Chapter: 12th Computer Applications : Chapter 16 : Electronic Payment Systems
Card Based Payments Systems
Card
Based Payments Systems
Payment cards are plastic cards that enable cashless
payments. They are simple embossed plastic card that authenticates the card
holder on behalf of card issuing company, which allows the user to make use of
various financial services. More than 90% of online payments are card based
payments, at the same time other e-payment methods are also gaining importance
now-a-days.
Based on the transaction settlement method there
are three widely used card based payment systems. They are
1. Credit
card based payment systems (pay later)
2. Debit
card based payment systems (pay now)
3. Stored
value card based payment systems (pay before)
1. Credit Card
Credit card is an electronic payment system
normally used for retail transactions. A credit card enables the bearer to buy
goods or services from a vendor, based on the cardholder’s promise to the card
issuer to payback the value later with an agreed interest. Every credit card
account has a purchase limit set by the issuing bank or the firm. A credit card
is different from a debit card where the credit card issuer lends money to
customer instead of deducting it from customer’s bank account instantly.
The term credit card was first mentioned in 1887 in the sci -fi novel “Looking Backward” by Edward Bellamy. The modern credit cards concept was born in the U.S.A, in the 1920s, when private companies began to issue cards to enable their customers to purchase goods on credit within their own premises.
In February 1950, Frank McNamara and Ralph Schneider created The Diners Club card which was made of paper-cardboard. Initially The card was accepted in only 27 restaurants and was used only by friends and acquaintances of the two founders (approximately 200 people). Later it was enhanced and accepted worldwide. From 1955, the card was made of plastic. The Diners Club still exists today under the name Diners Club International.

Advantages of credit card
● Most credit cards are accepted worldwide.
● It is not necessary to pay physical money at the
time of purchase. The customer gets an extra period to pay the purchase.
● Depending on the card, there is no need to pay
annuity.
● Allows purchases over the Internet in
installments.
● Some issuers allows “round up” the purchase price
and pay the difference in cash to make the transactions easy.
Key players in operations of credit card
1. Bearer:
The holder of the credit card account who is responsible for payment of
invoices in full (transactor) or a portion of the balance (revolver) the rest
accrues interest and carried forward.
2. Merchant:
Storekeeper or vendor who sell or providing service, receiving payment made by
its customers through the credit card.
3. Acquirer:
Merchant’s bank that is responsible for receiving payment on behalf of merchant
send authorization requests to the issuing bank through the appropriate
channels.
4. Credit
Card Network: It acts as the intermediate between the banks. The Company responsible
for communicating the transaction between the acquirer and the credit card
issuer. These entities operate the networks that process credit card payments
worldwide and levy interchange fees. E.g. Visa, MasterCard, Rupay
5. Issuer:
Bearer’s bank, that issue the credit card, set limit of purchases, decides the
approval of transactions, issue invoices for payment, charges the holders in
case of default and offer card-linked products such as insurance, additional
cards and rewards plan. See Figure 16.2
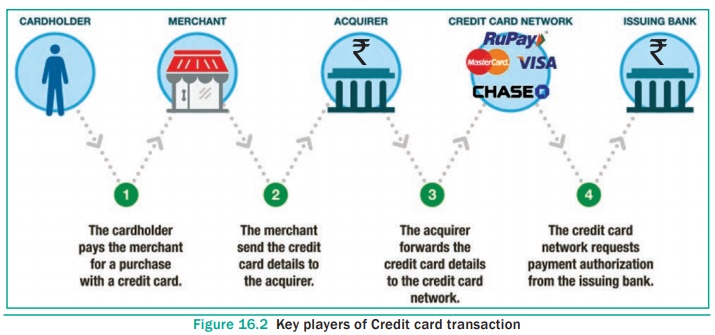
Anatomy of a credit card
All Payment cards (including debit card) are
usually plastic cards of size 85.60 mm width × 53.98 mm height, rounded corners
with a radius of 2.88 mm to 3.48 mm and thickness of 0.76 mm. These standards
dimensions are maintained universally in accordance with ISO/IEC 7810#ID-1. See
Figure 16.3
1. Publisher:
Emblem of the issuing bank (along with the sub category or scheme if any)
2. Credit
card number: The modern credit card number has 16-digit unique
identification number.
● The first digit of the credit card number is
Major Industry Identifier (MII). It identifies the issuer category. e.g. 1 –
Airlines, 4 – Banks
● The next 5 digits uniquely identifies the issuing
organization.
● The first 6 digits together called as Issuer
Identifier number (IIN) or Bank Identification number (BIN)
● The next 9 digits are the account number.
● The last digit is a check digit (based to the
Luhn algorithm).
3. Name of
the cardholder: It is visibly embossed on the front side (additionally
stored on the magnetic stripe) some cards like gift cards do not hold any name.
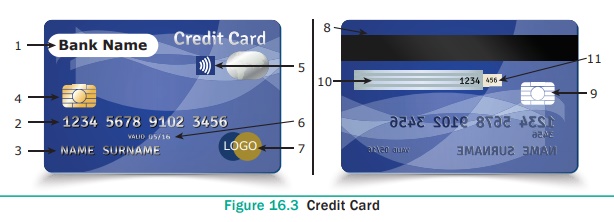
4. EMV chip:
It is integrated chip in addition to magnetic stripe to store cardholder’s
information. EMV stands for Europay, MasterCard, Visa. These three names
correspond to the names of the companies which are responsible to develop this
technology. It is categorized into Chip-and-Signature and Chip-and-PIN.
5. RFID
symbol: It is four curved lines radiating rightwards similar to a tilted
Wi-Fi symbol. It indicates that it is a contactless smartcard.
6. Expiration
month and year: It is visible on the front side (also stored on the
magnetic stripe or chip). The card is valid until the last day of the month
printed on it.
7. Card
brand logo: It is the name of the credit card network company. Visa and
MasterCard are leading credit card network companies. Rupay is Indian domestic
open loop card launched in 2012.
8. Magnetic
stripe: It is an iron based magnetic material containing encrypted data
about the card holder and account number.
9. Hologram:
Hologram is a security feature that prevents duplication. It is a 3-dimentional
image formed by interference of light beams.
10. Signature:
It is cardholder’s signature at the back of the card, used as an attempt to
identify cardholder’s identity. It also holds the last 4 digits of card number.
11. CVC/CVV:
Card Verification code/ value is a 3 digit code usually printed to the left of
signature pane validates the card. CVC2 is used in contact less transactions.
Apart from the these mentioned each credit card may
also holds issuer’s disclaimer, address and phone number.
2. Debit Card
Debit Card is an electronic payment card where the
transaction amount is deducted directly from the card holder’s bank account
upon authorization. Generally, debit cards function as ATM cards and act as a
substitute for cash The way of using debit cards and credit cards is generally
the same but unlike credit cards, payments using a debit card are immediately transferred
from the cardholder’s designated bank account, instead of them paying the money
back at a later with added interest. In modern era the use of debit cards has
become so widespread.
The debit card and credit card are identical in
their physical properties. It is difficult to differentiate two by their
appearance unless they have the term credit or debit imprinted.
Currently there are three ways of processing debit
card transactions:
1. EFTPOS (also known as online debit or PIN debit)
2. Offline debit (also known as signature debit)
3. Electronic Purse Card System
3. Stored value cards
Stored value card is a type of debit card that is
pre-loaded with certain amount(value), with which a payment is made. It is a
card that has default monetary value onto it. The card may be disposed when the
value is used, or recharged to use it again. The major advantage of stored
value card is that customers don’t need to have a bank account to get prepaid
cards. See Figure 16.4

Like a credit card or debit card it is a plastic
and has a magnetic strip on its back. The magnetic strip stores the monetary
value of the card. Stored value cards may not have the card holder’s name
always. It is also indistinguishable from a regular credit or debit card in
appearance. What look like a credit card or debit card act like a credit or
debit card. It is used to make purchases offline and online in the same way as
in credit card or debit card.
There are two varieties for stored value card.
1. Closed loop (single purpose)
In closed loop cards, money is metaphorically
stored on the card in the form of binary-coded data. Closed loop cards are
issued by a specific merchant or merchant group and can only be used to make
purchases from specific place. e.g. chennai metro rail travel card.
2. Open loop (multipurpose)
Open loop cards can be used to make debit
transaction at variety of retailers. It is also called as prepaid-debit cards. It
can be used anywhere the branded cards are accepted. e.g. Visa gift cards.
In some countries it is legal for
anyone to enter or leave the country with money that is stored on cards, unlike
carrying cash in high amounts which is believed a form of money laundering.
4. Smart
card
The modern version of card based payment is smart
cards. Smart cards along with the regular features of any card based payment
system holds a EMV chip. This chip is similar to well-known sim card in
appearance but differ in its functionalities. The advantage of Smart cards is
that it can provide identification, authentication, data storage and
application processing. Smart cards can be classified into Contact smart cards
and Contactless smart cards. See Figure 16.5

1. Contact
smart cards
Contact smart cards have a contact area of
approximately 1 square centimeter, comprising several gold-plated contact pads.
These pads provide electrical connectivity only when inserted into a reader,
which is also used as a communications medium between the smart card and a
host. e.g. a point of sale terminal(POS).
2. Contactless
smart cards Contactless smart card is empowered by RF induction
technology. Unlike contact smart cards, these cards require only near proximity
to an antenna to communicate. Smart cards, whether they are contact or contactless
cards do not have an internal power source. Instead, they use an inductor to
capture some of the interrupting radio-frequency signal, rectify it and power
the card’s processes. See Figure 16.6

Related Topics