Chapter: Obstetrics and Gynecology: Menopause
Cautions in Hormone Therapy
CAUTIONS IN HORMONE THERAPY
The results of the WHI in 2002
revealed epidemiologic findings that have modified the contemporary use of
hor-mone therapy. This large, multicenter, randomized clinical trial
(approximately 17,000 women) studied the effects of hormone therapy, dietary
modification, and calcium and vitamin D supplementation as related to heart
disease, frac-tures, breast cancer, and colorectal cancer. Although thereare features of this study that are not applicable to
many younger menopause patients, the overall results suggested that when
com-pared to placebo, a combination of conjugated equine estrogens and
continuous low-dose medroxyprogesterone acetate resulted in an increased risk
of heart attack, stroke, thromboembolic disease, and breast cancer, with a
reduced risk of colorectal cancer and hip frac-tures. Some of the data
contradicted prior large-scale obser-vational studies, and thus many physicians
have changed their practice regarding hormone therapy to center more on the
relief of short-term symptoms of estrogen depriva-tion, including hot flushes,
sleeplessness, and vaginal atro-phy. Although reappraisals of the study have
focused on its flaws, current opinion suggests that initiation early in
menopause is associated with a good risk-benefit ratio, with preference for the
transdermal route. Nonetheless, the current recommendations from numerous
organizations, including ACOG, is that hormone therapy should only be used for
the short-term relief of menopausal symptoms and should be individually
tailored to a woman’s need for treat-ment (Box 37.2).
Hormone therapy in women with
prior history of breast and endometrial cancer is controversial. Currently,
prospective studies are underway using low-dose hormone therapy in women with a
prior history of limited-lesion, successfully treated breast cancer. Similar
studies in women with prior treated limited-lesion endometrial cancer have been
completed and show no increased risk of recurrence for estrogen users.
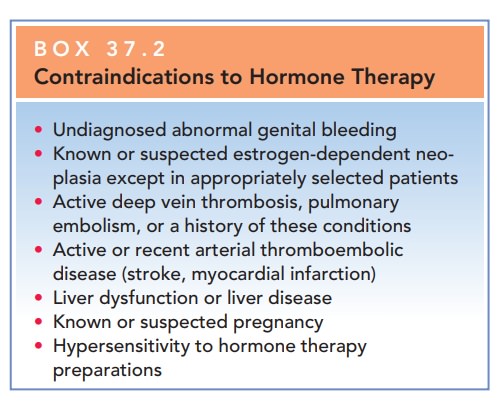
Box 37.2
Contraindications to Hormone Therapy
Undiagnosed abnormal genital bleeding
Known or suspected estrogen-dependent neo-plasia except in appropriately
selected patients
Active deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, or a history of these
conditions
Active or recent arterial thromboembolic disease (stroke, myocardial
infarction)
Liver dysfunction or liver disease
Known or suspected pregnancy
Hypersensitivity to hormone therapy preparations
Related Topics