Chapter: 11th Zoology : Chapter 2 : Kingdom Animalia
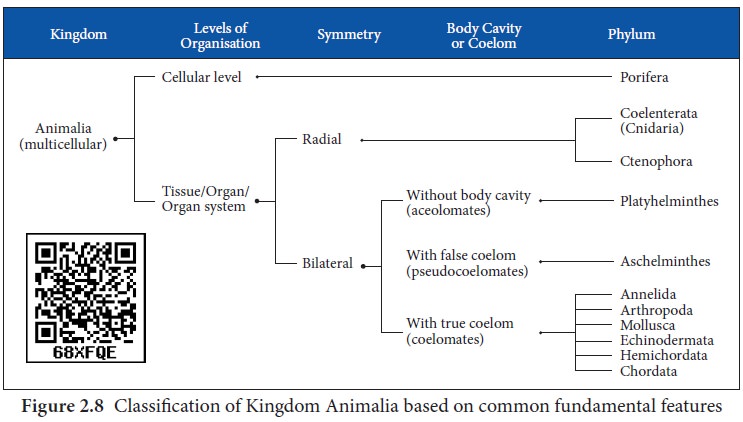
Classification of Kingdom Animalia
Classification
of Kingdom Animalia
Animal kingdom is divided into two sub-kingdoms, the Parazoa and Eumetazoa based on their organisation.
1. Parazoa: These include the multicellular
sponges and their cells are loosely aggregated
and do not form tissues or organs.
2. Eumetazoa: These include multicellular
animals with well defined tissues, which
are organised as organs and organ systems. Eumetazoans includes two
taxonomic levels called grades. They include Radiata and Bilateria.
Grade: 1 Radiata
Among the
eumetazoa, a few animals have an organisation of two layers of cells, the outer
ectoderm and inner endoderm, separated by a jelly like mesoglea. They are
radially symmetrical and are diploblastic.
Examples:
Cnidarians (sea anemone, jelly fish) and Ctenophores (comb jellies).
Grade: 2. Bilateria
The
eumetazoans other than Radiata, show organ level of organisation and are
bilaterally symmetrical and triploblastic. The grade Bilateria includes two
taxonomic levels called Division.
Division: 1. Protostomia (Proto: first; stomium: mouth)
Protostomia
includes the eumetazoans in which the embryonic blastopore develops into mouth.
This division includes three subdivisions namely acoelomata, pseudocoelomata
and schizocoelomata.
Division: 2. Deuterostomia -(deuteron: secondary; stomium: mouth)
Eumetazoans
in which anus is formed from or near the blastopore and the mouth is formed
away from the blastopore. It -includes only one subdivision Enterocoelomata.
They have a true coelom called enterocoel, formed from the archenteron.
Related Topics