Chapter: Human Neuroanatomy(Fundamental and Clinical): Gross Anatomy of the Cerebellum
Cerebellar Peduncles - Gross Anatomy of the Cerebellum
Cerebellar Peduncles
The fibres entering or leaving the cerebellum pass through three thick bundles called the cerebellar peduncles: superior, middle and inferior.
Inferior cerebellar peduncle
This peduncle is also called the restiform body. This is a thick bundle of fibres that connects the posterolateral part of the medulla with the cerebellum. The peduncle passes upwards and laterally along the inferolateral margin of the rhomboid fossa (floor of fourth ventricle, Fig. 20.12). Near the upper end of the medulla the peduncle lies between the superior cerebellar peduncle (on its medial side) and the middle cerebellar peduncle (laterally). The inferior peduncle then turns sharply backwards to enter the while core of the cerebellum.
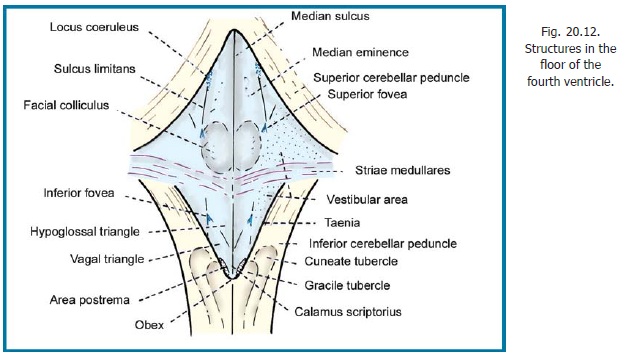
Over the medial part of the inferior cerebellar peduncle there are fibres that pass through the vestibular nuclei before entering the cerebellum. These fibres constitute the juxtarestiform body.
Middle cerebellar peduncle
The middle cerebellar peduncle begins as a lateral continuation of the ventral part of the pons. Its fibres, which arise in pontine nuclei, cross to the opposite side. The fibres of the peduncle form a thick bundle that passes laterally and backwards to enter the white core of the cerebellum through the horizontal fissure. On entering the cerebellum the fibres are placed lateral to those of the inferior peduncle (the superior peduncle being still more medial in position).
Superior cerebellar peduncle
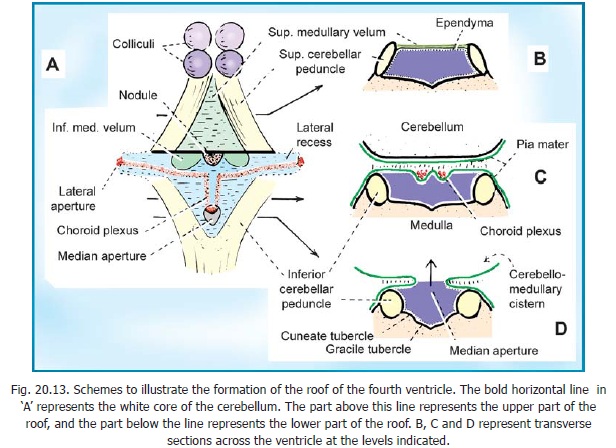
The superior cerebellar peduncle consists mainly of fibres arising in cerebellar nuclei (mainly the dentate nucleus). The fibres pass forwards, upwards and medially, lying along the upper and lateral margin of the rhomboid fossa. The right and left peduncles are connected by a thin lamina of white matter, the superior (or anterior) medullary velum. Along with the velum the peduncles form the upper part of the roof of the fourth ventricle (Fig. 20.13). The fibres of the peduncle enter the midbrain and cross to the opposite side before ending (mainly) in the red nucleus. Many of the fibres ascend to the thalamus.
Related Topics