Importance, Definition, Classification, Monosaccharides, Oligosaccharides, Polysaccharides - Carbohydrates - Biomolecules | 11th Biochemistry : Chapter 2 : Biomolecules
Chapter: 11th Biochemistry : Chapter 2 : Biomolecules
Carbohydrates - Biomolecules
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates,
otherwise known as saccharides (derived from the Greek Sakcharon– sugar; many
simple sugars taste sweet) are one of the abundant molecules in earth. They are
essential to maintain life in both plants and animals. They are synthesised in
plants by photosynthesis.
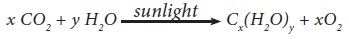
The
compounds that we come across in our daily life such as table sugar, wood,
cotton, starch, and honey etc... are all carbohydrates.
1. Importance
Carbohydrates
are widely distributed in both plant and animal tissues. They occur as food
reserves in the storage organs of plants and animals. They are the important
source of energy which is required for the various metabolic activities of
living organisms.
They
provide raw material for many important industries including textiles,
artificial silks, paper, films, plastics, lacquers, confectionary, drugs,
fermentation and explosives.
2. Definition
Carbohydrates
are defined as poly-hydroxy aldehydes or ketones. They contain hydrogen and
oxygen in the same ratio as in water (2:1)
The
names of most of carbohydrates are characterised by the ending ‘-ose’. For
example glucose, fructose, sucrose, cellulose, etc.
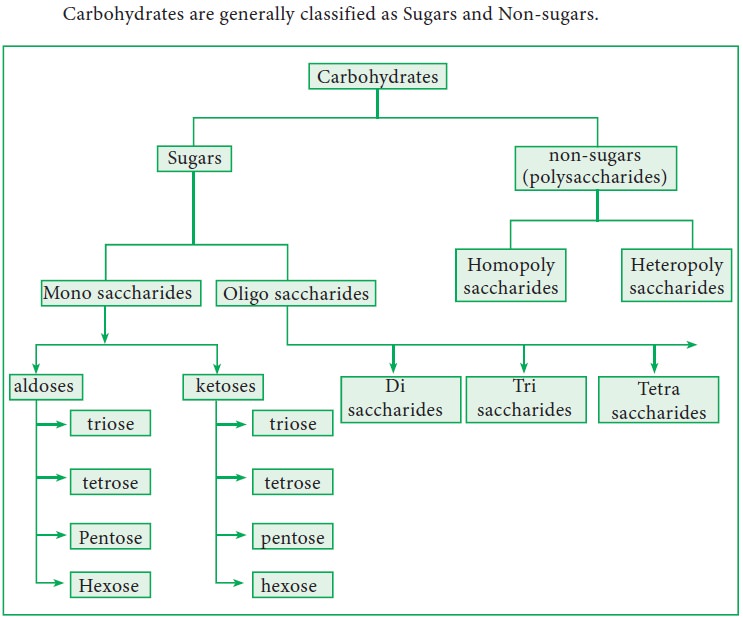
3. Classification
Carbohydrates are generally classified as Sugars and Non-sugars.
Sugars
Sugars
are sweet, crystalline and soluble in water. They are classified further as
below.
4. Monosaccharides
Mono
saccharides have a general formula Cn(H2O)n.
Based on the number of carbon atoms they are further classified into trioses,
tetroses, pentoses, hexoses etc. They can also be classified as aldoses and
ketoses based on the functional group present in them. They cannot be
hydrolysed into simpler units. This can be further classified as aldoses and
ketoses based on the functional group present in C1 position.
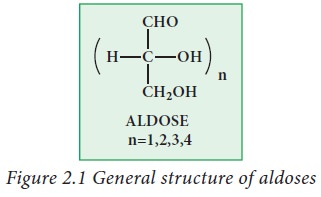
Aldoses:
Aldoses
contain aldehyde group (-CHO) as a functional group along with two or more
hydroxyl groups. Examples: glyceraldehyde, ribose, glucose galactose
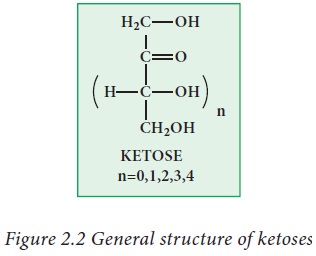
Ketoses:
Ketoses
contain keto group (>C=O) as a functional group along with two or more
hydroxyl groups.
Examples: dihydroxy acetone, ribulose,
fructose.
5. Oligosaccharides
Oligosaccharides
are sugars that yield 2 to 10 monosaccharide molecules on hydrolysis. This can
be further classified as di, tri, tetra saccharides etc. based on the number of
monosaccharide units present. In these molecules monosaccharide units are
interlinked by glyosidic bridges
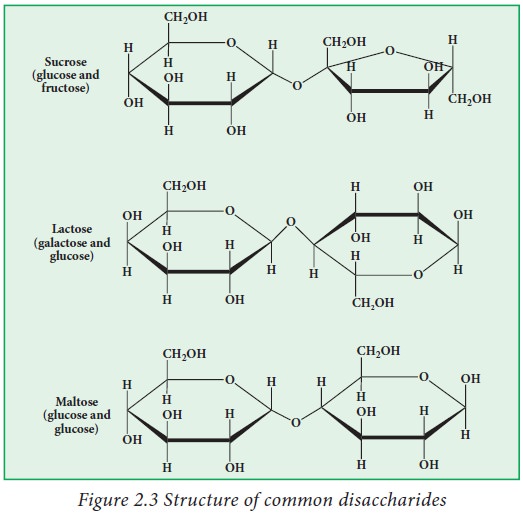
Disaccharides
Disaccharides
have a general formula Cn (H2O)n-1Example:
sucrose, lactose and maltose. In these molecules monosaccharide units are inter
linked by a glyosidicbridges.
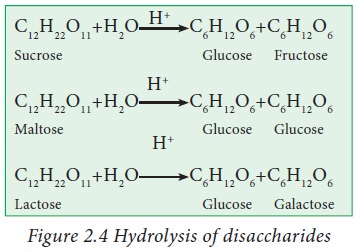
Hydrolysis
of disaccharides in presence of mineral acid yields corresponding monosaccharides.
For example hydrolysis of sucrose gives glucose and fructose. Similarly maltose
gives two molecules of glucose.
Trisaccharides
This
will give three monosaccharide units on hydrolysis. These have a general
formula as Cn(H2O)n-2 Example: raffinose,
stachyose.
6. Polysaccharides (Non Sugars)
Polysaccharides
are the carbohydrates that yield more than ten monosaccharide units upon
hydrolysis.They are further classified into homopoly saccharides and heteropoly
saccharides based on the monomeric units. Example: starch, cellulose, inulin
Homopolysaccharides
A
homopolysaccharide yields the same type of monosaccharide units on hydrolysis.
For example starch a homopolysaccharide yields only glucose upon hydrolysis.
Similarly glycogen and cellulose also yield glucose on hydrolysis.
Heteropolysaccharides
A
heteropolysaccharide yields more than one type of monosaccharide upon
hydrolysis. Eg. Hyaluronic acid, heparin, keratan sulphate and chondroitin
sulphate
These
are present in extra cellular matrix and therefore they are called as
mucopolysaccharides.
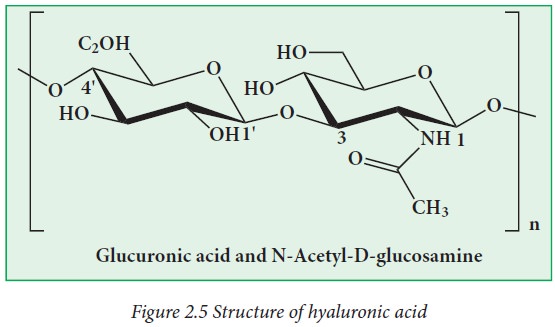
Hyaluronic
acid is made up of glucuronic acid and N-acetyl glucosamine.
Starch:
Starch
is the major form of stored carbohydrate in plants. Starch is composed of a
mixture of two substances namely amylose, a linear polysaccharide and
amylopectin, a branched polysaccharide. The detailed study of starch will be
discussed in the unit 5.
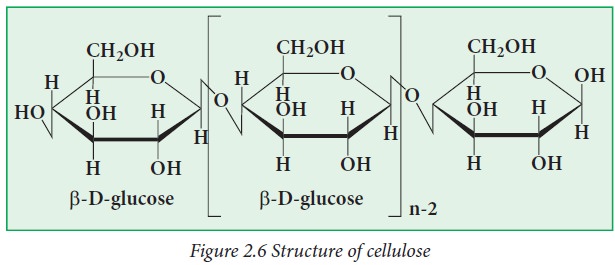
Cellulose:
Cellulose
is an unbranched polymer of β-D-glucose. Because of the absence of side chains,
molecules stay together to form rigid structures in plants. Wood is largely
made up of cellulose, and cotton is almost pure cellulose.
Cellulose
may be modified in the laboratory by treating it with nitric acid to produce
nitrocellulose or gun cotton which is an explosive component of smokeless
powder. Partially nitrated cellulose, known as pyroxylin, is used in the
manufacture of collodion, plastics, lacquers, and nail polish.
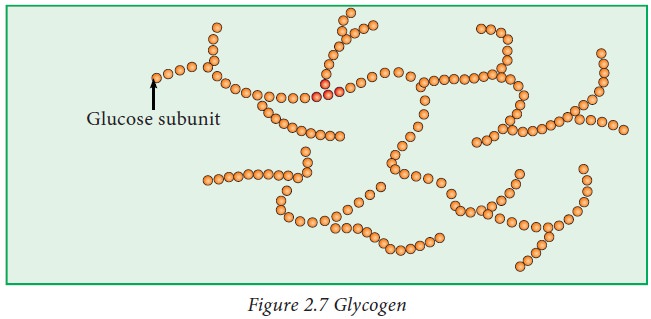
Glycogen:
Glycogen
is a storage form of glucose which is mainly present in liver and muscle.
Glycogen
is also known as animal starch. It is a multi branched polysaccharide of
glucose.
The
polysaccharide structure represents the main storage form of glucose in the
body
Related Topics