Example Programs in C++ - C++: Memory allocation of objects | 11th Computer Science : Chapter 14 : Classes and objects
Chapter: 11th Computer Science : Chapter 14 : Classes and objects
C++: Memory allocation of objects
Memory
allocation of objects
The
member functions are created and placed in the memory space only when they are
defined as a part of the class specification. Since all the objects belonging
to that class use the same member function, no separate space is allocated for member functions when the objects are created. Memory space required
for the member variables are only allocated separately for each object because
the member variables will hold different data values for different objects
Illustration 14.3 Memory allocation for objects
include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//The members will be allocated with memory space only after the
creation of the class type object
class product
{
int code, quantity;
float price;
public:
void assignData();
void Print();
};
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() int main()
int main()
{
product p1, p2;
cout<<”\n
Memory allocation for object p1 ” <<sizeof(p1);
cout<<”\n
Memory allocation for object p2 ” <<sizeof(p2);
return 0;
}
Output:
Memory allocation for object p1 12
Memory allocation for object p2 12
Member
functions assignData( ) and Print( ) belong to the common pool in the sense
both the objects p1 and p2 will have access to the code area of the common
pool.
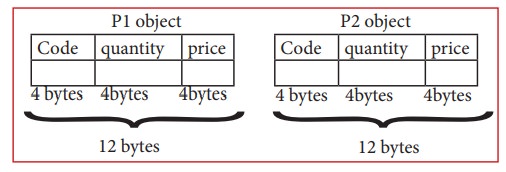
Memory
for Objects for p1 and p2 is illustrated:
Related Topics