Definition, Classification, Functions of lipids - Lipids - Biomolecules | 11th Biochemistry : Chapter 2 : Biomolecules
Chapter: 11th Biochemistry : Chapter 2 : Biomolecules
Lipids - Biomolecules
Lipids
1. Definition
Chemically, Lipids can be defined as
esters of fatty acids with alcohol. They are insoluble in water and soluble in
organic solvents such as alcohol, ether, benzene and chloroform.
2. Classification
Based on the chemical nature, lipids
are classified as
Simple lipids
These are esters of fatty acids with
glycerol or long chain alcohols. They are further classified as follows.
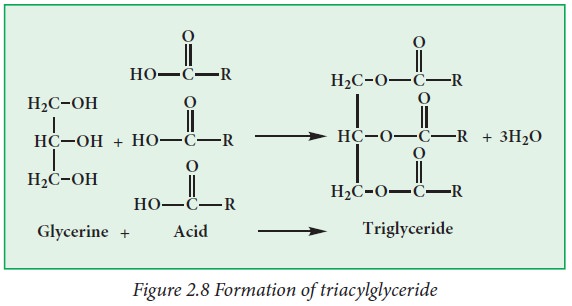
(a) Fats: Fats are glyceric esters of fatty acids. Lipids in animals are
called as fats while the lipids in plants are called as oils. Example: Triacylglycerol.
(b) Waxes: Waxes are esters of fatty acids with long chain monohydric
alcohols.
Examples: cerylmyristate (bees
wax).

Compound lipids
Compound
lipids are esters of fatty acids with alcohol, and they contain extra groups.
Depending upon the extra group present they are subdivided as follows:
a. Phospholipids (Phosphatides)
A glyceric ester containing phosphate
and nitrogen base or an alcohol are called phospholipids. These lipids are
present in large amounts in nerve tissue, brain, liver, kidney, pancreas and
heart. Phospholipids are further classified into three types based on the type
of group connected to phosphatidyl group.
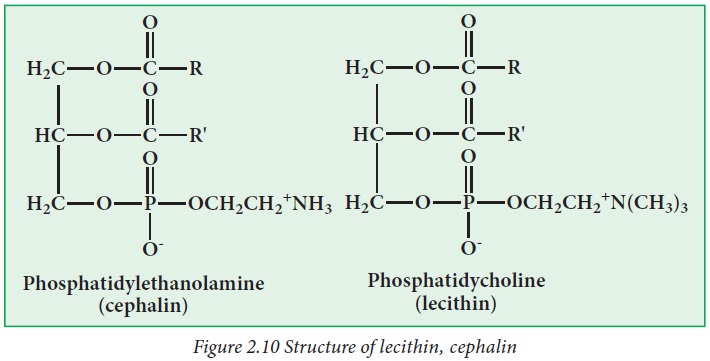
i. Glycerophosphatides:
In these phospholipids, a nitrogen
base is connected with phosphatidyl group.
Examples: Lecithin, Cephalin
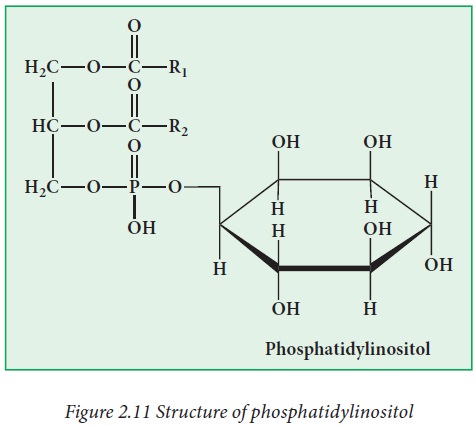
ii) Phosphoinositides:
In these
phospholipids, inositol is connected with phosphatidyl group.
Example:
Phosphatidylinositol (lipositol)
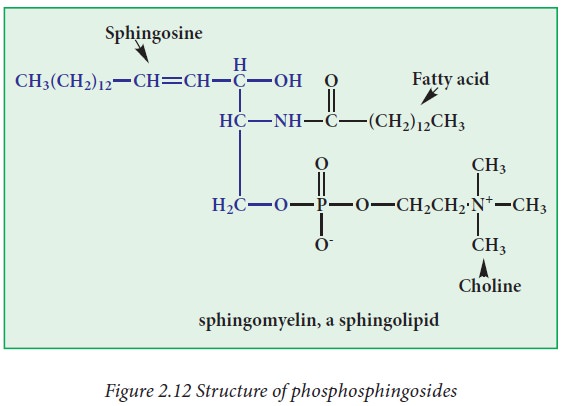
iii) Phosphosphingoside:
A group of phospholipids containing
1-phosphocholine combined with a ceramide (sphingosine + fatty acid). Example:
Sphingomyelin
b. Glycolipids
The
lipids which contain a carbohydrate moiety linked with ceramide is called a
glycol lipid.
Examples : Cerebroside and gangliosides.
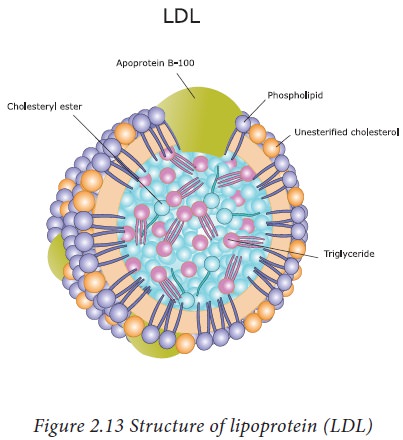
c. Lipoproteins
A
complex of proteins, lipid and cholesterol is called as a lipoprotein. The
protein moiety in the lipoprotein is known as apoprotein.
Examples:
Chylomicron
· Very low density lipoprotein (VLDL)
· Low density lipoprotein (LDL)
· High density lipoprotein (HDL)
Derived lipids:
Lipids
that are derived from the hydrolysis of simple and compound lipids are called
derived lipids.
Examples: diacylglycerol,
fatty acids, glycerol and cholesterol.
3. Functions of lipids:
Lipids perform several biological
functions such as,
· Triglycerides serve as energy reserve of the body.
· Lipids are important components of cell membranes which
regulates membrane permeability.
· Phospholipids, provide fluidity and flexibility to the cell
membranes.
· Lipids act as signalling molecules.
· Fat layer provides insulation from cold.
· Lipoproteins transports lipids throughout the body.
Related Topics