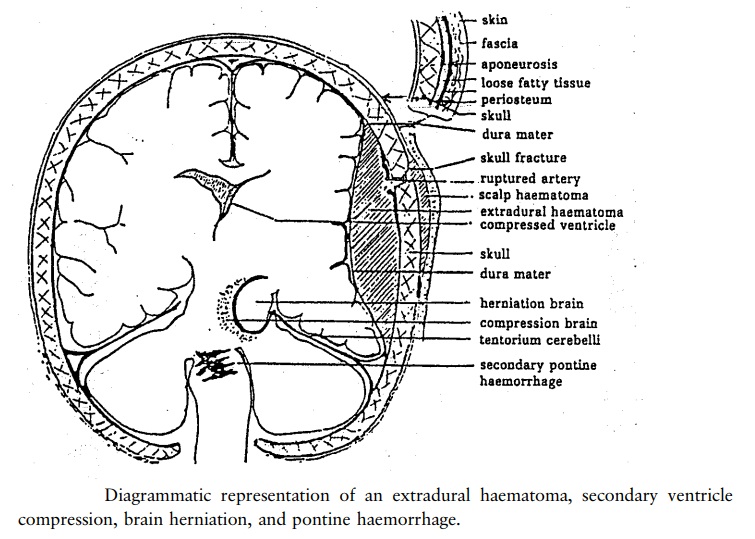
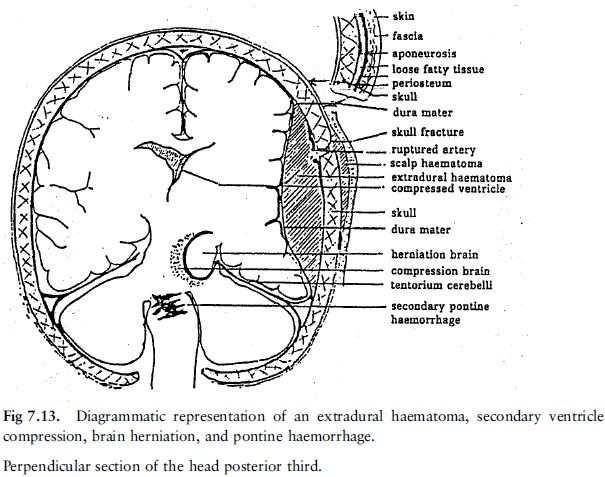
infarct, tumour or haemorrhage (fig 7.13).
The different types of head injury will now be
discussed in detail.