Mathematics - Cardinality and Practical Problems on Set Operations | 9th EM Mathematics : Set Language
Chapter: 9th EM Mathematics : Set Language
Cardinality and Practical Problems on Set Operations
Cardinality and Practical Problems on Set Operations
We have learnt about the union, intersection, complement and difference of sets.
Now we will go through some practical problems on sets related to everyday life.
Results :
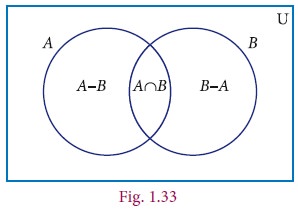
If A and B are two finite sets, then
n(A∪B) = n(A)+n(B) – n(A∩B)
(i) n(A∪B) = n(A)+n(B)– n(A∩B)
(ii) n(A–B) = n(A) – n(A∩B)
(iii) n(B–A) = n(B)– n(A∩B)
(iv) n(A′) = n(U) – n(A)

Example1.20
From the Venn diagram, verify that
n(A∪B) = n(A)+n(B) – n(A∩B)
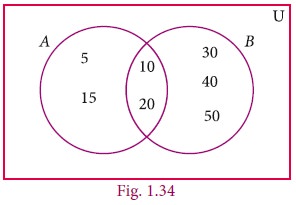
Solution
From the venn diagram,
A = {5, 10, 15, 20}
B = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50,}
Then A∪B = {5, 10, 15, 20, 30, 40, 50}
A∩B = {10, 20}
n(A) = 4, n(B) = 5, n(A∪B) = 7, n(A∩B) = 2
n(A∪B) = 7 ----- (1)
n(A)+n(B)–n(A∩B) = 4+5–2
=7 ----- (2)
From (1) and (2), n(A∪B) = n(A)+n(B)–n(A∩B).
Example 1.21
If n(A) = 36, n(B) = 10, n(A∪B)=40, and n(A′)=27 find n(U) and n(A∩B).
Solution
n(A) = 36, n(B) =10, n(A∪B)=40, n(A′)=27
(i) n(U) = n(A)+n(A′) = 36+27 = 63
(ii) n(A∩B) = n(A)+n(B)–n(A∪B) = 36+10-40 = 46-40 = 6
Example 1.22
Let A={b, d, e, g, h} and B = {a, e, c, h}. Verify that n(A–B) = n(A)–n(A∩B).
Solution
A = {b, d, e, g, h}, B = {a, e, c, h}
A – B = {b, d, g}
n(A–B) = 3 ... (1)
A ∩ B = {e, h}
n(A ∩ B) = 2 , n(A) = 5
n(A) – n(A∩B) = 5-2
= 3 ... (2)
Form (1) and (2) we get n(A–B) = n(A)–n(A∩B).
Example 1.23
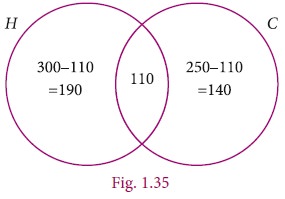
In a school, all students play either Hockey or Cricket or both. 300 play Hockey, 250 play Cricket and 110 play both games. Find
1. the number of students who play only Hockey.
2. the number of students who play only Cricket.
3. the total number of students in the School.
Solution:
Let H be the set of all students play Hockey and C be the set of all students play Cricket.
Then n(H) = 300, n(C) = 250 and n(H ∩ C) = 110
Using Venn diagram,
From the Venn diagram,
(i) The number of students who play only Hockey = 190
(ii) The number of students who play only Cricket = 140
(iii) The total number of students in the school = 190+110+140 =440
Aliter
1. The number of students who play only Hockey
n(H–C ) = n(H) – n(H∩C)
=300 –110 = 190
2. The number of students who play only Cricket
n(C–H ) = n(C) – n(H∩C)
=250 – 110 = 140
3. The total number of students in the school
n(H∪C) = n(H) + n(C) – n(H∩C)
= 300+250 – 110 = 440
Example1.24
In a party of 60 people, 35 had Vanilla ice cream, 30 had Chocolate ice cream. All the people had at least one ice cream. Then how many of them had,
1. both Vanilla and Chocolate ice cream.
2. only Vanilla ice cream.
3. only Chocolate ice cream.
Solution :
Let V be the set of people who had Vanilla ice cream and C be the set of people who had Chocolate ice cream.
Then n(V) = 35, n(C) = 30, n(V∪C) = 60,
Let x be the number of people who had both ice creams.
From the Venn diagram
35 – x + x +30 – x = 60
65 – x = 60
x= 5
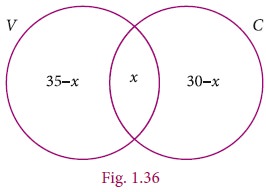
Hence 5 people had both ice creams.
(i) Number of people who had only Vanilla ice cream = 35 – x
= 35– 5 = 30
(ii) Number of people who had only Chocolate ice cream = 30 – x
= 30 – 5 = 25
Aliter
Number of people had both Vanilla and Chocolate ice creams
n(V∩C ) = n(V) + n(C) – n(V ∪C)
= 35+30 – 60 = 5
Number of people had only Vanilla ice creams
n(V–C ) = n(V) – n(V∩C)
= 35 – 5 = 30
Number of people who had only Chocolate ice creams
n(C–V ) = n(C) – n(V∩C)
= 30 – 5 = 25
Related Topics